These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Instructions for Chapter 18 Worksheets
- Make basic measurements and evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and atrial abnormality.
- Diagnose RVH if the QRS direction is either rightward, anterior, or both.
- Evaluate clinically.
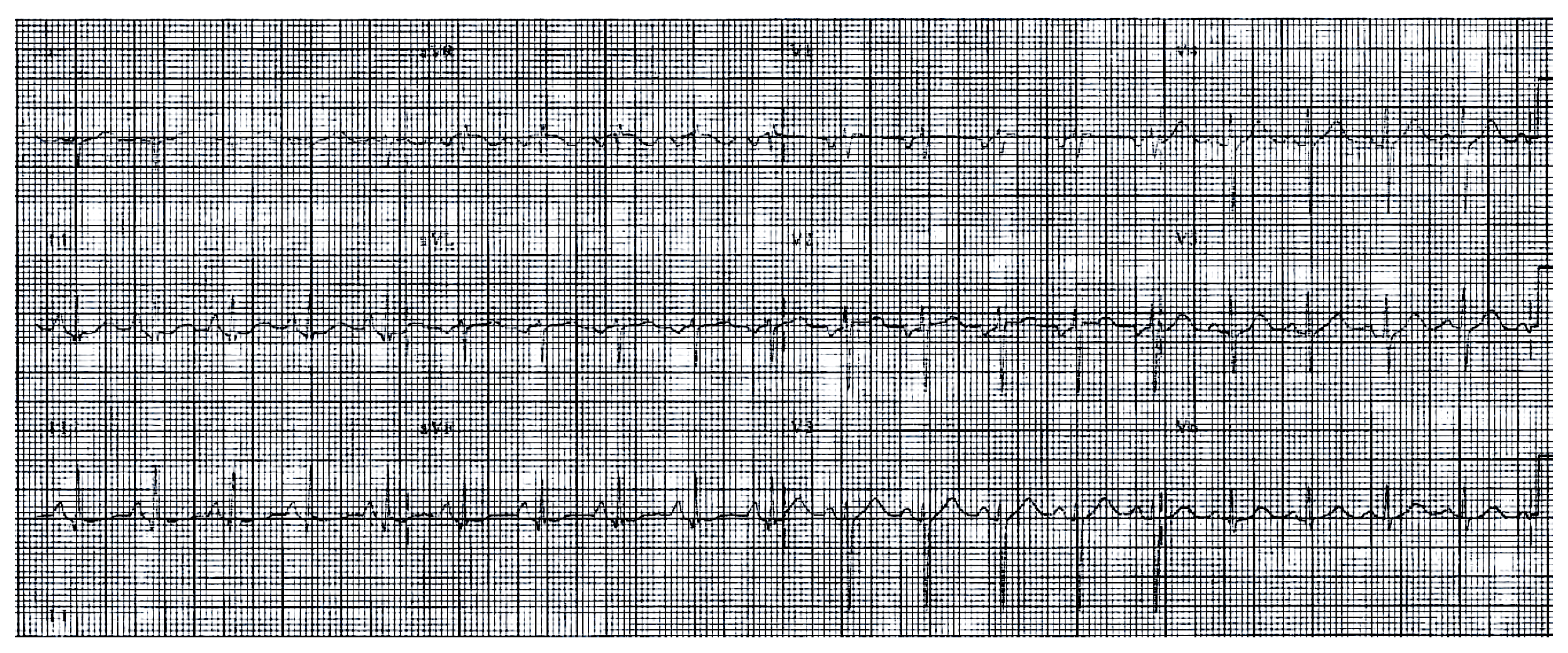
Clinically-Based Critical Thinking: Interpretation
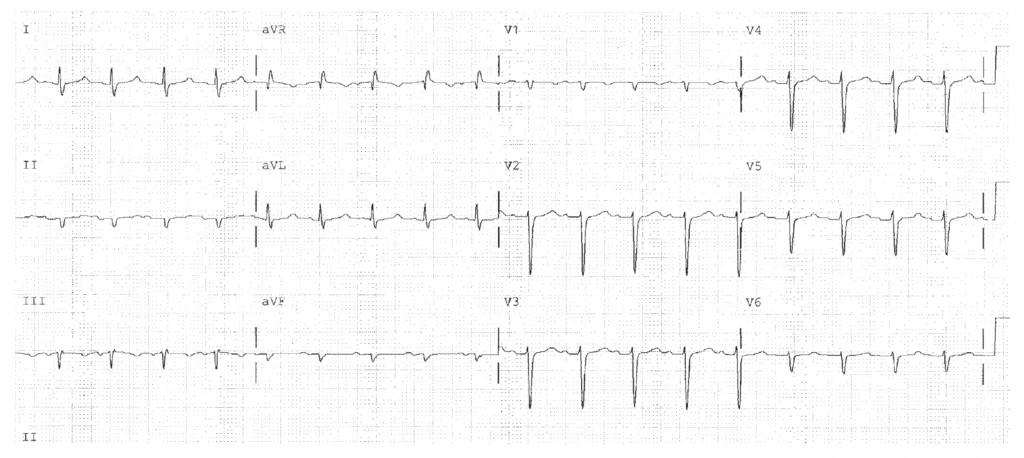
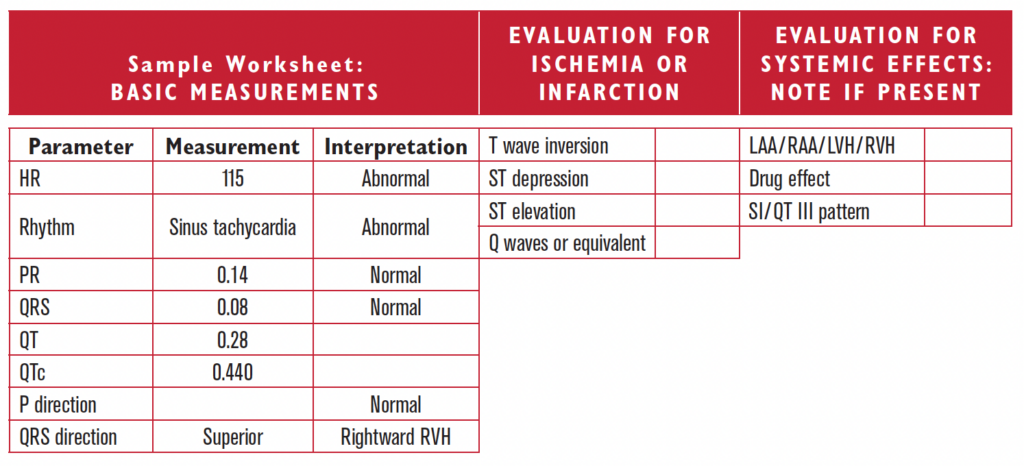
Sinus tachycardia is present and represents increased sympathetic activity. The QRS direction is rightward in the frontal plane (R less than S). This could represent RVH or LPHB. The HR of 115 confirms the patient is acutely ill regardless of the diagnosis.
Worksheet 18.1
Complete the basic measurements, diagnose RVH if the QRS direction is either rightward, anterior, or both, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| SI/QT III pattern |
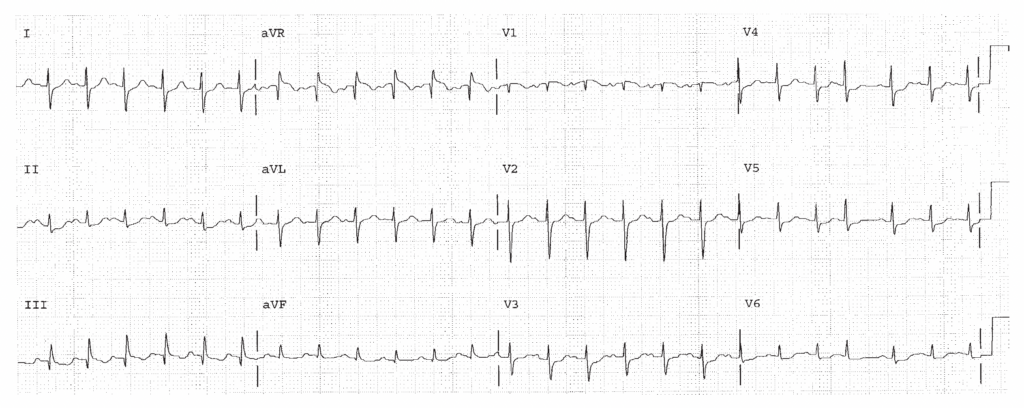
HR 150, sinus tachycardia with a PAC. The QRS is rightward indicating RVH or LPHB. There is an SI QTIII pattern suggestive of pulmonary embolism. There is diffuse ST segment depression (First Rule of the T waves applies).
Worksheet 18.2
Complete the basic measurements, diagnose RVH if the QRS direction is either rightward, anterior, or both, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| SI/QT III pattern |
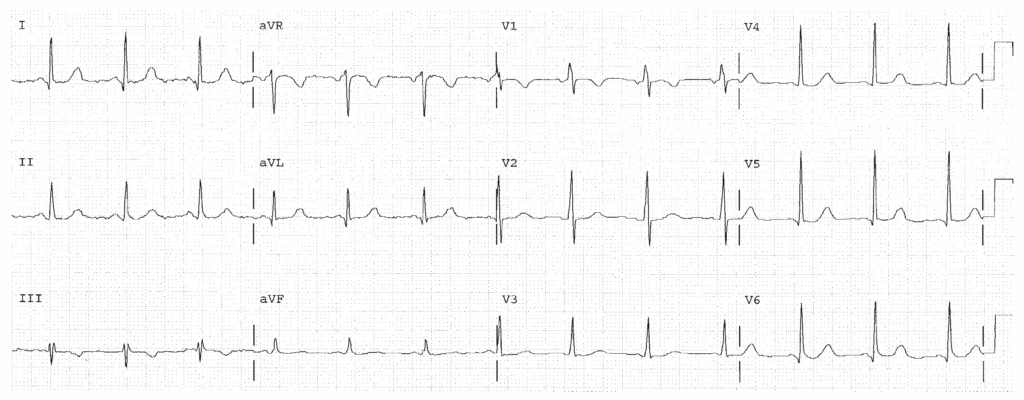
HR 75, sinus rhythm. QT 0.40. QTc is high. The QRS direction is anterior (positive in V1 and V2) indicating RVH.
Worksheet 18.3
Complete the basic measurements, diagnose RVH if the QRS direction is either rightward, anterior, or both, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| SI/QT III pattern |
HR 115, sinus tachycardia. Right and left atrial abnormality are present. The QRS direction is rightward indicating RVH, or LPHB. The combination of LAA, RAA, and RVH suggests mitral stenosis, with right sided hypertrophy.