These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Instructions for Chapter 12 Worksheets
- Complete basic measurements.
- If the QRS is ≥ 0.12 sec, diagnose BBB. Then visualize the extra piece at the end of the QRS in the frontal plane as right or left, and in the horizontal plane as anterior or posterior. Diagnose BBB further as LBBB if the end of the QRS points to the left ventricle (leftward and posteriorly). Do not analyze the QRS, ST segment, or T waves in LBBB. There are no agreed upon and reliable criteria for diagnosing ventricular hypertrophy, ischemia, or infarction in its presence.
- Provide an interpretation.
Clinically-Based Critical Thinking: Interpretation
LBBB is a very important finding on an EKG for two reasons. First (and unlike RBBB!) it is associated with underlying heart disease. Common associations with LBBB include coronary disease, hypertension, and cardiomyopathy. The cause of LBBB should be determined. Furthermore, the presence of systolic and diastolic dysfunction should be evaluated. Second, in LBBB (and unlike RBBB), the EKG cannot be further analyzed.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
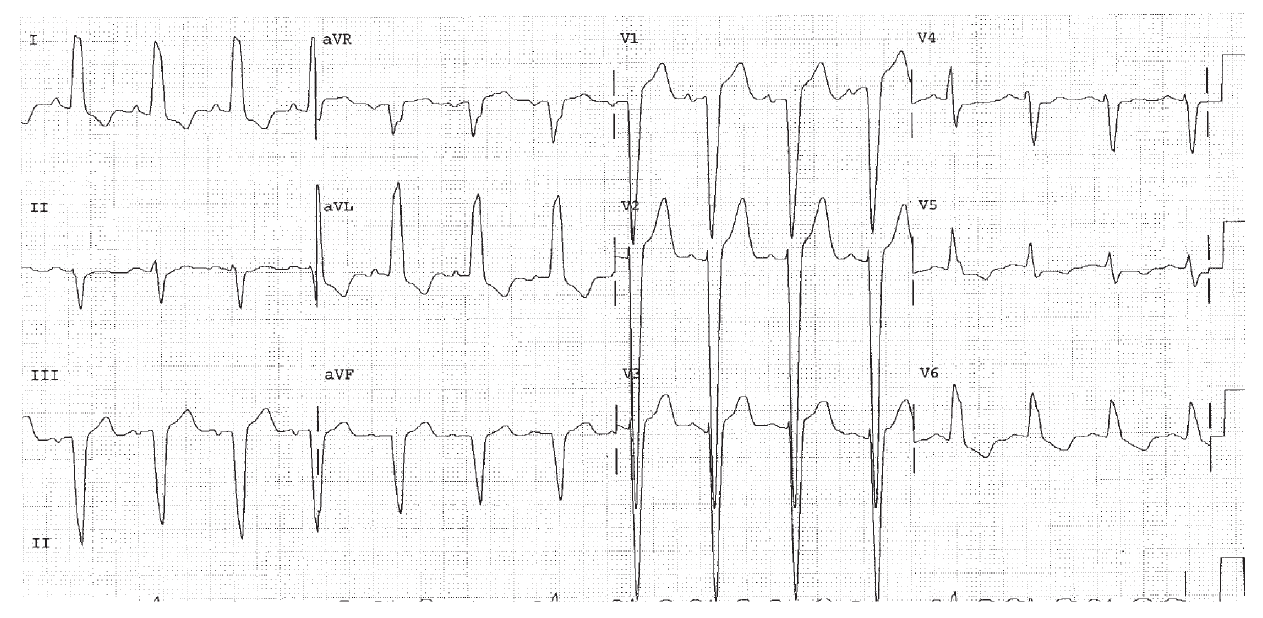
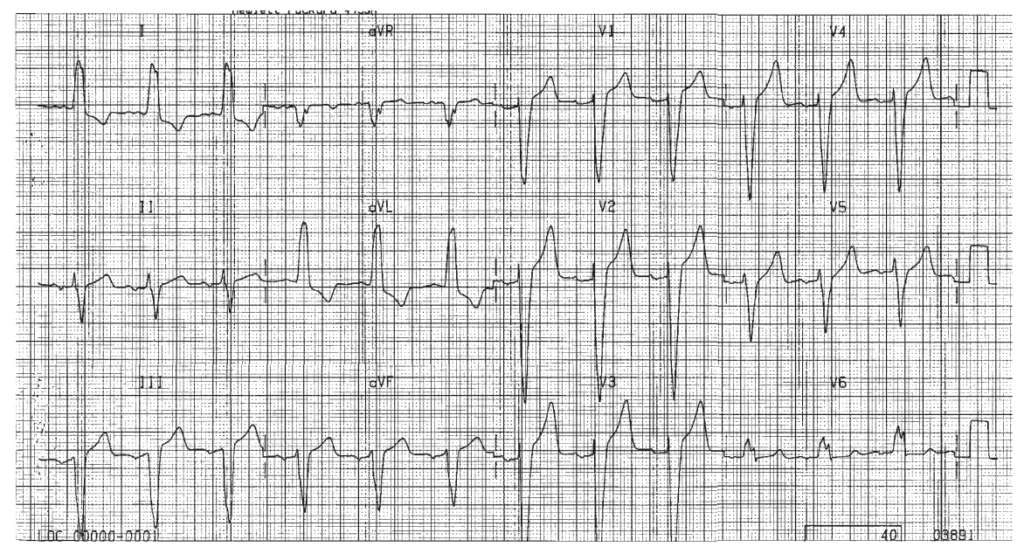
Rate 115, sinus tachycardia. PR 0.12, normal. QRS 0.12 BBB. The end of the QRS is positive in lead I and so points to the left ventricle. The end of the QRS is negative in lead V1, and so points posteriorly and to the left ventricle as well. This is LBBB. The QT interval is 0.32. The QTc is 0.44.
Worksheet 12.2
Complete the basic measurements, evaluation, and interpretation for the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
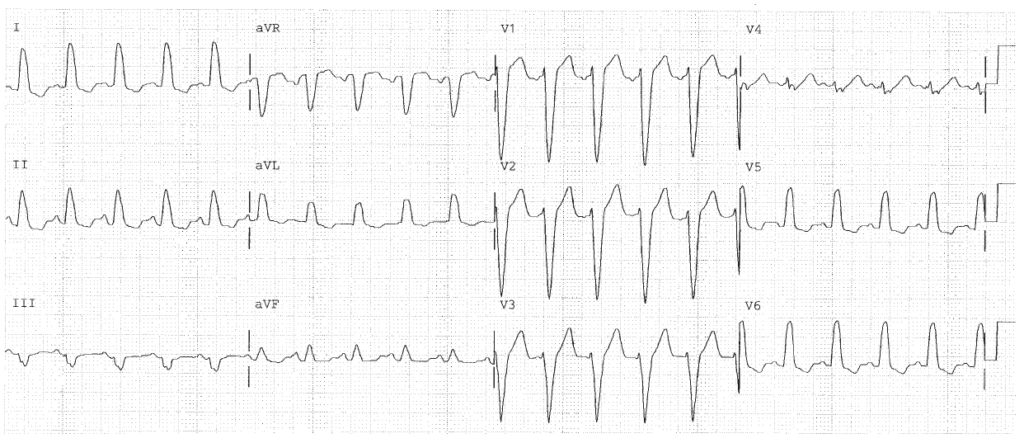
Wide QRS tachycardia at rate of 124. The P waves are not clearly visible. This may represent sinus tachycardia with LBBB. It may also represent ventricular tachycardia.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
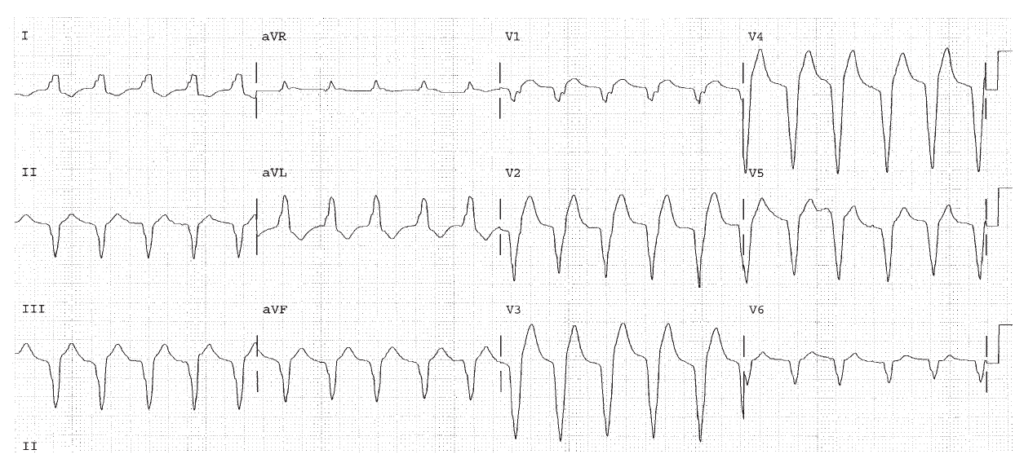
HR 75, sinus rhythm. The QRS is 0.16 seconds, BBB. The end of the QRS is positive in lead I, and negative in lead V1 pointing to the left ventricle and indicating LBBB.