Infections in the immunocompromised host
Learning goals Correlate types of opportunistic infections related to specific forms of immunodeficiency (cell-mediated, humoral, innate, adaptive, combined) Describe the epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment approach, and preventative strategies for the opportunistic infections caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii, JC Virus, and Cytomegalovirus Compare and contrast the nature and degree of immunosuppression and the associated opportunistic infections […]
Degraded Air Quality
This module explores how climate change and pollution degrade air quality, and the resulting health consequences, with attention to populations at greatest risk and strategies at multiple levels that create co-benefits for both climate and health. Sections Note Environmental and health policies evolve with changing political administrations. While federal approaches may shift, the scientific evidence […]
Protected: Lab 31: Dissection: Infratemporal Fossa and Floor of Mouth; Bony Anatomy of Pterygopalatine Fossa
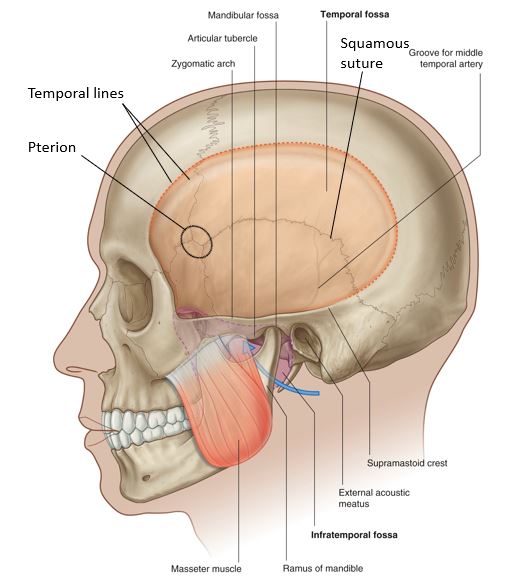
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Tips for success in the operating room
https://youtu.be/J_1zPZnXWN4 In this video (scrub through the video to see chapters) 0:05 Your Hosts 0:24 What to wear 0:49 Operating room locker room 1:16 What to do with watches, iPads, cell phones? 1:23 Tips for before you scrub 3:32 Tips for if you have to find and open your own gown and gloves 5:15 Tips for your first scrub of the day […]
Differential diagnosis of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia
Feature HUS TTP Scleroderma Renal Crisis (SRC) HELLP Malignant HTN Typical setting Child after diarrheal illness (EHEC) Adults; autoimmune or idiopathic Systemic sclerosis (esp diffuse, early disease) Pregnancy (3rd trimester/postpartum) Long-standing uncontrolled HTN Key trigger Shiga toxin ↓ ADAMTS13 RAAS activation from endothelial injury Placental endothelial dysfunction Severe BP elevation Platelets ↓ ↓↓↓ ↓ ↓ […]
Immune system and rheumatology resources
Systemic sclerosis and Raynaud’s phenomenon
Case study 1: Hae Tap the arrow to view the case.Hae, a 40-year-old woman, is evaluated for a 9-month history of Raynaud phenomenon. She reports no difficulty swallowing, dyspnea on exertion, or hand stiffness. She has recently developed gastroesophageal reflux disease.On physical examination, vital signs are normal. The skin between the distal and proximal interphalangeal […]
Protected: Lab 29: Neck: Anterior Triangle of Neck
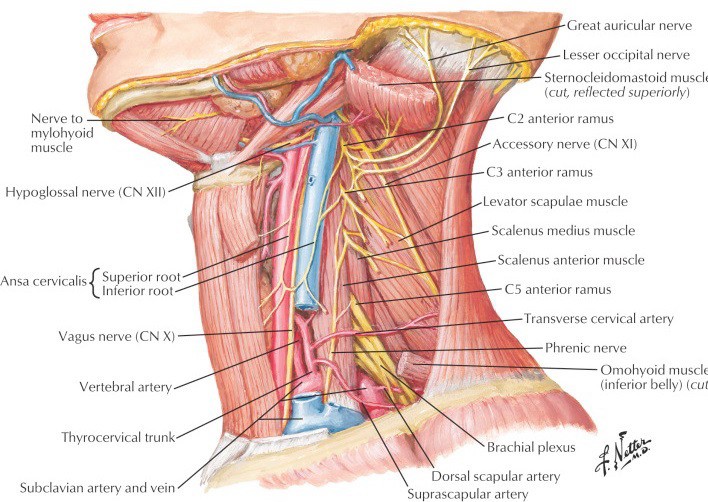
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Miscellaneous rheumatology
Case study 1: Maribell Tap the arrow to view the case.Maribell, a 72-year-old woman, is evaluated for a 3-month history of abdominal and back pain and 4-month history of an increasingly rounded face. On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 29. Bilateral lacrimal and parotid glands are enlarged. Laboratory evaluation shows a hemoglobin A1c value […]
Climate Change and Heat Impacts

Sections