Neuroanatomy lab knowledge checks

Station 1. Meninges and ventricles Ventricles Interactive 1 On a mid-sagittal image, label the parts of ventricular systems highlighted in blue: 3rd ventricle 4th ventricle cerebral aqueduct lateral ventricle (Tap to open; use your Apple Pencil to draw) Labeled image Interactive 2 What do each of the yellow lines indicate on this T2-grayscale inverted […]
Neuroanatomy lab introduction
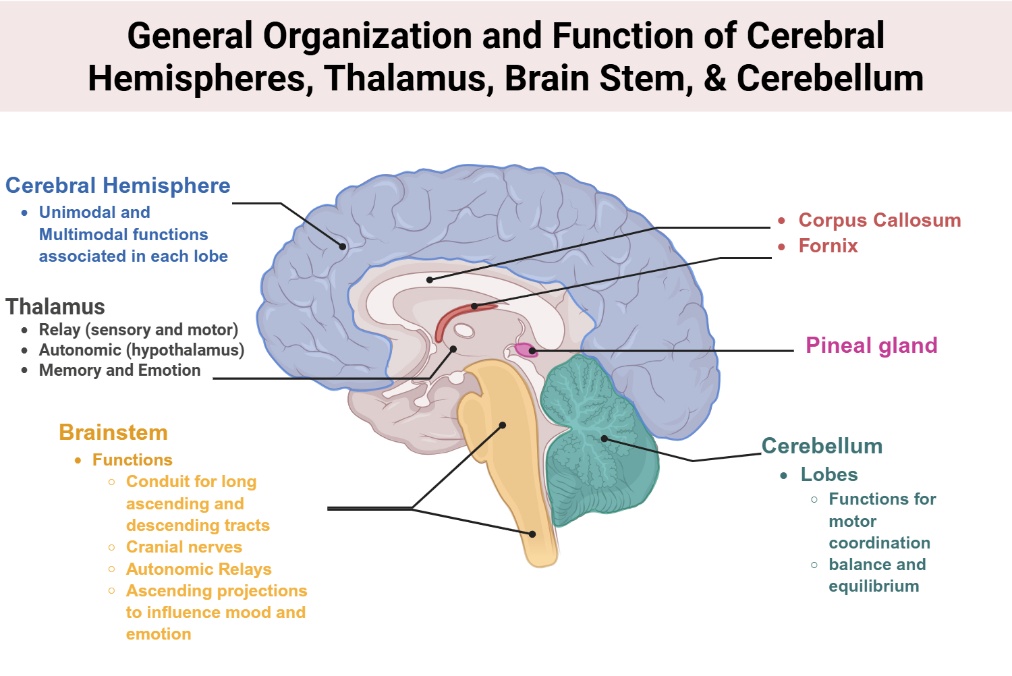
Neuroanatomy provides the essential framework for understanding the principles of neurology. This lab is designed to help you build that foundation through hands-on exploration and clinical application. Key focus areas Topographic anatomy Ventricular system, cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum Three-dimensional relationships Ventricular system and its connections to cerebral and brain stem structures Clinical imaging […]
Station 1. Meninges and ventricles
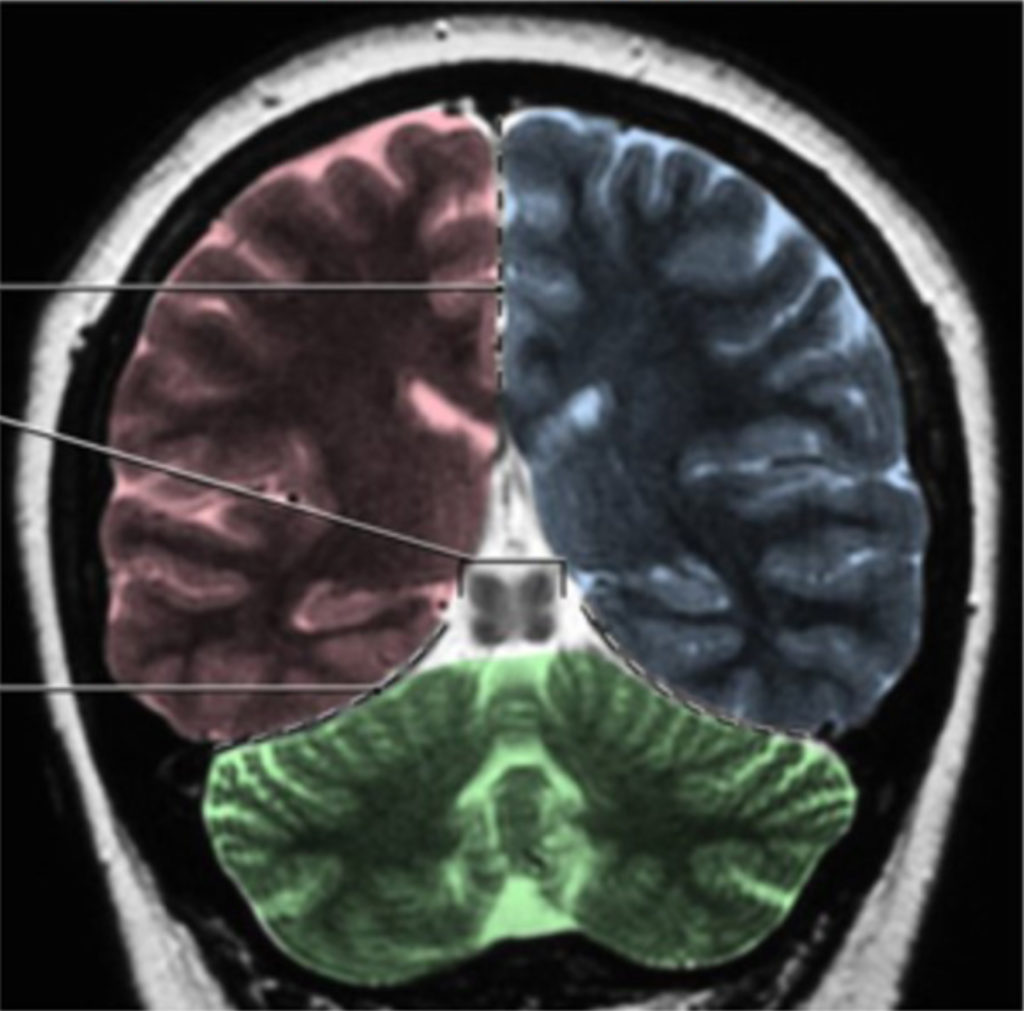
Neuroanatomy lab navigation Identify the parts of the ventricular system on a mid-sagittal brain, coronal sections, and model. The formation of the ventricular system, as it relates to development, was discussed in the Neuroembryology session. Review the clinical significance of the flow and blockage of CSF For further reference Figure 1. Figure 2. Lateral ventricles […]
Station 5: Blood supply and circulation
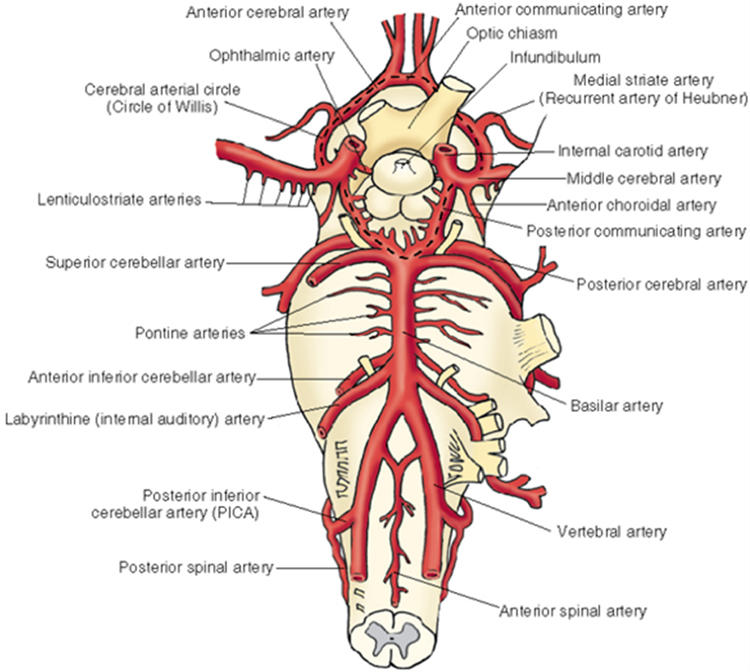
Neuroanatomy lab navigation Arterial blood supply Review and identify the arterial supply. Vertebral arteries supplying the brainstem and cerebellum Anterior and posterior spinal Posterior inferior cerebellar Basilar (unpaired)—multiple pontine branches also come directly off the basilar artery Anterior inferior cerebellar Superior cerebellar Posterior cerebral Posterior communicating Internal carotid supplying the midbrain, thalamus, hypothalamus, and cerebrum […]
Station 3. Diencephalon
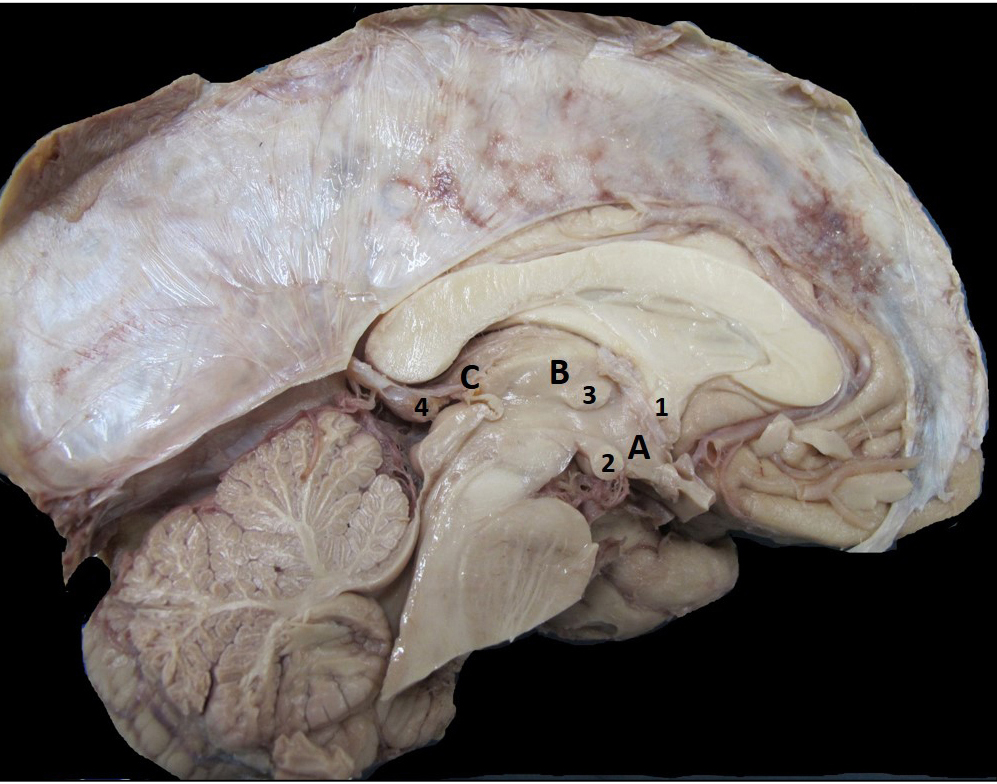
Neuroanatomy lab navigation The diencephalon is composed of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus. Thalamus The thalamus is key structure that relays information to the cortex associated with motor and sensory information. There are also thalamus nuclei that form the connections in the memory and emotion circuit from the hippocampal formation. This portion of the thalamus […]
Station 2. Cerebrum, sulci, and gyri

Neuroanatomy lab navigation Introduction to neuroanatomy Figure 1. Anatomic directional terms. From Neuroanatomy: A Laboratory Guide (2e); Jansen and Lampa. Introduction to the Central Nervous System Watch this excellent Introduction to the Central Nervous System from University of British Columbia Neuroanatomy. Cerebrum, sulci, and gyri Lobes of the cerebrum Recall that the surfaces of the […]
Station 4: The brainstem
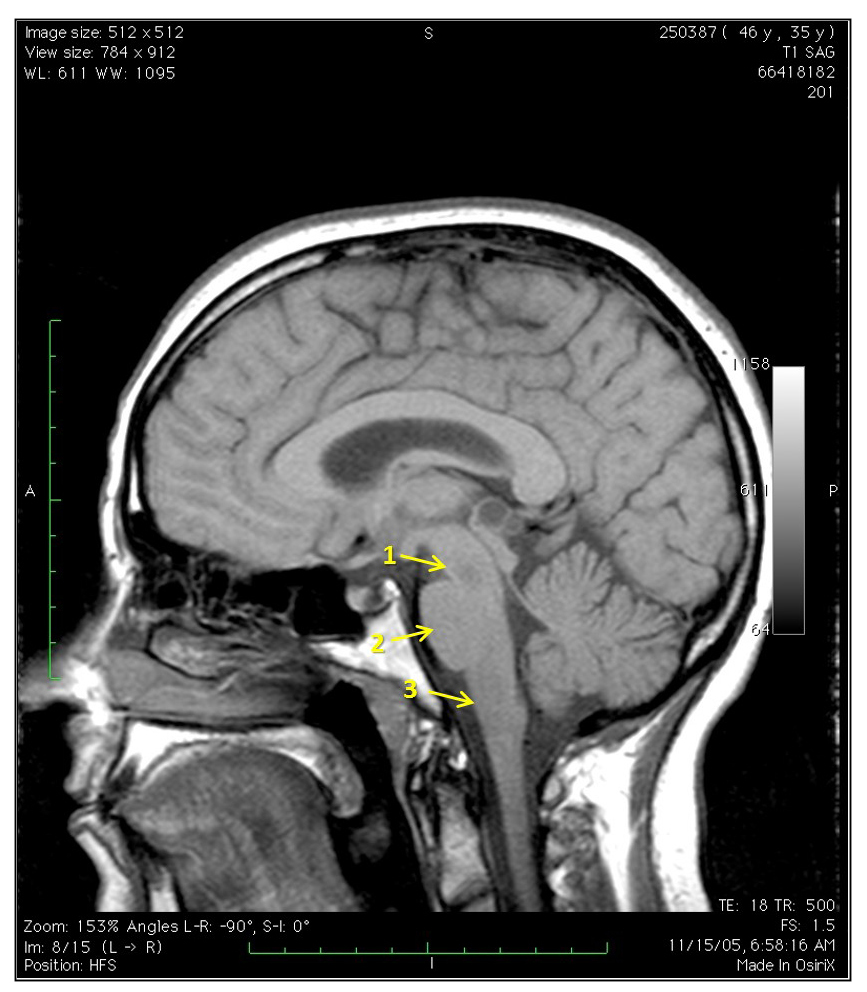
Neuroanatomy lab navigation Parts of the brainstem Midbrain Mesencephalon Pons Metencephalon Medulla Myelencephalon The basal subdivision of the brainstem is the most anterior and contains mostly the descending fiber tracts. The tegmentum is the location of the cranial nerve nuclei, ascending fiber tracts, and the reticular formation. In the medulla, it also contains important neurons […]
4. Limbic neurotransmitters and relevant neuroanatomy
Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) Primary location Concentrated in the hypothalamus, medial limbic system, locus ceruleus (rostral pons), and medulla. Functions Modulates alertness, attentiveness, and arousal. Clinical relevance Degeneration of noradrenergic projections from the rostral pons is implicated in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders. Current research explores its role in cognitive and behavioral changes (e.g., Holland et al., 2021). […]
3. Long-term potentiation and memory consolidation
Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) is a form of synaptic plasticity where repeated stimulation of a synapse increases its strength, enhancing the likelihood of future activation and contributing to memory formation. LTP mechanisms Glutamate release NMDA receptor activation Calcium influx Retrograde signaling via nitric oxide Leading to increased neurotransmitter release and synaptic responsiveness The LTP process Image […]
2. Memory function and the neuroanatomy
Key definitions Learning is a neural mechanism by which the organism’s behavior changes because of an experience or stimulus. Memory is the storage mechanism for what is learned. Normally, once memory information is encoded, it is no longer dependent on the hippocampus for retrieval. Memory involves distinct brain regions Hippocampus Critical for encoding and consolidating […]