Lab 14 navigation
Station 4: Male Perineum
Complete anatomy
Male perineum
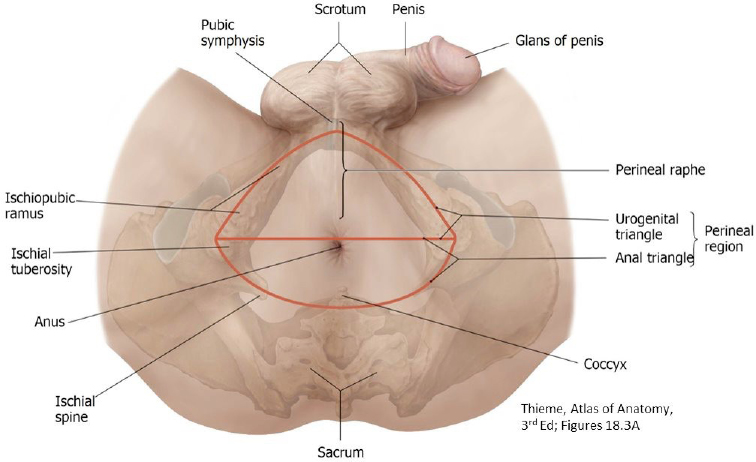
This station covers the male urogenital triangle. The anal triangle has a similar construction in both sexes—it is covered at Station 2.
- As in the female, the UG triangle contains: (1) the external genitalia and (2) two fascia-lined spaces: superficial and deep perineal pouches.
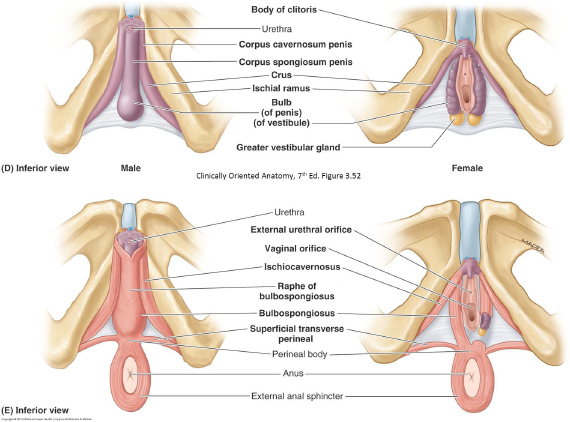
Male External Genitalia
Identify these structures on the donor:
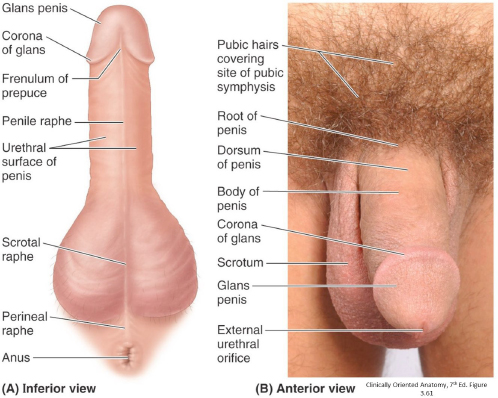
Scrotum and scrotal raphe (raphe = seam; where two halves come together)
Penis (the penis has three parts: Root, body, and glans—the latter two are visible externally)
Body (shaft)
Glans and corona of glans
Surfaces of penis: Dorsal and urethral
Prepuce (foreskin) of penis (if present)
External urethral orifice
Dorsal nerves of penis (2)
Dorsal arteries of penis (2)
Deep dorsal vein of penis (1)
Note
The clitoris has these structures on its dorsal surface too, but they are smaller and harder to identify.
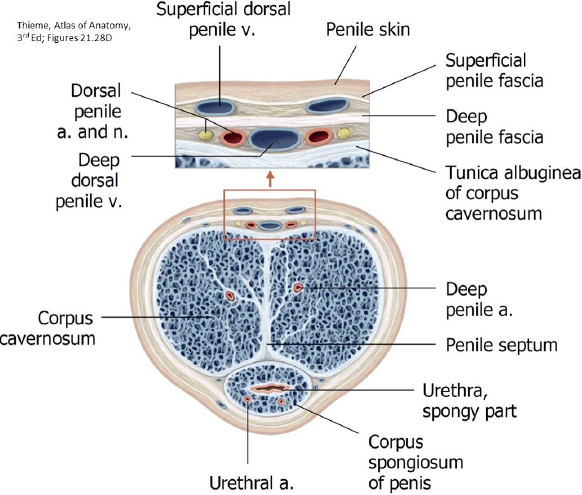
Cross Section of Penis (Figure 25):
Complete anatomy
Cross-section of the penis
Erectile bodies: Corpora cavernosa (2) and Corpus spongiosum
Spongy urethra—within the corpus spongiosum
Deep arteries of penis—in the center of the corpora cavernosa
The erectile bodies have a capsule called the tunica albuginea
Deep penile fascia (Buck’s fascia)—surrounds the erectile bodies and binds them together
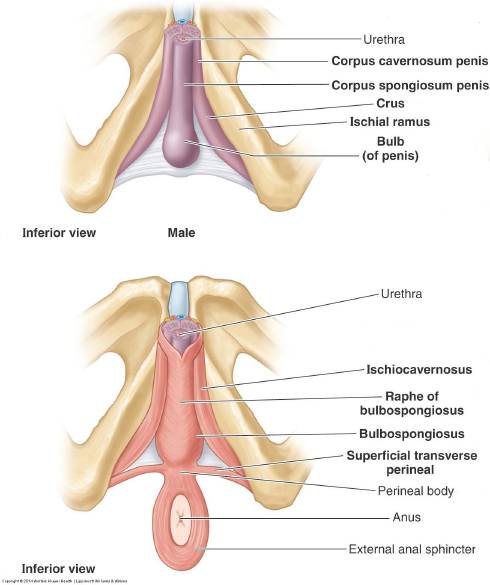
Superficial Perineal Pouch
Review of Boundaries:
- Floor: Superficial perineal fascia (Colle’s Fascia)
- Roof: Perineal membrane (a robust layer of deep fascia)
- Lateral: Ischiopubic rami
- Anterior (apex of triangle): Pubic symphysis
- Posterior (base of triangle): Line between ischial tuberosities—the fascias of the UG triangle fuse here
Contents of the male superficial perineal pouch (donor and models):
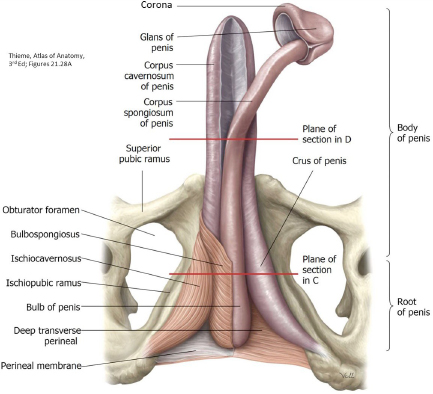
Root of the penis:
Crura (2) (these are the proximal parts of the corpora cavernosa—they attach to the ischiopubic rami)
Bulb of the penis (expanded proximal part of the corpus spongiosum—attached to the perineal membrane)
Ischiocavernosus muscles (cover the crura)
Bulbospongiosus muscles (two muscles, but they are fused in a midline raphe—they cover the bulb of the penis)
Superficial transverse perineal muscles
Question
What is the male counterpart of the female greater vestibular (Bartholin’s) glands? Are these located in the male superficial perineal pouch?”
Checklist, Lab #14
Checklist items at each of the five stations are indicated by checkboxes.