Protected: Lab 14, Station 1: Pelvic Skeleton and Ligaments

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 14, Station 2: Pelvic Cavity and Anal Triangle of Perineum

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 13: Dissection: Posterior Abdominal Wall (PAW) and Kidneys
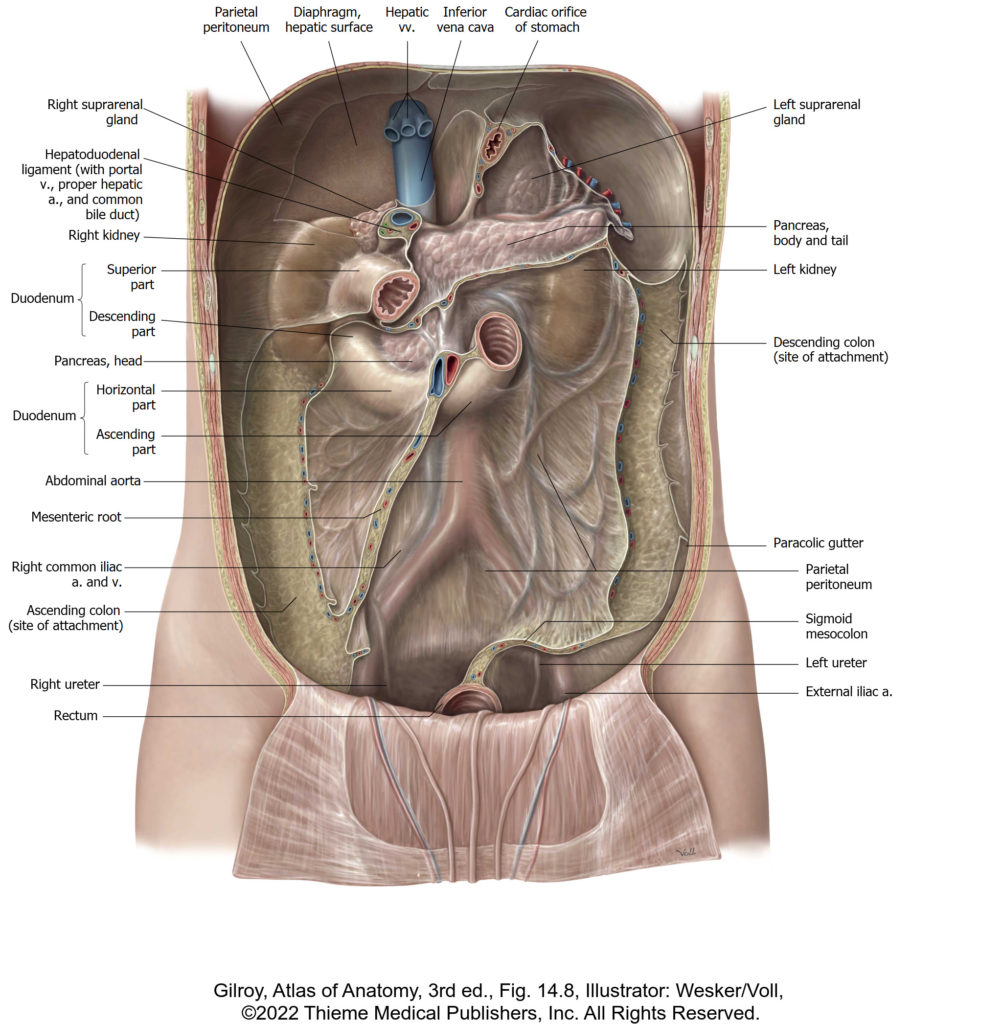
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 12: Infracolic Region
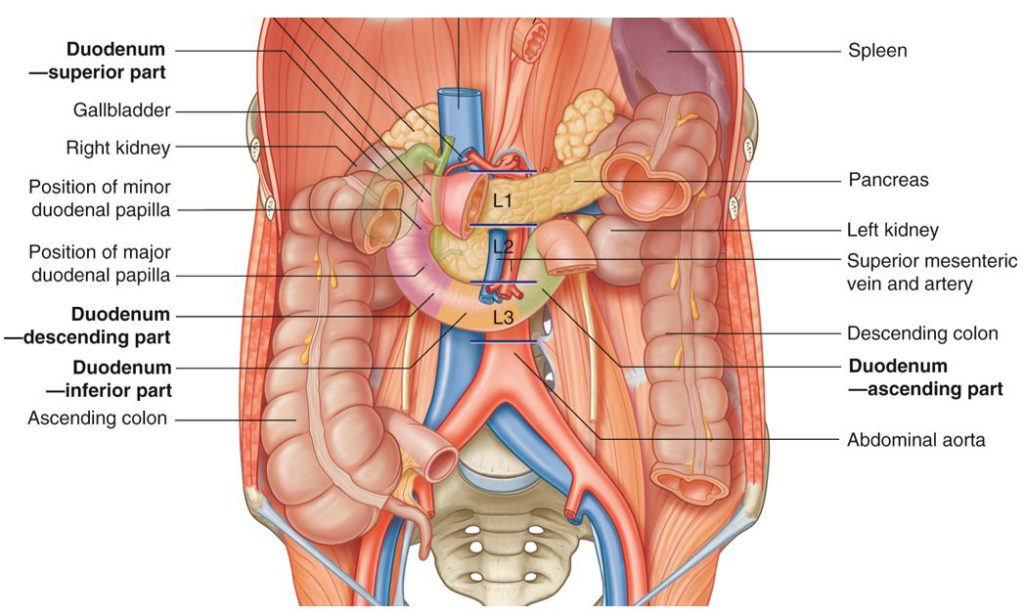
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 24: Peritoneal Cavity and Supracolic Region
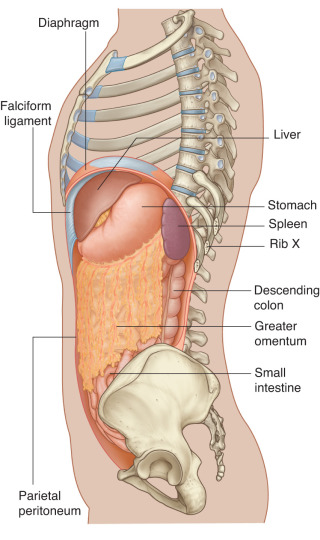
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 25: Infracolic Region

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 23: Oral Cavity, Pharynx, and Muscles of Mastication
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 23, Station 5: Oral Region and Salivary Glands—Lateral View

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 23, Station 4: Oral Cavity and Pharynx—Sagittal View

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 23, Station 3: Nerves and Vessels Associated with the Oral Cavity

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.