Authors
Keely Coxon, MD
Dawn DeWitt, MD
In this module
Introduction
-
Excessive, disorderly neuronal activity (“hyperexcitability”) in the abnormal brain, intermittent or episodic (except in the case of status epilepticus).
- Normal electrical impulse transmission: Action potential causes depolarization via net-positive movement of ions across the cell membrane.
- Hyperexcitability prevented by inhibitory neurotransmitters and counterbalance of negative ions (e.g., Cl–).
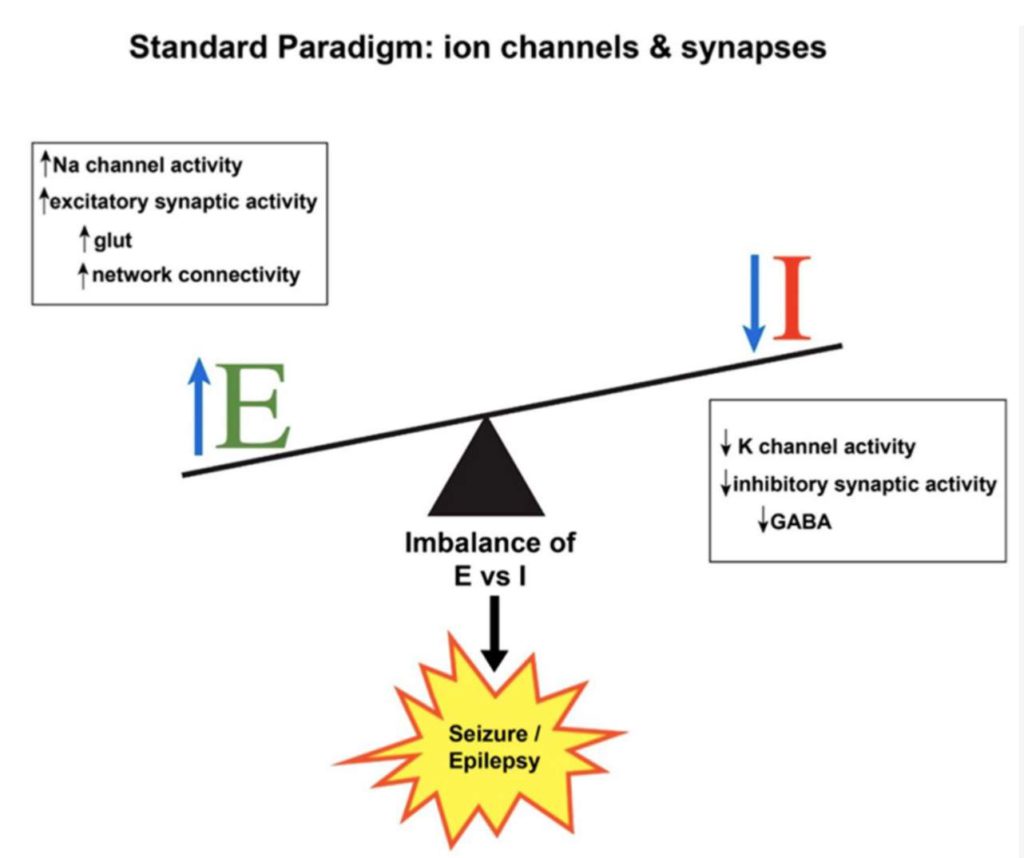
- Seizure impulses: Alteration in voltage-gated ion channels → imbalance between excitatory transmission (increased) and inhibitory signaling (decreased) → state of neuronal hyperexcitability → combination of synchronized neuronal hyperexcitability with epileptic focus = seizure.
- Primary excitatory neurotransmitter = glutamate
- Primary inhibitory neurotransmitter = GABA
Kumar A, Maini K, Arya K, et al. Simple Partial Seizure. [Updated 2020 Nov 19]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500005/
Image: Shao L-R, Habela CW, Stafstrom CE.Pediatric Epilepsy Mechanisms: Expanding the Paradigm of Excitation/Inhibition Imbalance. Children. 2019; 6(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/children6020023
- Causes
Determining the cause of a seizure is not always easy. In many cases, there is no identifiable etiology (“idiopathic seizure”).
Known causes of seizures include:
-
- Developmental abnormalities/genetic
- High fever (“febrile seizures”)
- Vascular lesions/AV malformations
- Brain tumors
- Meningitis/focal encephalitis
- Head Trauma
- Hypoxic brain injury
- Surgery: Post-surgical changes and neuronal irritation
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Endocrine disorders
- Medications and toxins (including ETOH)
Categories
- Has an identifiable, proximate cause.
- Common triggers are lack of sleep, ETOH withdrawal, cardiac issues, febrile illness (kids), and hypoglycemia.
- If stimulus is removed, these are not expected to recur.
- No identifiable cause.
- Higher risk of recurrence than in provoked seizures.
- > 1 unprovoked seizure = epilepsy.
- Two major sub-categories
- Motor
- Non-motor (absence)
- EEG: Generalized epileptiform waves; bilateral and symmetric.
- Simple focal
- Complex focal
- Begin as partial/focal, then spread to both sides of brain
