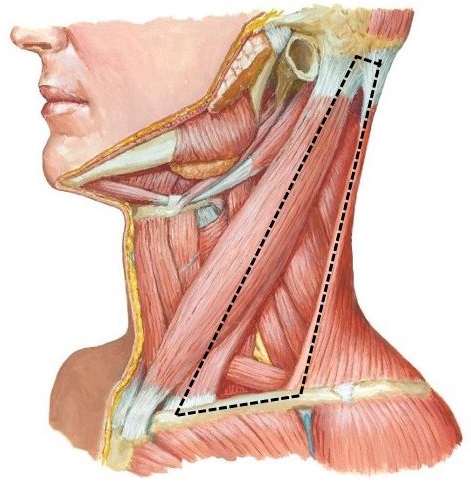
Protected: Lab 29: Neck: Anterior Triangle of Neck
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Orbit, eyelids, and lacrimal apparatus
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Head chapter, Orbits, eyeball, and accessory visual structures section through Lacrimal apparatus; Extra-ocular muscles of orbit section through Surface anatomy of eye and lacrimal apparatus. The orbit is the bony “eye socket” that contains the eyeball, extra-ocular muscles, nerves and vessels, and the lacrimal gland. It is protected […]
Protected: Lab 20: Dissection: Pericardium, Heart, and Mediastinum
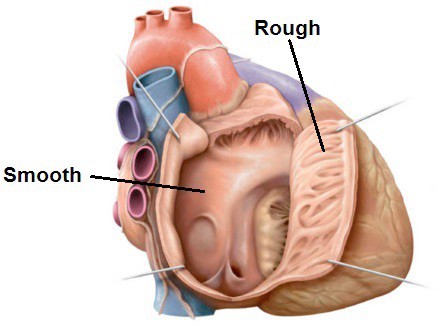
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
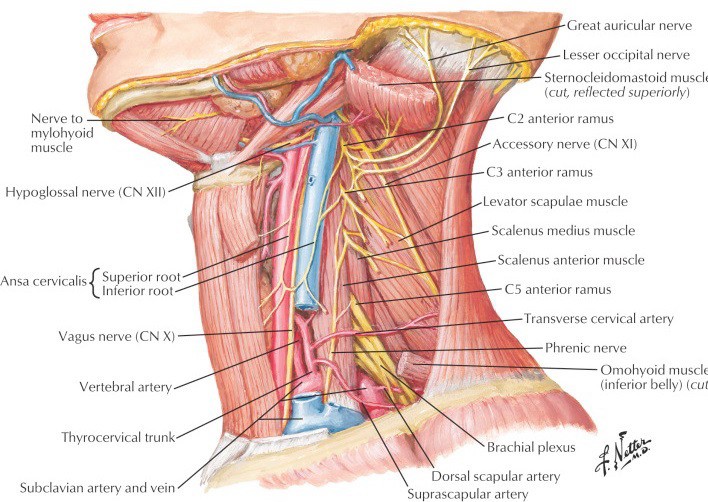
Protected: Lab 30: Dissection: Posterior Triangle of Neck, Deep Neck, and Root of Neck
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 28: Dissection: Orbit and Ear
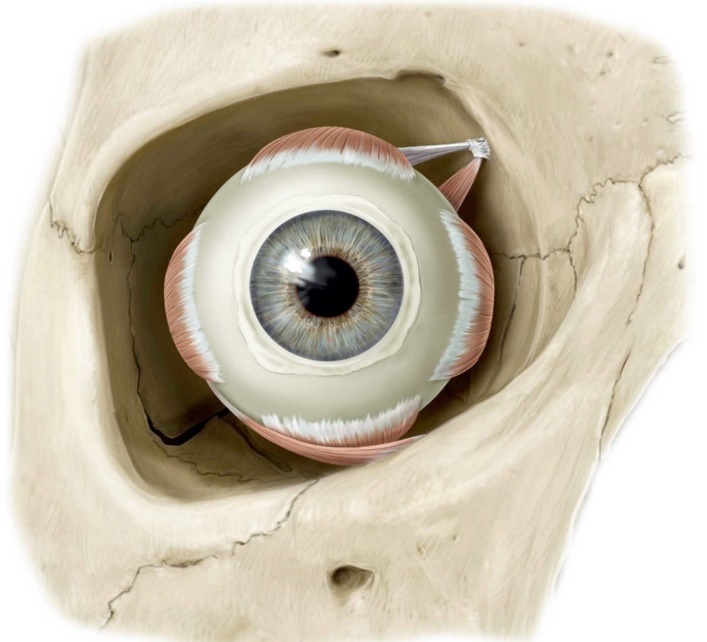
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 19: Posterior Leg and Plantar Foot
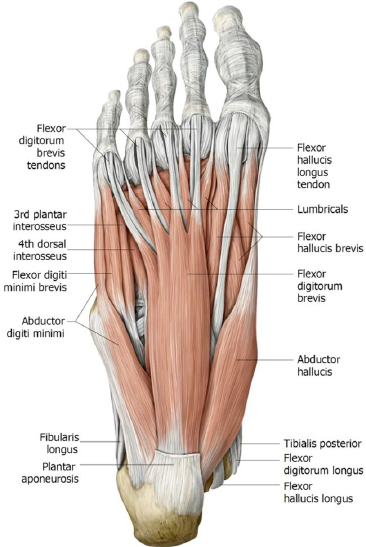
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 18: Anterior and Lateral Leg, Knee and Ankle Joints, and Dorsum of Foot
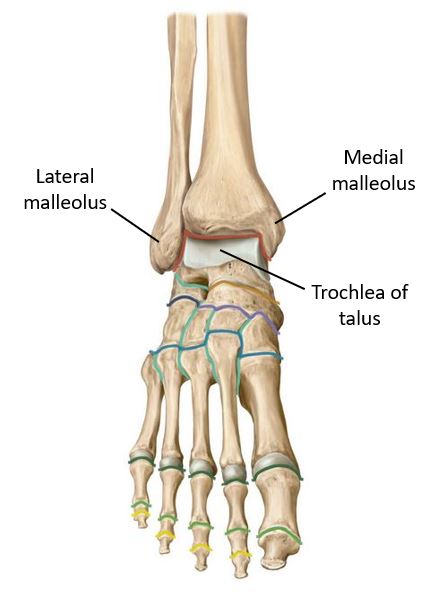
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 27: Face, Parotid Gland, and Superficial Neck
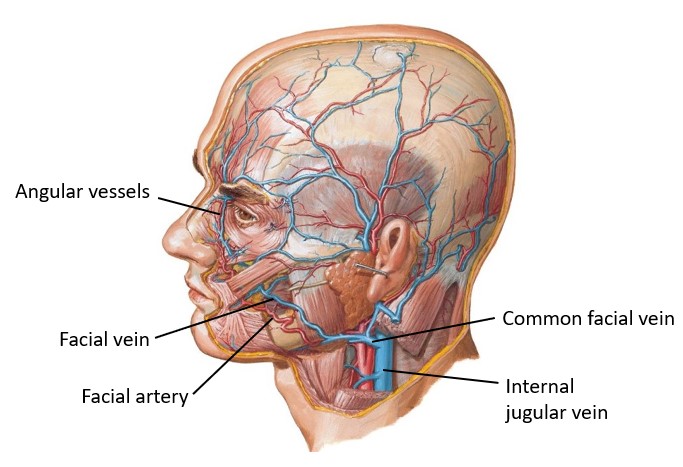
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 26: Scalp, Cranial Cavity, and Meninges
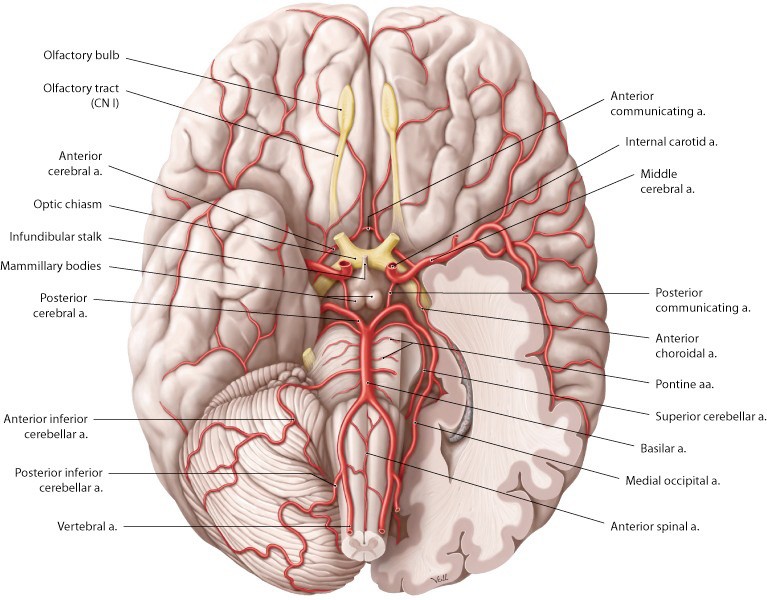
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 17: Gluteal Region, Posterior Thigh, and Popliteal Fossa
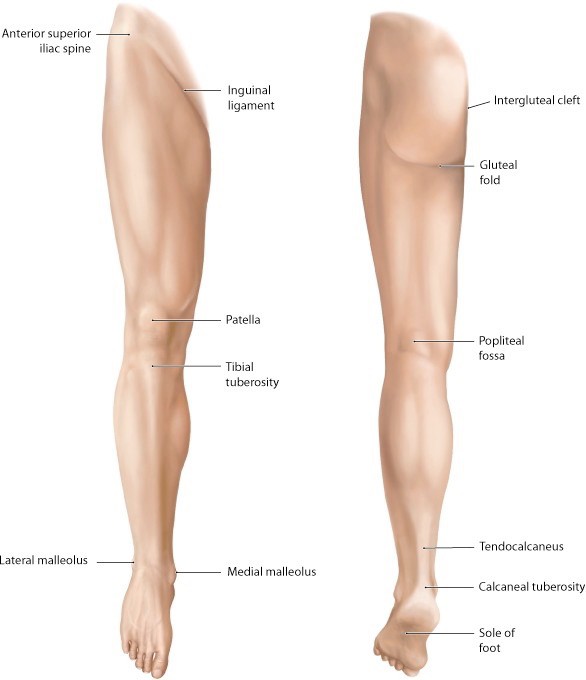
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.