Perineum
Optional Reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Perineum section. The perineum is the inferior-most region of the trunk, located between the thighs and buttocks. In the anatomic position the perineum is partially hidden because the thighs are together. When the thighs are abducted, the perineum has a diamond shape. Due to the forward tilt of […]
Development of genital organs (internal and external genitalia)
Optional Reading The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 12th ed., chapter 12, Development of genital system section through Anomalies of uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina. The adult organs that will be discussed in this chapter are the gonads and the accessory sex organs. Testicular Based Ovo-uterine Based In the phenotypic male, the gonad is the […]
The pleura and lungs
Optional Reading Moore, Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Viscera of thoracic cavity section through Clinical box: Pleurae, lungs, and tracheobronchial tree; The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 11th ed., chapter 10. Pleura and pleural sacs Pleura is a serous membrane associated with the lungs. Pleura comes in two varieties: Visceral pleura Visceral pleura invests each […]
The larynx
Optional Reading Moore, Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Viscera of neck: Larynx section through Nerves of larynx. The larynx is an organ of the respiratory system and the part of the airway situated between the pharynx and trachea. It is located anterior to the lower pharynx and esophagus, between the levels of C-4 to C-6 […]
The oral region and pharynx
Optional Reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Oral region section through Sublingual glands; The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 11th ed., Development of tongue section through Development of salivary glands. The oral region The oral region includes the lips, cheeks, oral cavity (mouth), gingivae (gums), teeth, tongue, palate, and oral fauces (the area connecting the […]
Nose, nasal cavities, and paranasal sinuses
Optional Reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed., Nose section through Transillumination of sinuses; The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 11th ed., Development of nasal cavities section thorough Postnatal development of paranasal sinuses. The nose The nose is the portion of the respiratory tract above the palate. It consists of two parts: an external nose on […]
Prenatal and postnatal circulation
Prenatal circulation Oxygenated blood reaches the fetus from the placenta via the umbilical vein (within the umbilical cord). Once in the fetus, the umbilical vein reaches the liver by passing through the falciform ligament. Much of this blood bypasses the liver through the ductus venosus. Oxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the inferior vena […]
Lab 19: Dissection: Pericardium, Heart, and Mediastinum
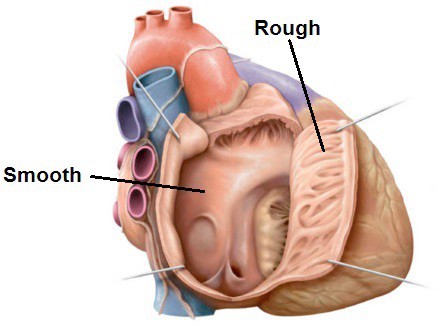
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Review the parts of the pericardium and spaces of the pericardial cavity. Define the boundaries and subdivisions of the mediastinum. Clean and review the structures of the superior and posterior mediastinum. Review the blood supply and venous drainage of the posterior thoracic wall. Clean the epicardium of the […]
Lab 31: Dissection: Infratemporal Fossa and Floor of Mouth; Bony Anatomy of Pterygopalatine Fossa
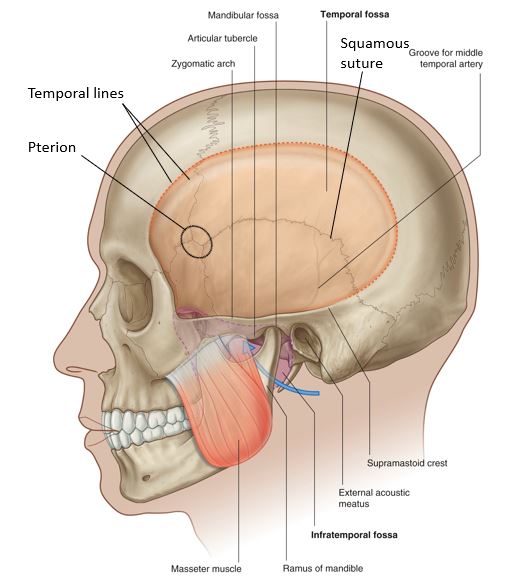
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Identify the temporal fossa and temporalis muscle. On a skull, identify the borders of the infratemporal fossa (ITF) and the foramina that connect it other regions in the head. Clean the masseter muscle on one side of the face and remove it from the mandible. Use an autopsy […]
Lab 30: Dissection: Posterior Triangle of Neck, Deep Neck, and Root of Neck
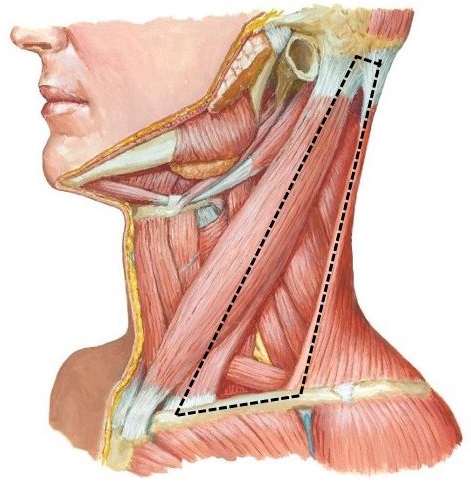
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Clean and identify the contents of the posterior triangle of the neck. Perform a deep dissection on one side of the neck to examine the sympathetic trunk and prevertebral muscles. Review the bony anatomy of the superior thoracic aperture and identify its contents. Clean and identify the structures […]