Learning goals
- Differentiate the viral structure, mode of transmission, epidemiology, and risk of chronic infection for viral hepatitis caused by hepatitis A, B, C, D and E
- Use clinical presentation and laboratory testing, including serology and molecular testing (PCR), to distinguish acute infection, chronic infection, resolved infection, and post-vaccination for hepatitis A, B, and C
- Describe complications, including extrahepatic conditions, associated with chronic Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C viral infection
- Compare and contrast treatment of Hepatitis A, B, and C, list the pharmacologic classes of drugs used to treat Hepatitis B and C, and describe ways to prevent viral hepatitis, including active and passive immunization
Required pre-class materials
-
Sherris Medical Microbiology, 8e
Use Sherris Chapter 13 to complete the following Hepatitis Chart worksheet.
The following are the recommended sections and notes of what to focus on:
Chapter 13: Hepatitis Viruses
-
Hepatitis A: Blue boxes provide pertinent details: Overview, key-points, and Key conclusions
-
Section on Hepatitis B:
-
Figure 13-5: Replication cycle of hepatitis B virus—note the use of reverse transcriptase in replication cycle
-
Hepatitis B Disease:
-
Epidemiology
-
Pathogenesis: Note the consequence of immune response to HCV infection and immune complexes in extra-hepatic manifestations.
-
Clinical aspects
-
-
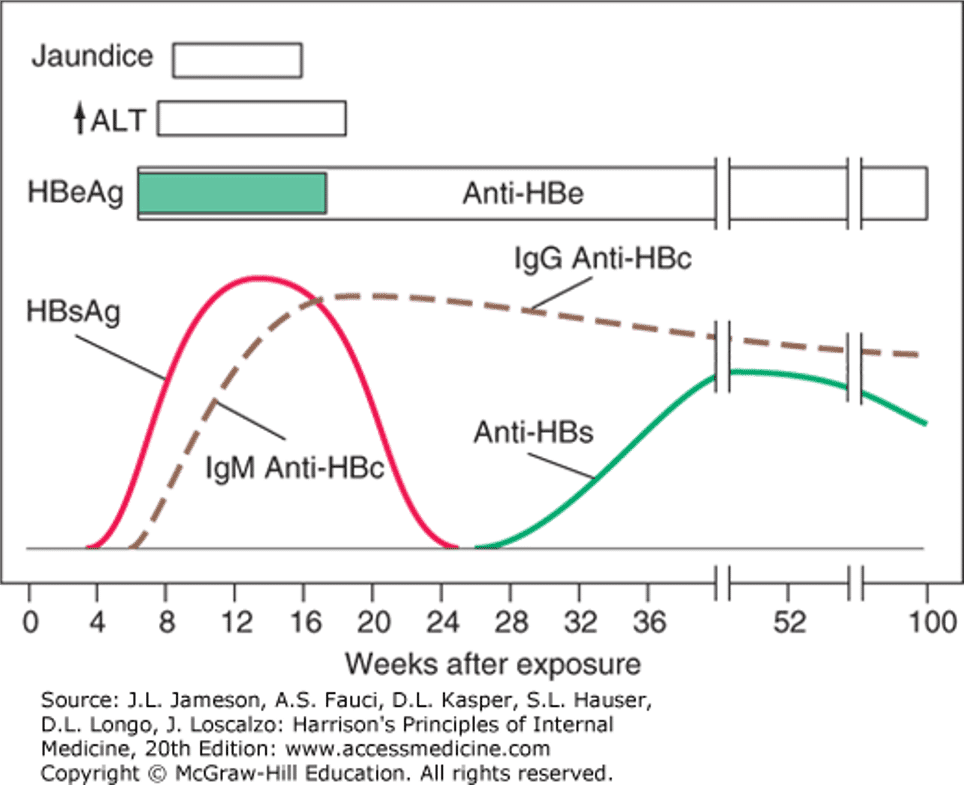
Figure 13-7: Sequence and appearance of viral antigens and antibodies in acute self-limiting cases of hepatitis B.
-
Figure 13-8 Sequence of appearance of viral antigens and antibodies in chronic active hepatitis B (compare and contrast to figure 13-7).
-
-
Hepatitis C:
-
Hepatitis C disease:
-
Epidemiology
-
Pathogenesis: Note the consequence of immune response to HCV infection and immune complexes in extra-hepatic manifestations (compare/contrast with HBV.
-
Treatment and prevention: Note types of antivirals used and the principles of combination therapy.
-
-
Figure 13-12: Sequence of appearances of viremia, ALT, symptoms, antibodies in acute HCV infection, and progressions to chronic infection
-
-
Hepatitis E: Focus primarily on Epidemiology and Clinical Aspects
Recommended study materials
These are not required; they are supplementary to large group session. They are intended as a curated guide to content focused on the learning objectives. There are both textbook and video resources for this session for students to use per their preference.
Click the blue icons below to go to the resources listed.
-
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 20e
Chapter 332: Acute Viral Hepatitis
- Figure 332-4. Scheme of typical clinical laboratory features of acute Hepatitis B.
-
Sherris Medical Microbiology, 7e
Chapter 47: The Systemic Fungal Pathogens: Cryptococcus, Histoplasma, Blastomyces, Coccidioides, Paracoccidioides
- Focus on mycology, clinical aspects, and recognizing organism on pathology.
For those who prefer audio/video resources, these are good, quick, and relevant videos.