Face and parotid gland
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Head chapter, Face and scalp section through Surface anatomy of face; Parotid and temporal regions, infratemporal fossa, and temporomandibular joint section through Infratemporal fossa. The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 12th ed., Development of salivary glands section through Atresia of the nasolacrimal duct. The face is the anterior part […]
Scalp and cranial cavity
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Head chapter, Internal surface of cranial base section through Posterior cranial fossa; Face and scalp section through Lymphatic drainage of face and scalp; Cranial meninges section through Arachnoid mater and pia mater; Cerebral arterial circle section and Venous drainage of brain section. Scalp The scalp covers the skull and […]
Protected: Lab 16: Anterior and Medial Compartments of Thigh; Hip Joint
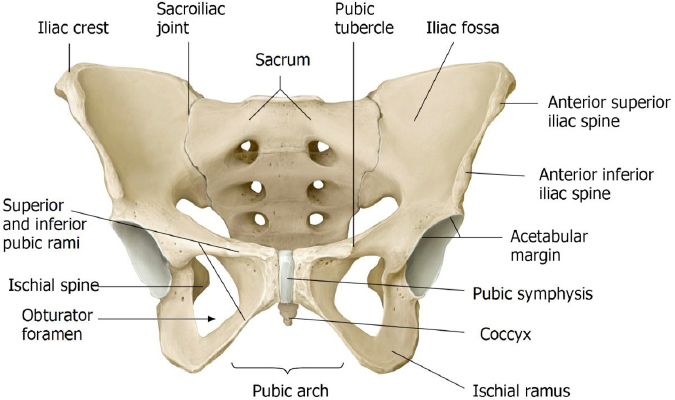
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 13: Dissection: Posterior Abdominal Wall (PAW) and Kidneys
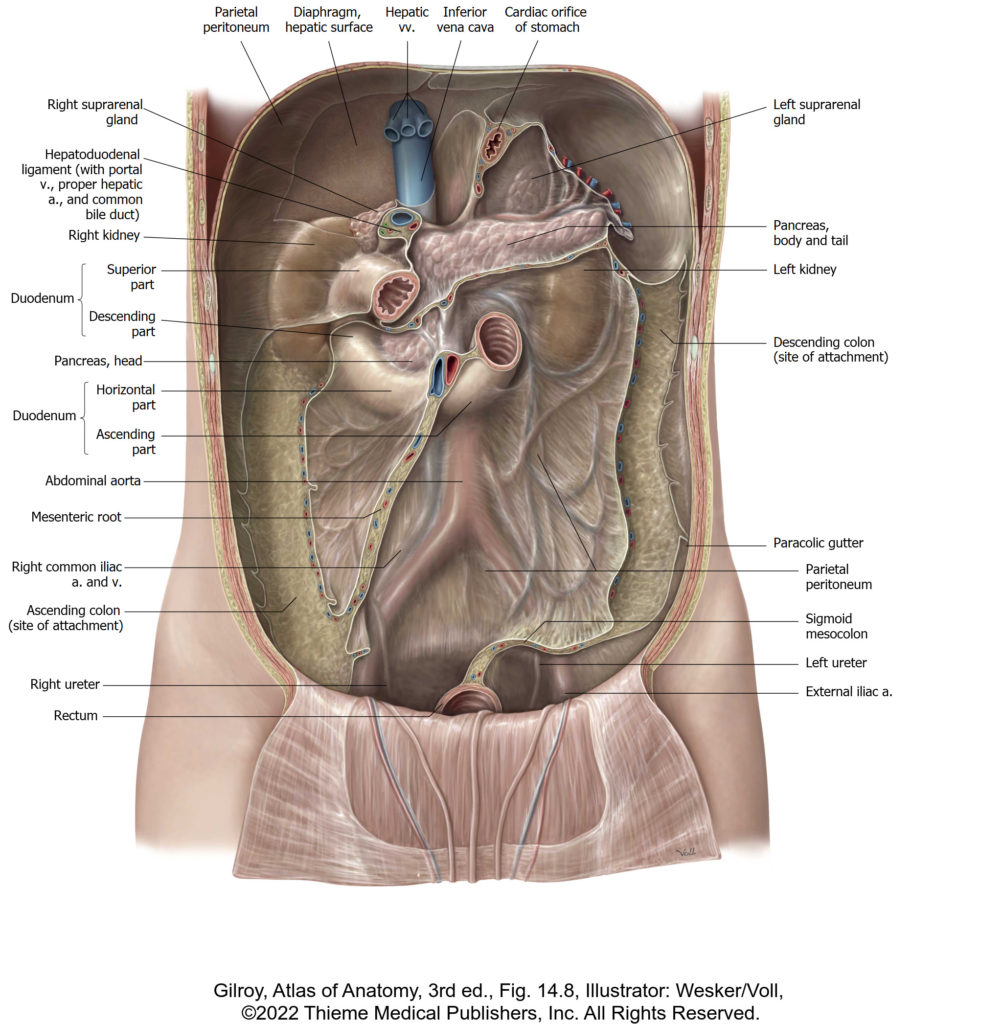
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Temporal and infratemporal regions; temporomandibular joint
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed., Temporomandibular joint section through Arthritis of TMJ. Temporal region Figure 1. Attachments of temporal fascia. GRAY’S ANATOMY FOR STUDENTS, FIGURE 8.138. Figure 2. GRAY’S ANATOMY FOR STUDENTS, FIGURE 8.139. The temporal fossa is the sunken area located on the lateral skull above the zygomatic arch. Boundaries Its floor […]
Protected: Lab 24: Peritoneal Cavity and Supracolic Region
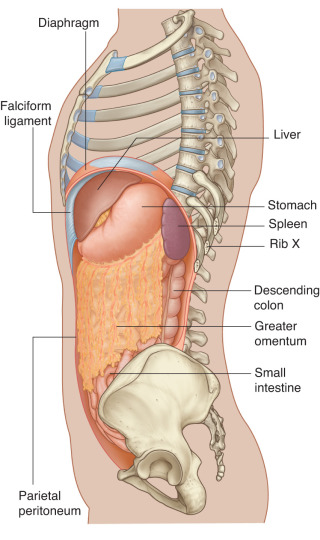
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 25: Infracolic Region
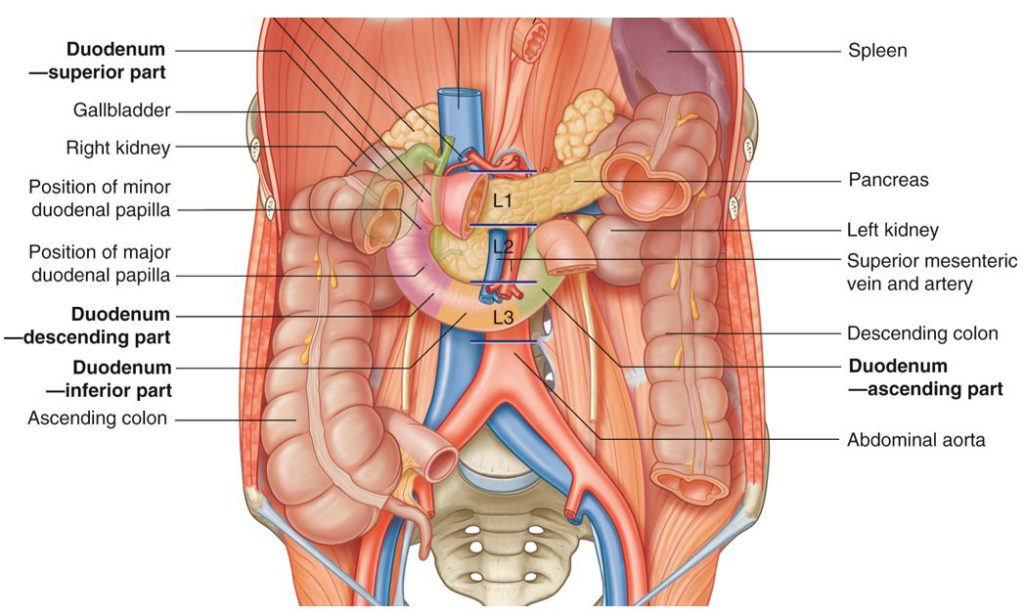
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 23, Station 5: Oral Region and Salivary Glands—Lateral View
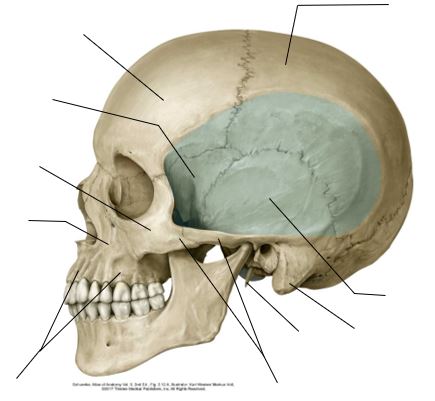
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 23, Station 4: Oral Cavity and Pharynx—Sagittal View

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 23, Station 3: Nerves and Vessels Associated with the Oral Cavity

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.