46. Overview of the neck viscera; thyroid and parathyroid glands
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 8th ed., chapter 5, Abdominal viscera. Recall from The peritoneal cavity and mesenteries that the peritoneal cavity is divided into supracolic and infracolic regions, using the transverse colon and its mesentery (transverse mesocolon) as the borderline. In Organs in the supracolic region, the supracolic organs were described. In this chapter, […]
Lab 3: Dissection: Shoulder and Pectoral Region
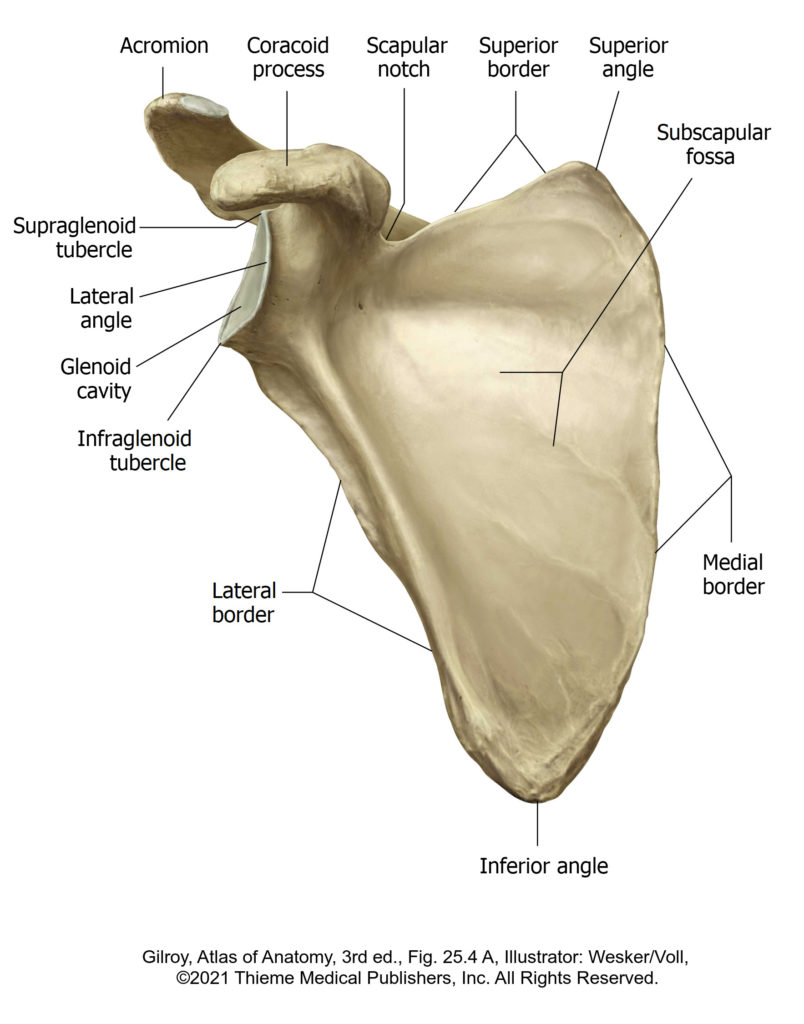
Dissector instructions Tap the Dissector Instructions menu on the left side of your screen to open the steps of your dissection. It’s sticky, so it will scroll with you as you progress through the lab. Need to log in to view the dissector?
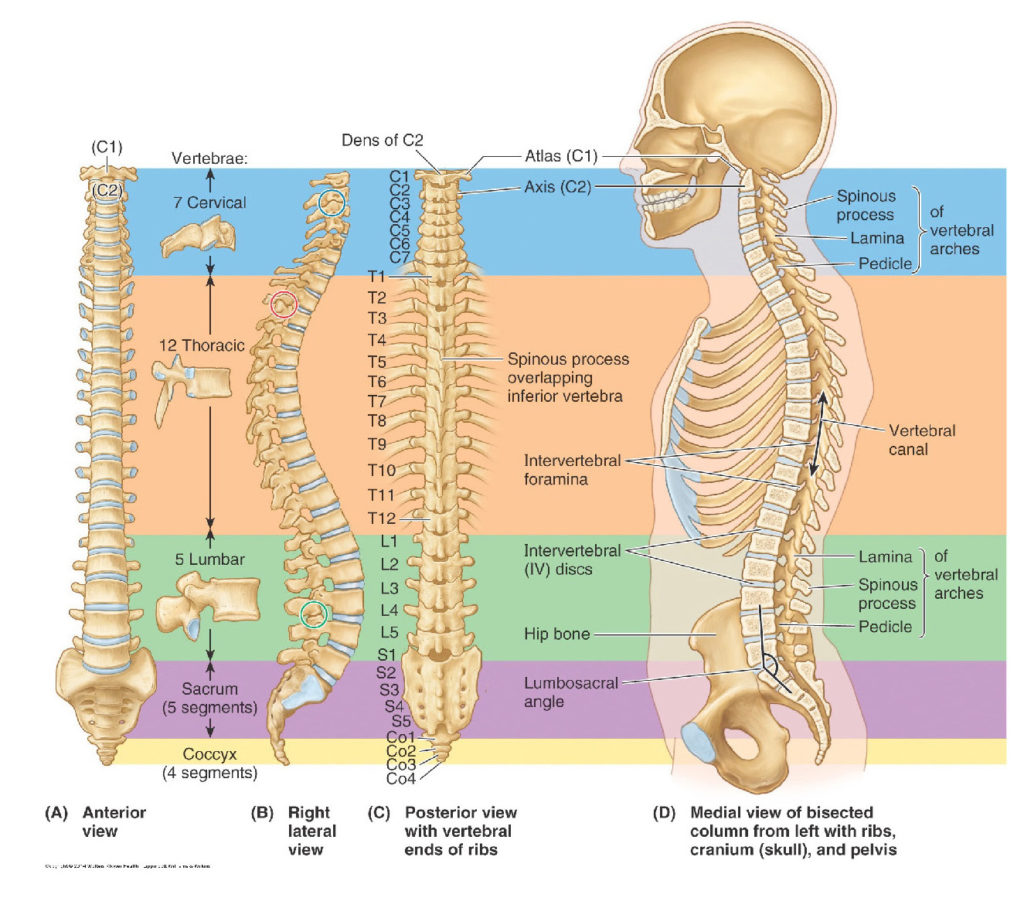
Lab 2 Introduction: Vertebral Column; Spinal Cord; Spinal Nerves; Back Muscles
Need to log in to view the dissector?
Lab 2, Station 4: Spinal Cord
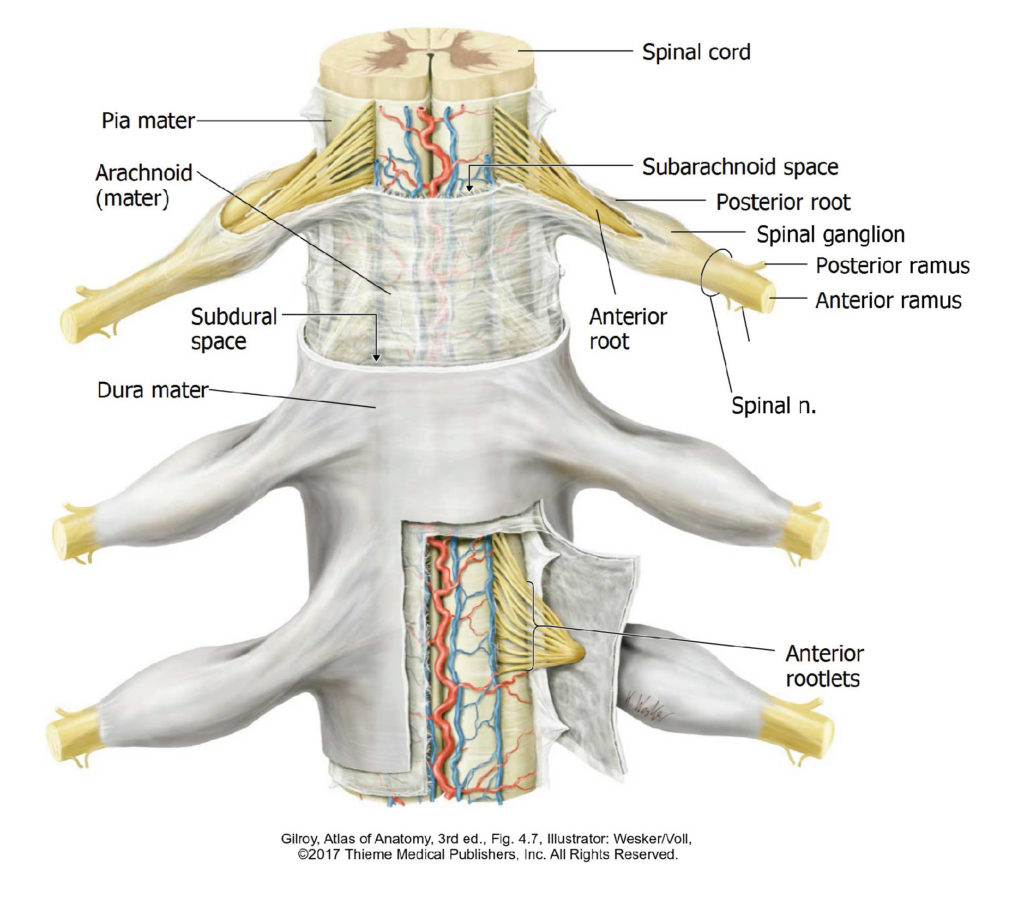
Lab 2 navigation Complete anatomy Spinal nerves Identify the following on the spinal cord prosection or isolated spinal cord: ■Dorsal and ventral roots—because the cadaver is prone, only the dorsal roots will be easily visible. Rootlets gather together to form the roots. ■Dorsal root ganglion—what does this contain? ■Spinal nerves—formed by the union of dorsal […]
Lab 2, Station 5: Spinal Nerves
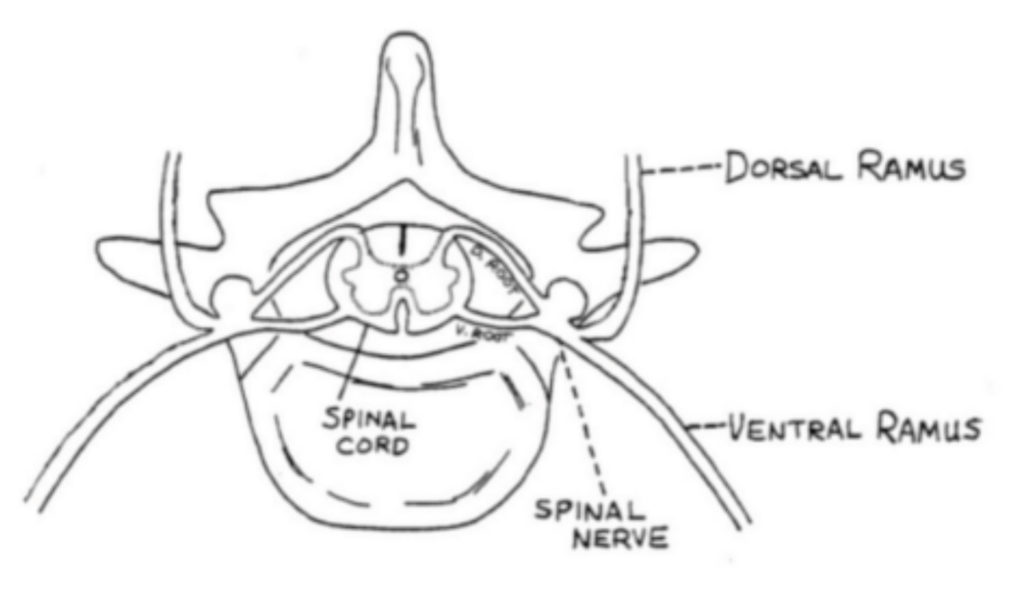
Lab 2 navigation On the whiteboard, draw a cross section of the spinal cord and spinal nerves. You can omit the vertebra in your drawing if you like. Label the following in your drawing: ■Dorsal and ventral horns of gray ■Dorsal and ventral roots ■Dorsal root ganglion ■Spinal nerve ■Dorsal and ventral rami Questions Which […]
Lab 2, Station 6: Muscles of the Back and Posterior Shoulder
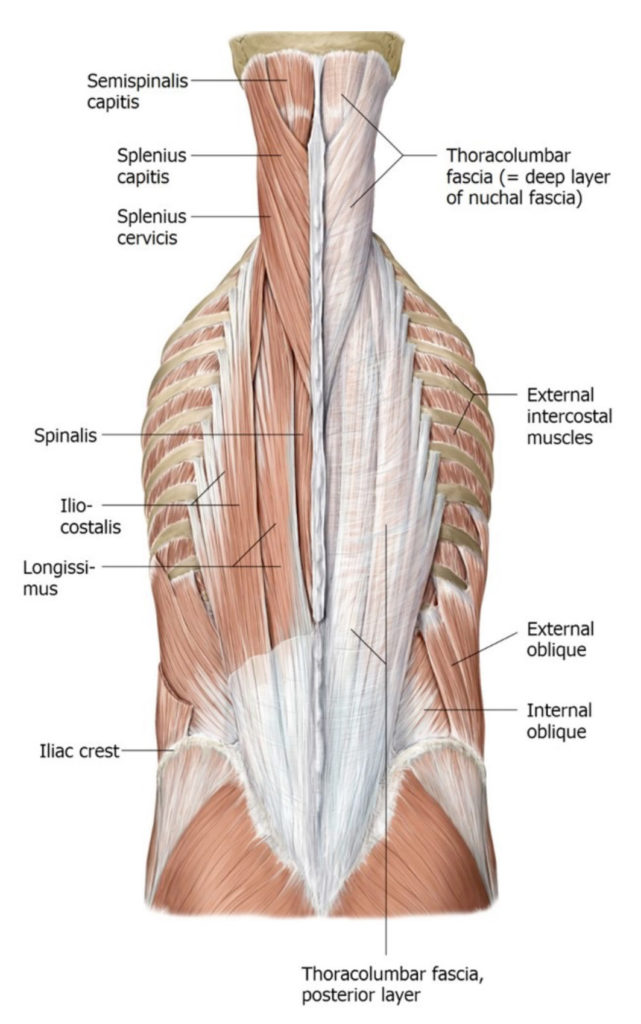
Lab 2 navigation Complete anatomy Deep muscles of the back The prosection is in the prone position: Let’s begin with muscles that extend the spine and head. These are worth knowing about since back pain and muscle spasm are so common. Splenius Muscles Splenius translates to “bandage”—indeed these muscles look like bandages applied to the […]
Lab 2, Station 3: Imaging of the Vertebral Column

Lab 2 navigation Radiography of the Spine Radiography involves using radiation (x-rays) to provide images of the tissues, organs, and bones, that comprise the human body. To create a radiograph, a patient is positioned so that the part of the body being imaged is located between an x-ray source and an x-ray detector. When the […]
Lab 2, Station 1: Vertebral Column
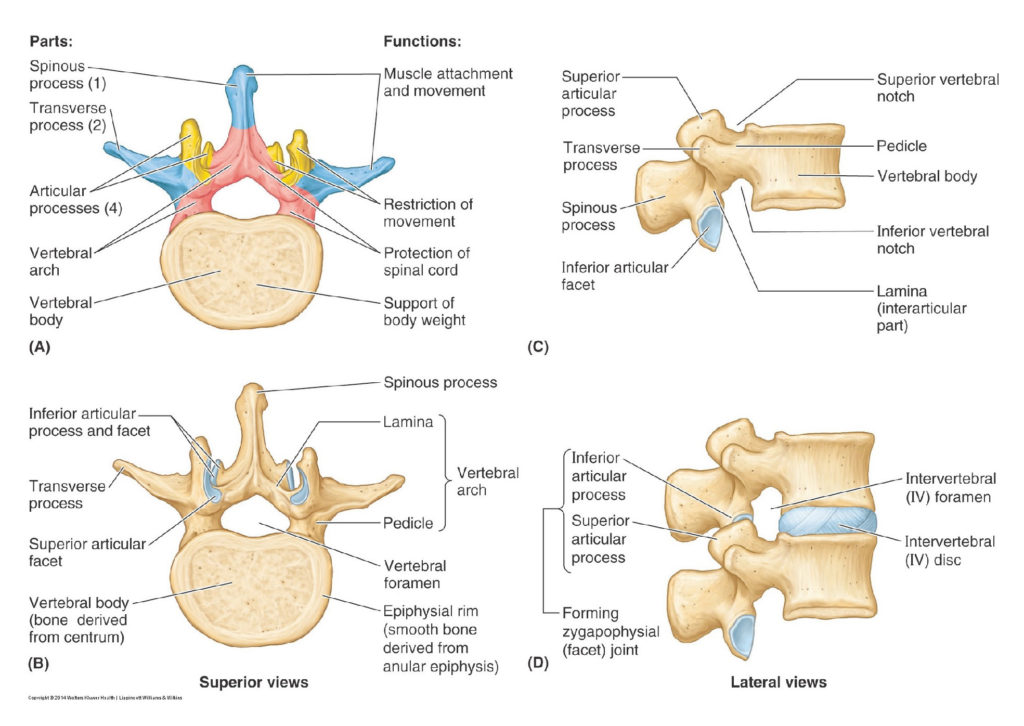
Lab 2 navigation The Vertebral Column as a Whole Complete anatomy Vertebral column Identify these features of the vertebral column: ■Primary curvatures ■Thoracic and sacral Question Primary curvatures = What is the concept? ■Secondary curvatures ■Cervical and lumbar Question Secondary curvatures = When are these acquired? ■Cervical vertebrae (7) ■Thoracic vertebrae (12) ■Lumbar vertebrae […]
Lab 2, Station 2: Vertebral Column 2
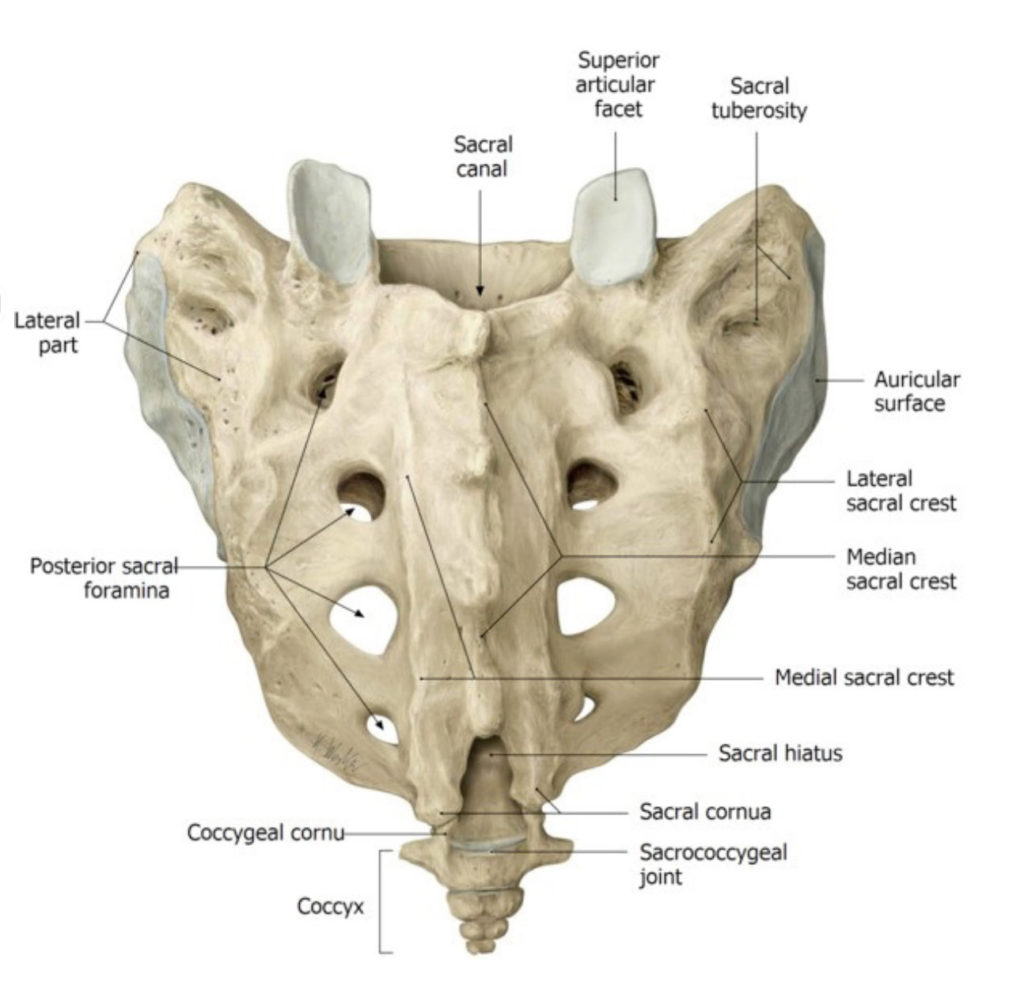
Lab 2 navigation Complete anatomy Sacrum ■Sacrum (5 fused vertebrae) ■Promontory ■Alae (singular is Ala = “wing”). There are two of these, on either side of the promontory ■Anterior and posterior sacral foramina ■Sacral canal ■Sacral hiatus ■Coccyx (4 vertebrae fused into 1-2 pieces) Figure 2.7. Sacrum and coccyx, anterior view. From Gilroy, Atlas of […]
Lab 1: Introduction to Anatomy
Need to log in to view the dissector? Tap here for instructions on how to show the keyboard on the displays in the anatomy lab Download this lab as a PDF Lab outline Overview of the anatomy thread in the curriculum Anatomy lab safety, policies, and procedures The Willed Body Program Meeting your “First Patient” […]