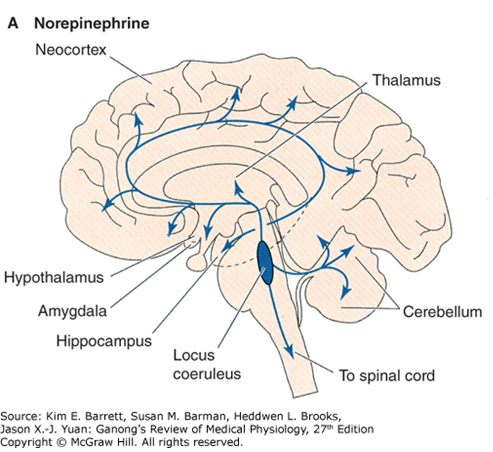
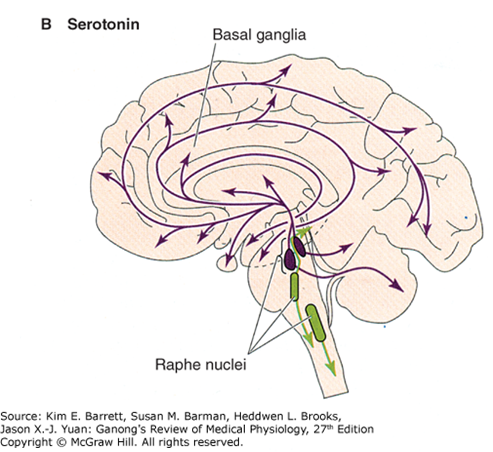
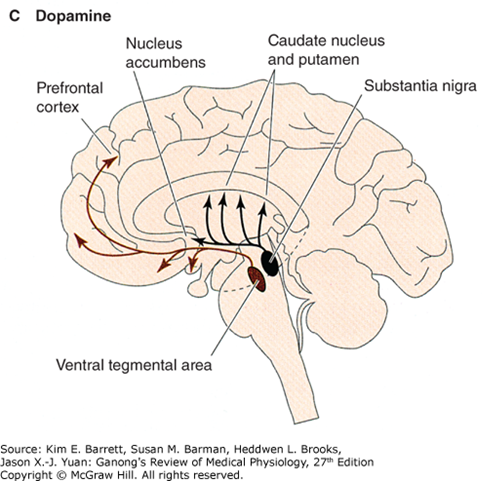
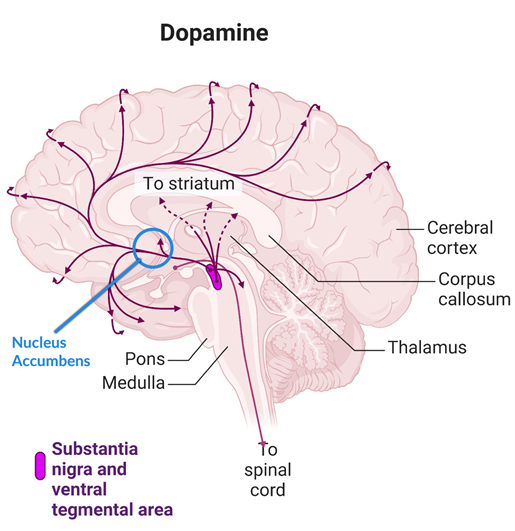
Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline)
Primary location
Concentrated in the hypothalamus, medial limbic system, locus ceruleus (rostral pons), and medulla.
Functions
Modulates alertness, attentiveness, and arousal.
Clinical relevance
- Degeneration of noradrenergic projections from the rostral pons is implicated in neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders.
- Current research explores its role in cognitive and behavioral changes (e.g., Holland et al., 2021).
Serotonin (5-HT)
Primary location
Originates in raphe nuclei of the brainstem; projects to amygdala, septal nuclei, and limbic-associated cortex.
Functions
Regulates mood, sleep, appetite, temperature, pain perception, blood pressure, and vomiting.
Clinical relevance
SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) are first-line treatments for depression, enhancing serotonin availability in synapses.
Dopamine
Primary location
Originates in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and substantia nigra; projects via medial forebrain bundle and nigrostriatal pathway.
Functions
Involved in reward, motivation, and motor control.
Clinical relevance
- Dopamine projections to nucleus accumbens mediate drug addiction and reward behaviors.
- Aberrant stimulation of substantia nigra can induce severe depressive reactions.
- Schizophrenia hypothesis: Excess dopamine activity may impair prefrontal cortex function, affecting thought organization and behavior.
Image credits
Unless otherwise noted, images are from Adobe Stock.