Development of urinary organs
Optional Reading The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 11th ed., Development of urinary system section through Development of suprarenal glands. The urinary and reproductive (genital) systems have several features in common and are sometimes considered together as the uro-genital system. Most shared features are developmental in nature: Both the kidneys and the gonads arise from […]
Lab 29: Neck: Anterior Triangle of Neck
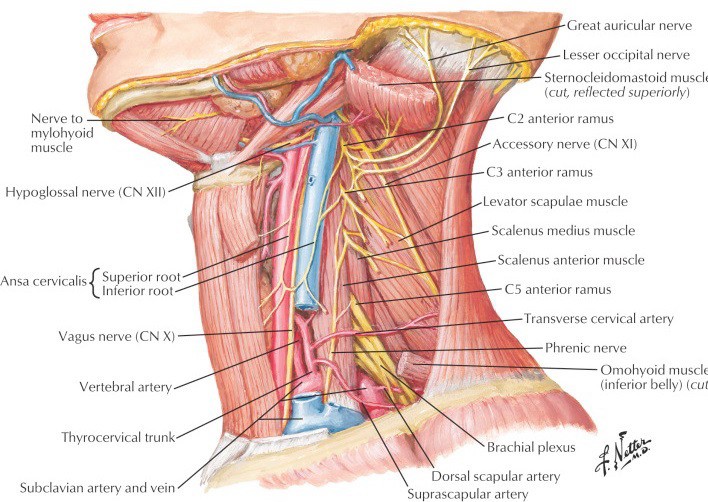
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Review the bony anatomy of the cervical vertebrae and the hyoid bone. Clean the muscles and landmarks that define the triangles of the neck. Dissect the contents of the anterior triangle focusing on these subtriangles: carotid, muscular, and submental. Study prosected specimens. Osteology of the Neck Cervical Vertebrae […]
Lab 18: Dissection: Posterior Abdominal Wall (PAW) and Kidneys
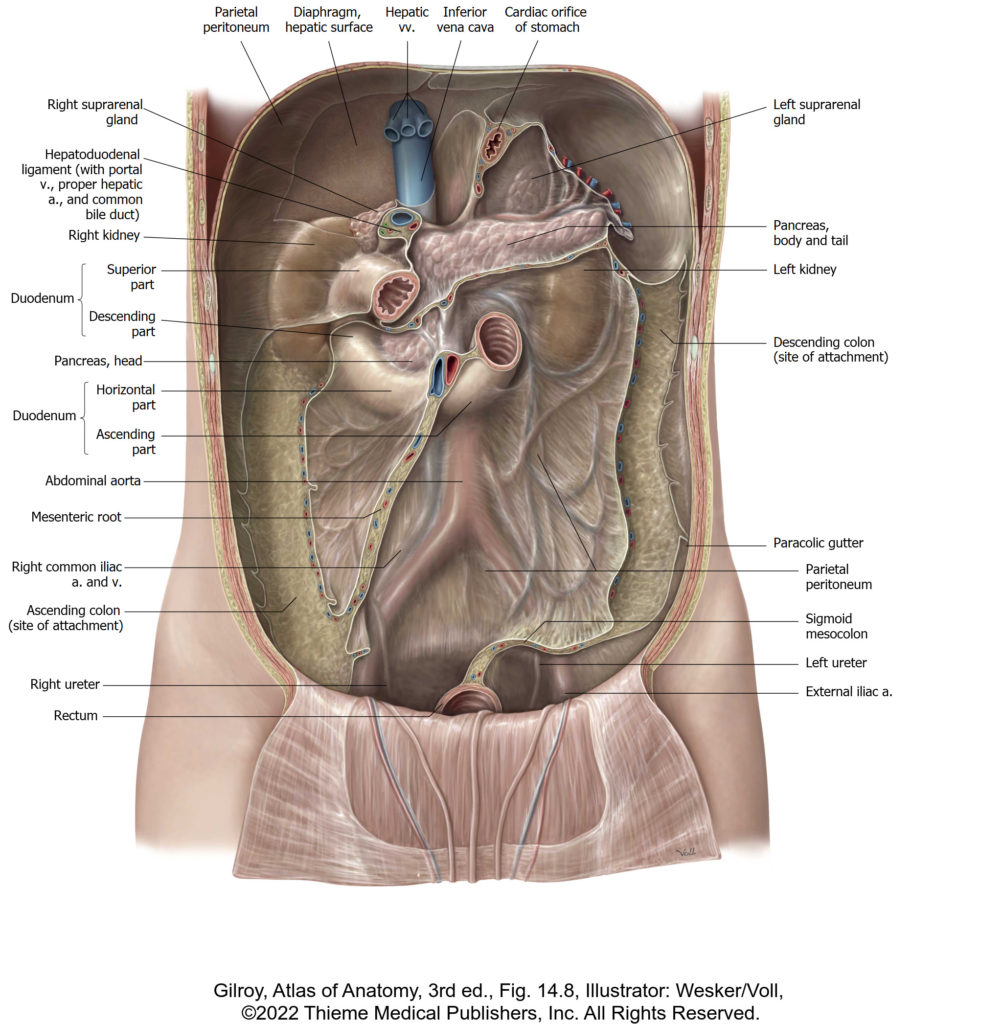
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Demonstrate the fascias surrounding the kidneys. Clean the kidneys and identify features of their external and internal anatomy. Identify the ureters and trace them into the pelvis. Identify the suprarenal glands and name their parts. Identify the parts of the diaphragm. Clean and identify the muscles of the […]
Lab 28: Dissection: Orbit and Ear
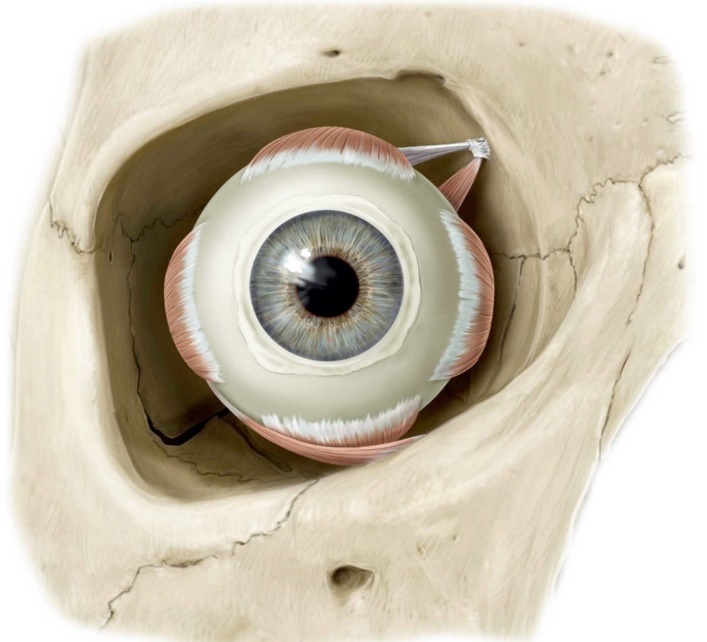
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Identify the bony walls and foramina of the orbit. Open the orbit via a superior approach on both sides and dissect its contents. Find the lacrimal gland in the cadaver and study the lacrimal apparatus on a model. Dissect the orbit from an anterior approach on both sides […]
Lab 27: Face, Parotid Gland, and Superficial Neck
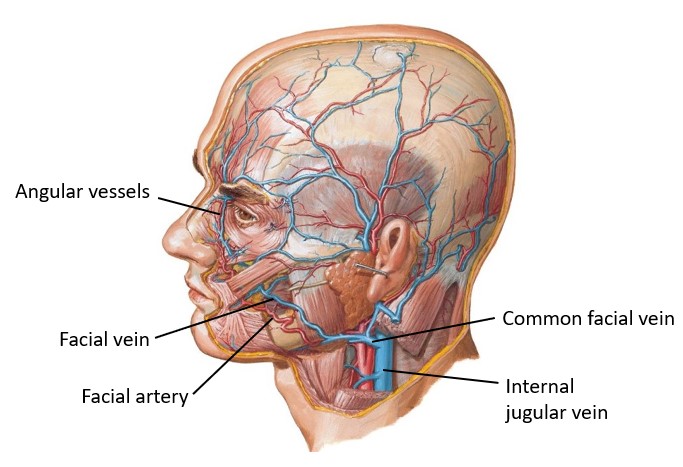
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Identify the bones associated with the face and parotid gland. Identify surface landmarks on the face. Clean and identify muscles of facial expression. Identify branches of the facial nerve on the face. Locate the major sensory nerves of the face. Identify the facial artery and vein. Identify the […]
Lab 26: Scalp, Cranial Cavity, and Meninges
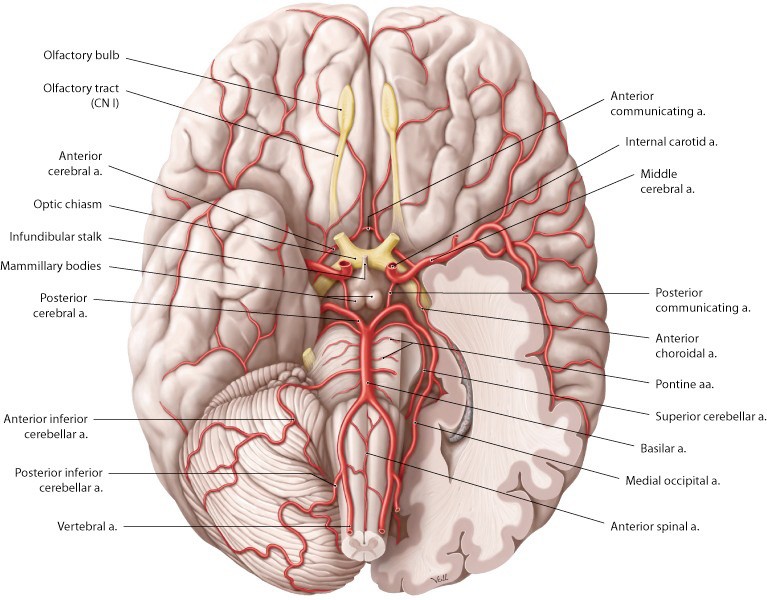
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Identify the layers of the SCALP. Examine the dura mater and the dural septae. Remove the brain and study: meningeal coverings, gross features, and arterial supply (circle of Willis). Examine the internal aspect of the base of the skull and the cranial fossae. Identify cranial nerves and blood […]
Protected: Lab 17, Station 5: Head and Neck Anatomy—Sagittal View

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Lab 17, Station 4: Blood Vessels

Lab 17 navigation Station 4: Blood Vessels Major Arteries Common carotid artery Carotid bifurcation Carotid body—vascular structure that lies in the “crotch” of the carotid bifurcation—contains chemoreceptors that monitor the status of blood gases (may not be visible in prosection) Internal carotid artery Carotid sinus—a swelling of the proximal internal carotid artery—contains baroreceptors that monitor […]
Lab 17, Station 3: Gross Topography of the Brain

Lab 17 navigation Station 3: Gross Topography of Brain Cerebrum Composed of left and right hemispheres. The hemispheres are connected across the midline by a thick tract of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum. Each hemisphere contains a cavity called a lateral ventricle—filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Lab 17, Station 2: Cranial Base and Cranial Nerves

Lab 17 navigation Station 2: Cranial Base and Cranial Nerves The cranial cavity is the space within the neurocranium. It contains the brain, meninges, blood vessels, and the proximal parts of the cranial nerves. The floor is the cranial base. Foramina in the cranial base transmit cranial nerves and blood vessels. The cranial base has […]