Multiple choice
Questions
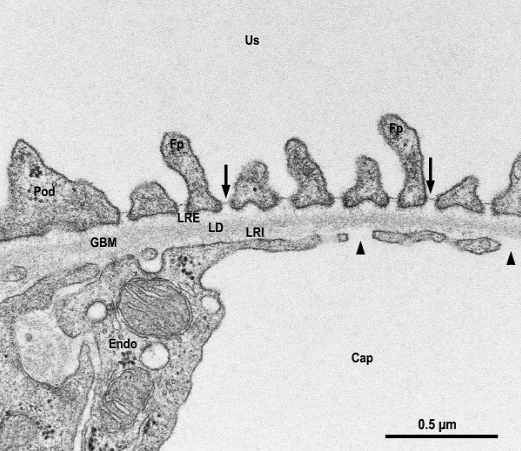
The glomerular filtration barrier is composed of pedicles of podocytes (visceral epithelium of Bowman’s capsule), glomerular basement membrane (GBM) or basal lamina (produced by both endothelial and epithelial cells), and the fenestrated endothelium of glomerular capillaries.
The glomerular filtration barrier is structurally composed of three layers, the capillary endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) and the podocyte filtration slit membrane. The barrier is freely permeable to water, solutes, and small molecules however, increasing size of macromolecules causes increasing restriction to filtration as do negative charge.
The contents of the cell are protected from the outside environment by a cell membrane. This cell membrane is made up of lipids that create a barrier that only certain substances can cross to reach the cell interior.
A potential difference is generated across the filtration barrier by the passage of the water and ions within the plasma across the glomerular filter. This potential influences the passage of negatively charged albumin across the filtration barrier.
Questions
Why do sodium, water, and glucose easily filter across the glomerular capillary?
The filtration membrane lies between the blood in the glomerulus and the filtrate in the Bowman’s capsule. This filtration membrane is fenestrated, which allows the passage of small molecules such as water, sodium, and glucose.
What protein significantly contributes to the glomerular basement membrane?
Laminin
Name Two Diseases that directly affect GBM.
- Turcot syndrome (27).
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome (5).
Question
- NFP is an algebraic sum of opposing hydrostatic and osmotic forces acting across the capillary.
- NFP = forces inducing filtraction – forces opposing filtration.
- NFP = (Pgc + πbc) – (Pbc + πgc)
Pgc: Glomerular hydrostatic pressure.
πgc: Glomerular oncotic pressure.
Pbc: Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure.
πbc: Bowman’s capsule oncotic pressure.
Question
Describe the Glomerular Starling Forces by labeling the vectors of: (Pgc, πgc, πbs, Pbs). Tap the
Plus signs to reveal the answer.
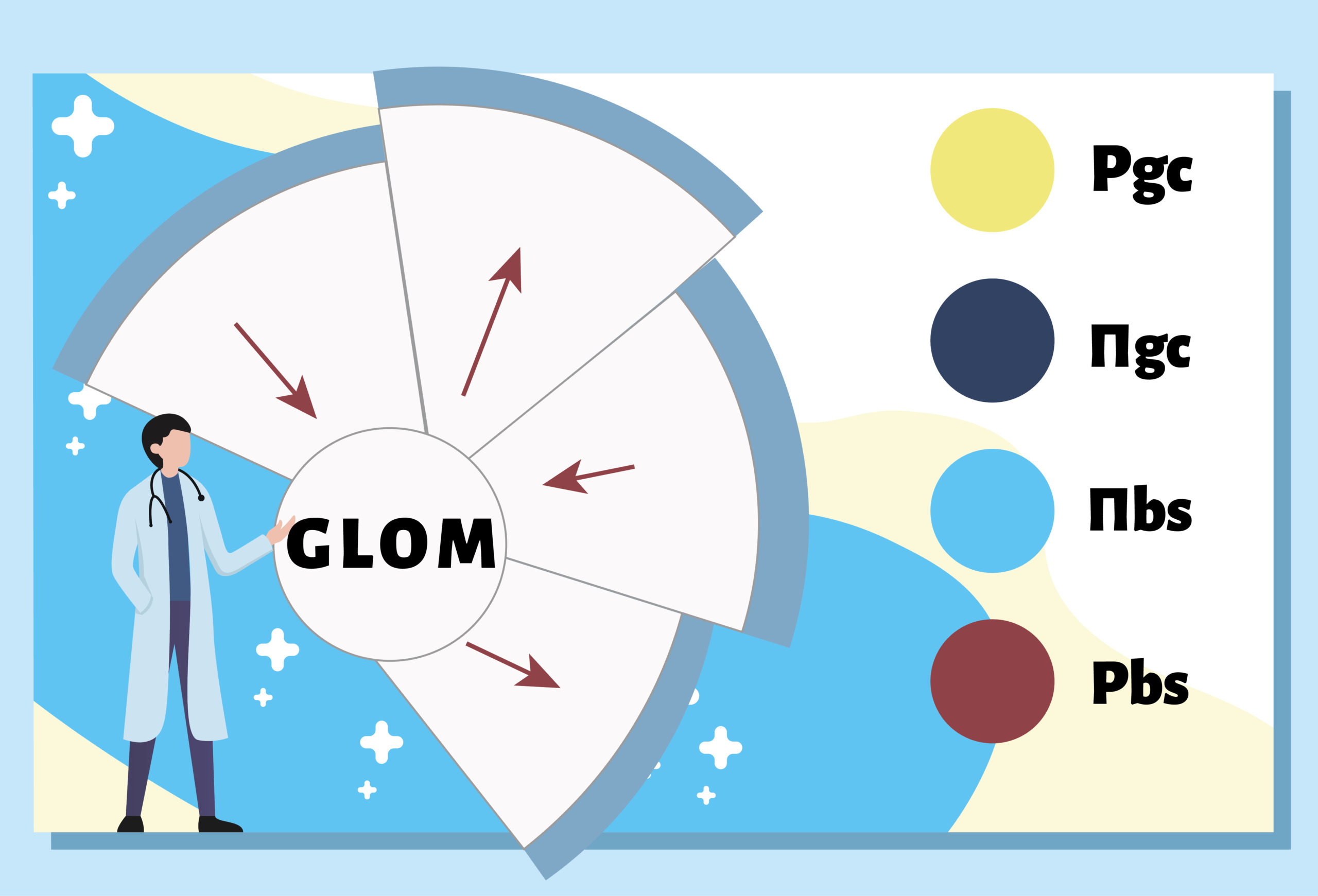
Pbc
Pbs
πgc
πbs
Question
What effect would an obstructing kidney stone or hydronephrosis have on NFP?
If a stone or calculus is blocking a major calyx, it will increase the capsular hydrostatic pressure and thus, there will be a decrease in net filtration pressure.
What two hormones allow for autoregulation of renal blood flow?
- Vasopressin
- Atrial natriuretic peptide
Where is renin produced?
Juxtaglomerular cells (JGCs), which releases renin from storage granules.
Question
Name 3 principal stimuli for renin release.
1
Baroreceptors in your arterial vessels detect low blood pressure.
2
Your kidneys detect low sodium levels.
3
Beta 1 adrenergic receptors detect activity in your sympathetic nervous system.
Questions
Name two different drugs that attenuate aldosterone activity.
- Spironolactone (Aldactone and CaroSpir).
- Eplerenone (Inspira).
What drug can lead to gynecomastia?
Spirolactone.
Name a drug that can help a patient who has both CHF and acne.
Aldactone.
What receptor does it effect and which part of the tubule?
Androgen receptor.
Distal convoluted renal tubule.
Recall the steps of filtration → reabsorption → secretion.
Questions
What does it mean if compound X in the urine > blood?
Answer.
What does it mean if compound X in the urine = blood?
Answer.
Semantics
GFR ~= CrCl CrCl = (U) x (V)
I doubt there will be written calculations, but be able to do quick mental math.