Station 1. Meninges and ventricles
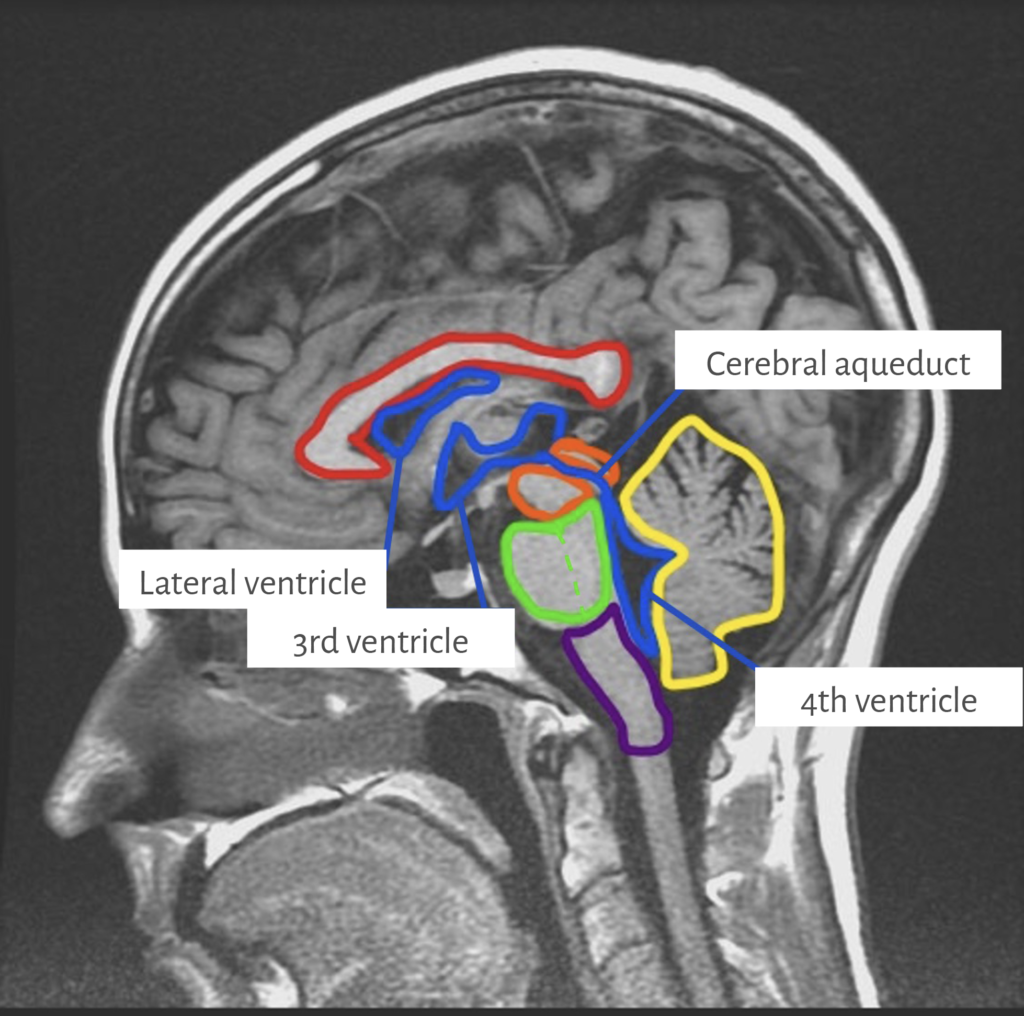
Ventricles
Interactive 1
On a mid-sagittal image, label the parts of ventricular systems highlighted in blue:
-
- 3rd ventricle
- 4th ventricle
- cerebral aqueduct
- lateral ventricle
(Tap to open; use your Apple Pencil to draw)
Interactive 2
What do each of the yellow lines indicate on this T2-grayscale inverted @ level hypothalamus, lateral and 3rd ventricles? (Tap the + for labels)
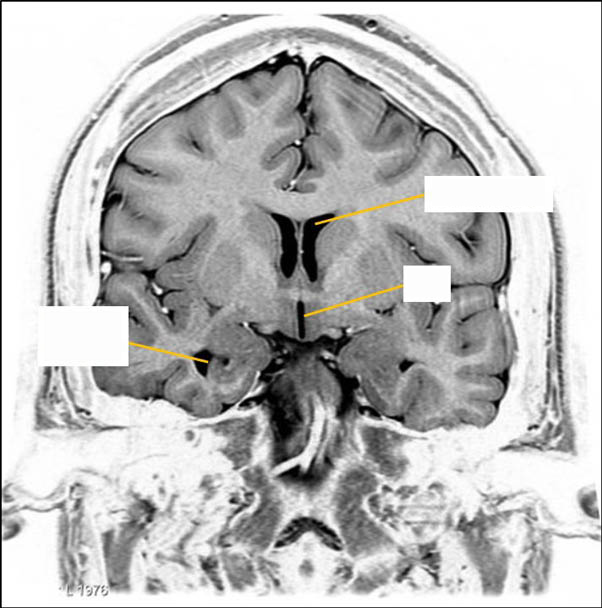
Inf. horn LV
3V
Ant. horn LV
Wikimedia.org by Frank Gaillard [GFDL 1.3CC BY SA 3.0, GFDL 1.3], Modified Lampa 7/09/18.
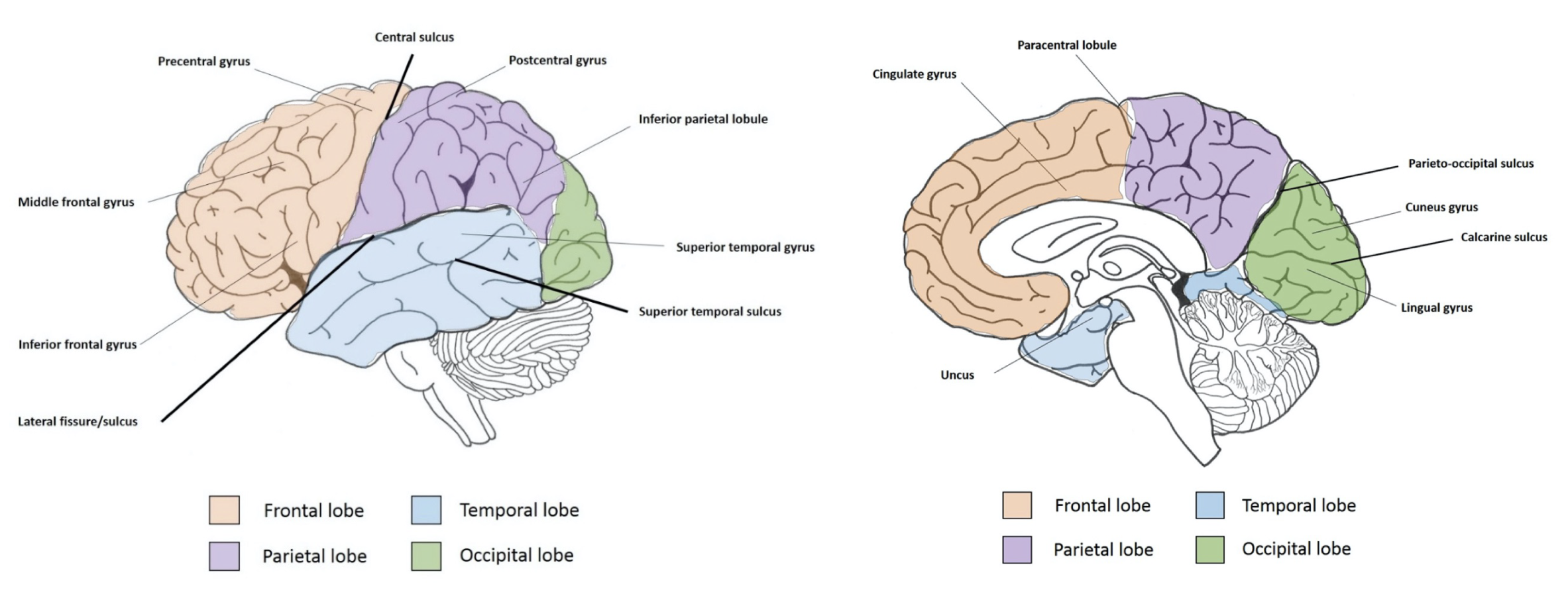
Station 2. Cerebrum, sucli, and gyri
Lobes of the cerebrum
interactive 3
Check your base knowledge of the functions of the cerebrum by filling in the blank cells. (Tap the right arrow for answers)
Sulci/fissures of the cerebrum
Interactive 4
Name the major sulcus on the medial surface separating the lobes. (Tap to open; use your Apple Pencil to draw)
Interactive 5
Identify the major sulci and gyri. The sulci are indicated by the dashed line, and major gyri/regions are indicated by the solid lines. Use Figures 10-5 and 10-6 in Clinical Neuroanatomy, 29e, by Stephen G. Waxman, for help in identification. (Tap to open; use your Apple Pencil to draw.)
Helpful hint
Use the sulci to map out the gyri of the cerebrum for identification.
Major gyri of cerebral lobes
interactive 6
What are each of these colored parts?
The coronal section is through the mid-thalamus and anterior portion of the midbrain and pons. Specimen from Neuroanatomy Collection, Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine. (Tap the right arrow for labels)
Portions of the medial temporal lobe outlined in green and light blue is an area where degeneration of cortical tissue occurs during Alzheimer’s disease (which will be discussed in the limbic system lecture in FMS 512 using case examples and providing clinical contexts).
Axonal fiber bundles of the cerebrum
Interactive 7
Which fiber bundles of cerebrum are each of these labeled parts?
Specimen from Neuroanatomy Collection, Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine. (Tap the right arrow for labels)
Station 3. Diencephalon
Epithalamus
Interactive 8
What are each of these labeled parts?
Diencephalon components and associated structures.
Specimen from Neuroanatomy Collection, Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine.
(Tap the right arrow for labels)
Station 4. The brainstem
Parts of the brainstem
Interactive 11
What do the yellow arrows on this T1-MRI of brainstem regions, mid-sagittal, indicate? (Tap the + for labels)
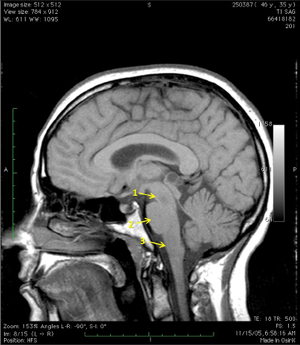
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
Image from Neuroanatomy Image Archive, Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine.
Interactive 12
Subdivisions of the brainstem; mid-sagittal plane. (Tap the right arrow for labels)
Specimen from Neuroanatomy Collection, Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine.
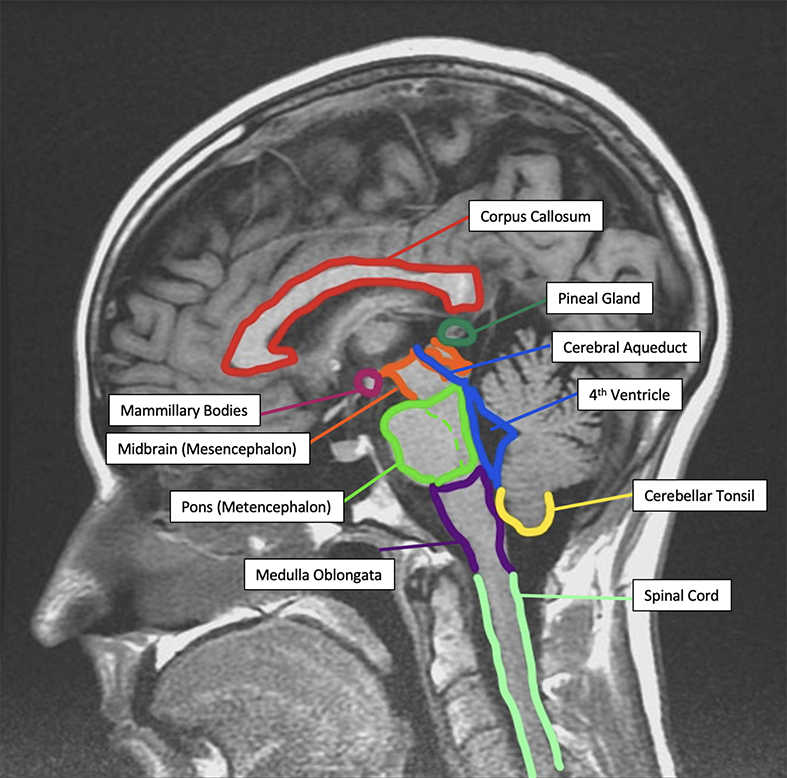
Interactive 13
Label the anatomic terms on an MRI:
-
- Corpus Callosum
- Pineal Gland
- Mammillary Bodies
- Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
- Cerebral Aqueduct
- 4th Ventricle
- Pons (Metencephalon)
- Spinal Cord
- Cerebellar Tonsil
- Medulla Oblongata
(Tap to open; use your Apple Pencil to draw)
Station 5. Blood supply and circulation
Interactive 14
Color and label the different vessels forming the circle of Willis. (Tap to open; use your Apple Pencil to draw)
Interactive 15
Color and label the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes lobes on the medial and lateral surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres. Use Figures 10-5 and 10-6 in Clinical Neuroanatomy, 29e, by Stephen G. Waxman, for help in identification. (Tap to open; use your Apple Pencil to draw.)
Interactive 16
Using the list below, identify what each of the white lines indicate on thisaxial MRI of cerebral circulation.
-
- ACA: Anterior cerebral artery
- ACoA: Anterior communicating artery
- ICA: Internal carotid artery
- MCA: Middle cerebral artery
- PCA: Posterior cerebral artery.
(Tap the + for labels)
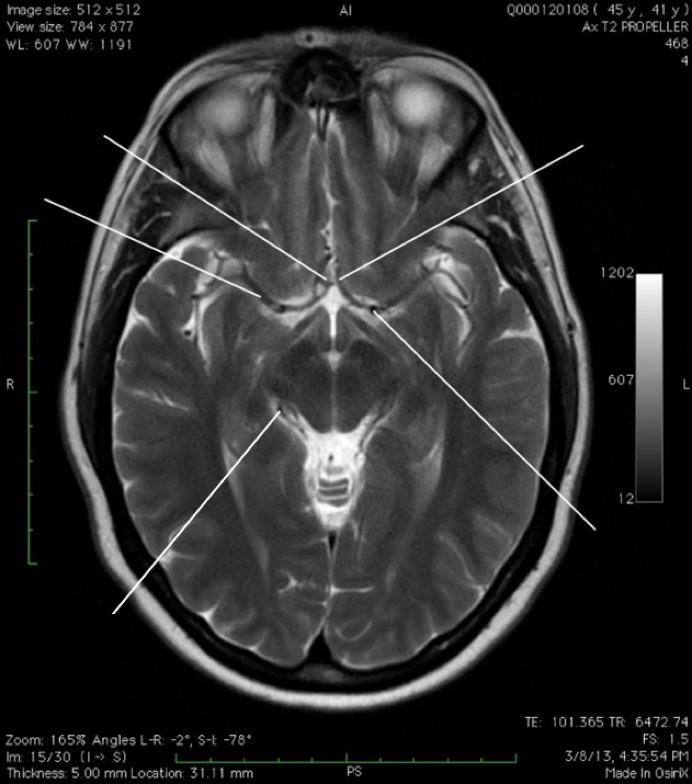
AcoA
MCA
PCA
ACA
ICA
Image from Neuroanatomy Image Archive, Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine.
Venous circulation
Appendix of Additional Stroke Images (MRI/CT)
For these images, try to come up with the signs/symptoms that a patient would present with.