- Suggested reading
- Need to Know
If you do all these readings, it’s about two chapters worth. It’s not a bad read, but be mindful of your time. Look at the NTK guide and adjust your preparation as needed.
The amino acid pdf below is a short read. I would not stress about memorizing the structures. However, it would be good to know the classifications of the amino acids.
This is not the full chapter on “Globular Proteins”—only part of it. The rest of this chapter (or at least the concepts) will come back during the Heme component of the curriculum.
The Fibrous Protein chapter in Lippincott is a bit long. However, it is full of useful information and high yield information. You may want to look at the NTK guide to help you with the reading.
Compare and contrast the structure and function of myoglobin and hemoglobin, and explain how their differences relate to oxygen transport and storage
-
Heme
-
Myoglobin
-
Hemoglobin
-
Quaternary structure in hemoglobin
-
T form
-
R form
-
Oxygen binding to myoglobin and hemoglobin
Compare and contrast the structure and function of collagen and elastin, and explain how mutations in these proteins contribute to connective tissue disorders
-
Prolyl hydroxylase
-
Lysyl hydroxylase
-
Procollagen peptidases
-
Lysyl oxidase
-
α1-antitrypsin (AAT)
-
Elastase
-
Collagen
-
Fibril forming collagen
-
Fibril-associated collagen
-
Network forming collagen
-
Fibrillin
-
Desmosine cross-link
-
Collagen and the different abundant types
-
Vitamin C-dependent hydroxylation
-
Scurvy
-
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
-
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Identify and describe the side chains of the 20 common amino acids, and explain how the side chains play different roles in protein structure
Identify and describe the side chains of the 20 common amino acids, and explain how the side chains play different roles in protein structure
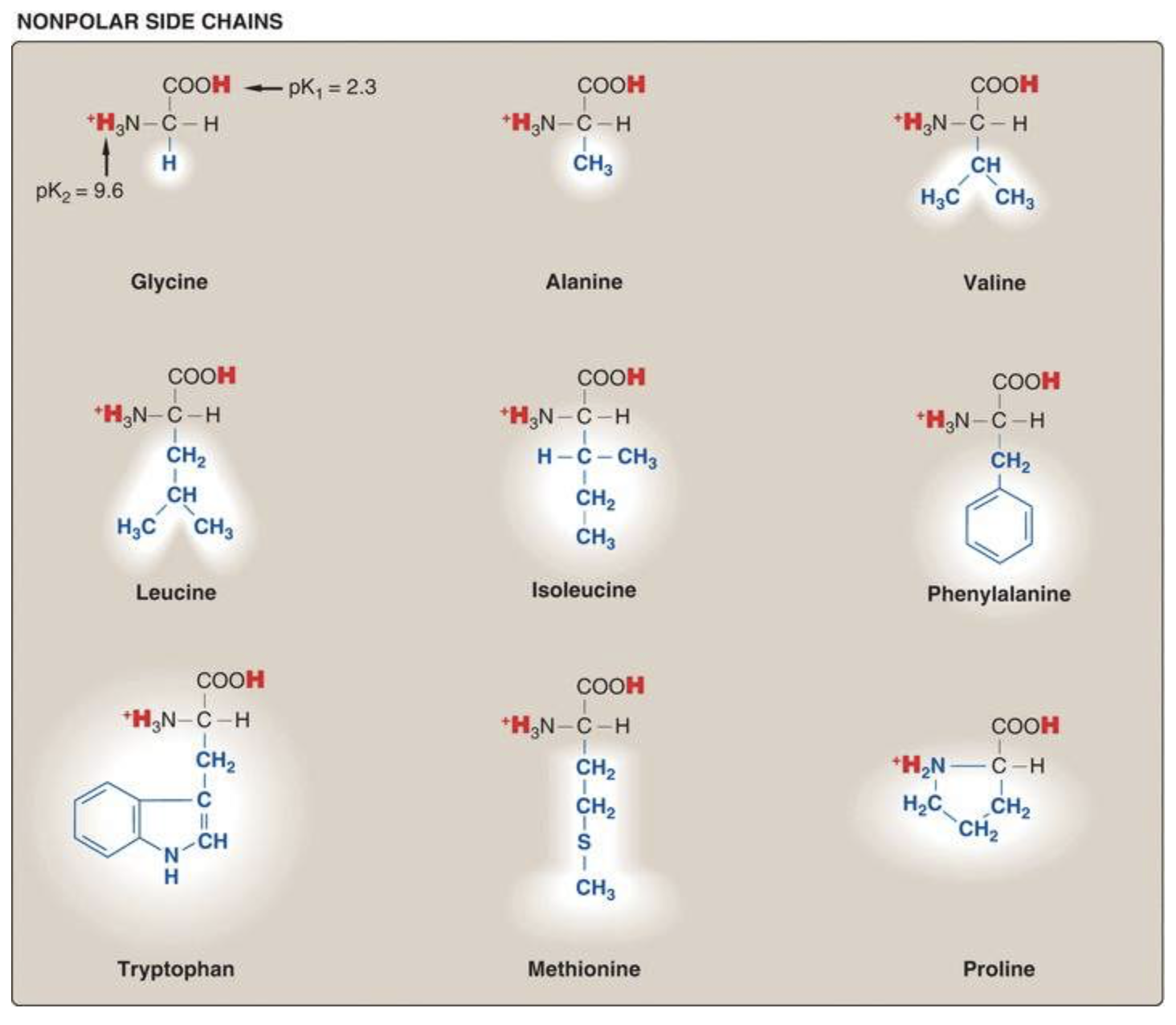
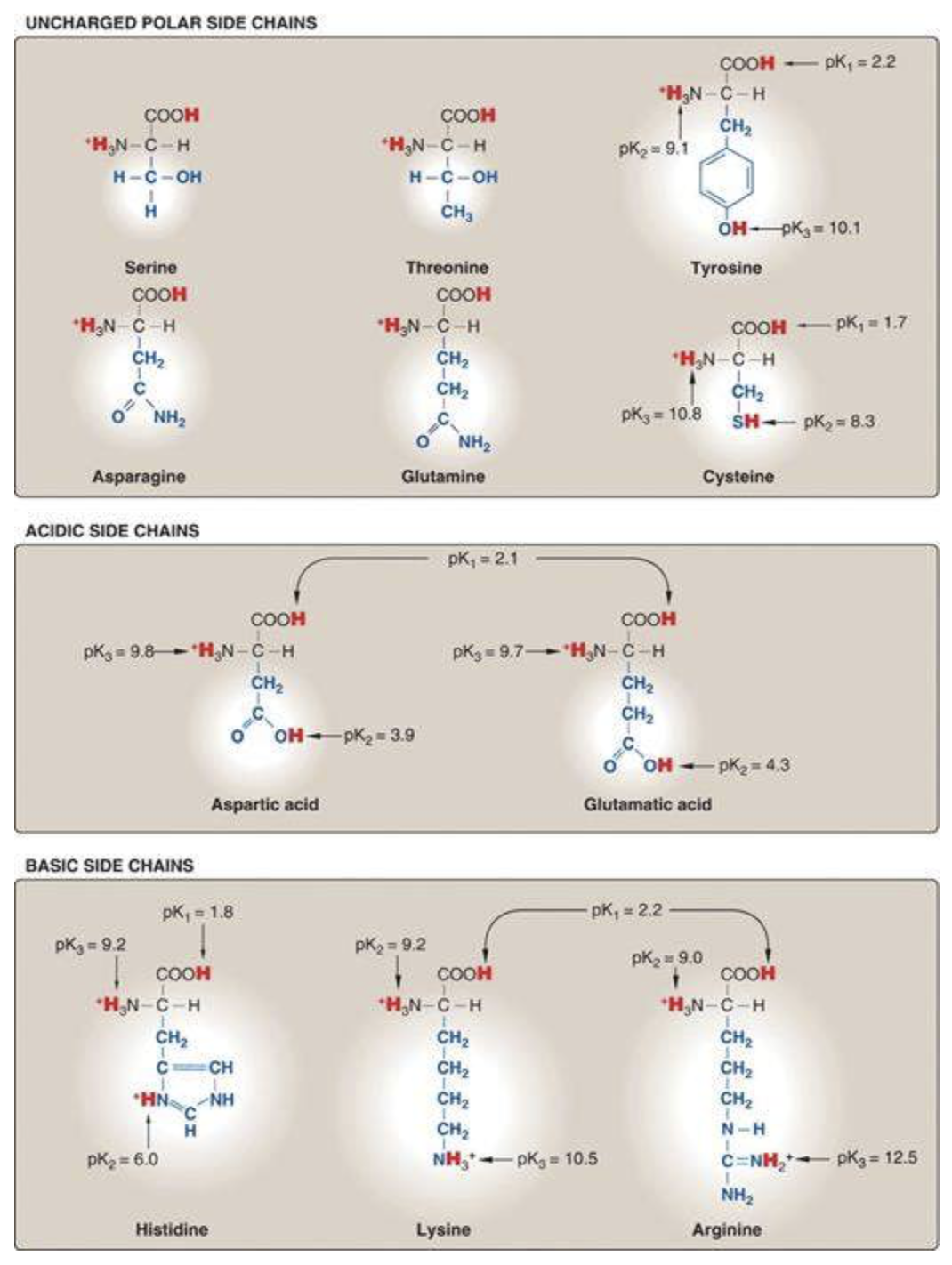
There are 20 standard amino acids. It’s good to be able to classify them based on their biochemical properties. These figures, taken from Lippincott, are a good way to organize all twenty.
This Osmosis video on amino acids and protein folding is worth watching if you are unfamiliar with the amino acids and protein structure.
Nonpolar amino acids tend to be in the interior of soluble proteins and cluster on the surface of membrane proteins.
Compare and contrast the structure and function of myoglobin and hemoglobin, and explain how their differences relate to oxygen transport and storage
This video is a good comparison and contrast of hemoglobin and myoglobin. There is some information that is not as pertinent for this learning goal. However, if you want a quick video to look at, this is not a bad one. We will discuss this in class.
Compare and contrast the structure and function of collagen and elastin, and explain how mutations in these proteins contribute to connective tissue disorders
This video (which I believe Dr. Helbling also used) briefly talks about collagen and elastin. This will be discussed in class.
These three videos on disease states are worth watching. All three of these diseases are “high-yield” to know. Once again, these will be discussed in class (if you don’t have the time to watch them).