Amphotericin B
Ampho B
- Broad spectrum, little resistance
- GI and renal toxicity limit dose
- Binds ergosterol causing cytoplasmic membrane holes
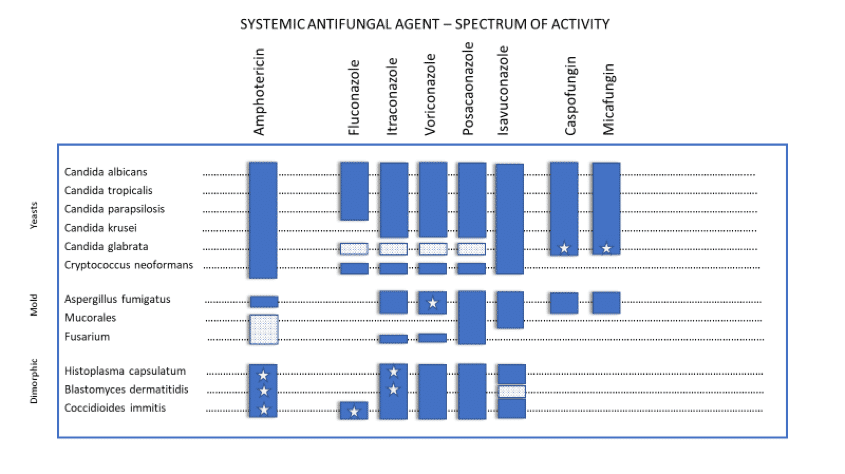
Azoles
Fluconazole, Miconazole, Itraconazole, Voriconazole, Posaconazole, Isavuconazole
- Inhibits ergosterol synthesis in cytoplasmic membrane
- Topical Rx for dermatophytes and skin
- Candida (clotrimazole, miconazole)
- Systemic Rx specific to different fungi
- Voriconazole is best for aspergillus
Echinocandins
Caspofungin, Micafungin, Anidulafungin
- Inhibit glucan synthesis in cell wall
Flucytosine
5-FC
- Inhibits DNA and RNA
- Easily induces resistance so always combine with another drug, especially Ampho B
Griseofulvin and Terbinafine
- Used orally for dermatophytes
Nystatin
- Topical Rx for oral or cutaneous Candida
Terbinafine (Lamisil, Lamisil AT)
-
Class(es)
Antifungal
-
Clinical use(s)
FDA approved: Dermal mycosis, onychomycosis due to dermatophyte, Tinea capitis.
-
Mechanism(s) of action
Inhibits the biosynthesis of ergosterol, an integral component of fungal cell membrane.
-
Key adverse effects
Nasopharyngitis (oral granules, 10% ), increased liver enzymes (oral tablets, 3.3% ), Terbinafine 1% topical cream or gel has been associated with local burning, pruritus, skin discoloration, or erythema (2%).
-
Key drug/food interactions
Strong CYP2D6 inhibitor. Avoid drugs primarily metabolized by CYP2D6 (e.g., codeine, tramadol, metoclopramide).
-
Special considerations
Available orally and topically only. Contraindicated in chronic or active liver disease.
Nystatin (Mycostatin)
-
Class(es)
Polyene antifungal
-
Clinical use(s)
FDA approved: Candidiasis infection treatment.
Off-label/clinical use: Candidiasis infection prophylaxis. -
Mechanism(s) of action
Binds to sterols in the fungal cell membrane leading to loss of membrane barrier selectivity.
-
Key adverse effects
Skin irritation.
-
Key drug/food interactions
None significant.
-
Special considerations
Powder: Very moist lesions are best treated with topical powder.
Oral suspension: For oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis, have patients swish and swallow. For oral thrush, have patients swish and spit.
Fluconazole (Diflucan)
-
Class(es)
Triazole/Antifungal
-
Clinical use(s)
FDA approved: Candidiasis, cryptococcal meningitis, antifungal prophylaxis in allogenic bone marrow transplant patients.
Off-label/clinical use: Coccidioidomycosis, cryptococcal pneumonia, primary antifungal prophylaxis in pediatric oncology. -
Mechanism(s) of action
Interferes with fungal cytochrome P450 activity decreasing ergosterol synthesis and inhibiting cell membrane formation.
-
Key adverse effects
Nausea, headache, elevated liver enzymes.
-
Key drug/food interactions
QT prolonging medications, warfarin, carbamazepine.
-
Special considerations
Risk QT prolongation.
Renally adjusted: CrCl < 50 ml/min.
Voriconazole (Vfend)
-
Class(es)
Triazoles/Antifungal
-
Clinical use(s)
FDA approved: Aspergillosis, candidemia, candidiasis of the esophagus, invasive candidiasis, mycosis, serious infections due to scedosporium apiospermum and fusarium spp.
Off-label/clinical use: blastomycosis, candida endophthalmitis, febrile neutropenia, mycosis due to scedosporium prolificans, oropharyngeal candidiasis, pulmonary aspergillosis. -
Mechanism(s) of action
Inhibits fungal cytochrome P450-dependent ergosterol synthesis resulting in loss of ergosterol in the fungal cell wall.
-
Key adverse effects
Hallucinations, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting.
-
Key drug/food interactions
QT prolonging medications, St. Johns Wort, food (may ↓ voriconazole absorption).
-
Special considerations
Risk of QT prolongation.
Amphotericin B (Amphocin, Fungizone)
-
Class(es)
Antifungal
-
Clinical use(s)
FDA approved: Aspergillosis (invasive), candidemia and other candida infections, candidiasis esophageal, fungal infections, empiric therapy.
Off-label/clinical use: Candidiasis oropharyngeal, other candida infections. -
Mechanism(s) of action
Inhibits synthesis of β(1,3)-D-glucan, an essential component of the cell wall of susceptible fungi.
-
Key adverse effects
Elevated liver enzymes, hypotension, tachycardia, elevated serum creatinine.
-
Key drug/food interactions
Cyclosporine, rifampin, tacrolimus.
-
Special considerations
Hepatically adjusted: Moderate-severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B/C).
Black box warning: Should not be used in noninvasive forms of fungal infections.
Caspofungin (Cancidas)
-
Class(es)
Echinocandin/Antifungal
-
Clinical use(s)
FDA approved: Aspergillus, candidemia, candidiasis of esophagus, febrile neutropenia (empiric antifungal), invasive candidiasis.
Off-label/clinical use: Aspergillosis, candida endophthalmitis, candidiasis (cardiovascular/osteoarticular), oropharyngeal candidiasis, pulmonary aspergillosis. -
Mechanism(s) of action
Inhibits synthesis of β(1,3)-D-glucan, an essential component of the cell wall of susceptible fungi.
-
Key adverse effects
Hypotension, diarrhea, elevated liver enzymes.
-
Key drug/food interactions
Cyclosporine, tacrolimus, rifampin.
-
Special considerations
Hepatically adjusted: Moderate-severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B/C).