Nervous System—Draft

Intro paragraph from system directors (placeholder text): Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo. Nervous system resources Neuroanatomy Gross Anatomy textbook Clinical Skills videos Cellular physiology Pharmacology Library resources LibGuide Library Resources for Medicine: Nervous Guidance for the neurological examination
Neuroanatomy

The material contained in the Nervous System volumes on the Medicine Digital Learning site addresses fundamental concepts of Neuroanatomy and Basic Neurology that will serve to reinforce the content in FMS 512. These resources are supplemental but succinctly organized and include: A review of nervous system development starting with neurulation, neural crest formation, and partitioning […]
Lab 5: Supplemental
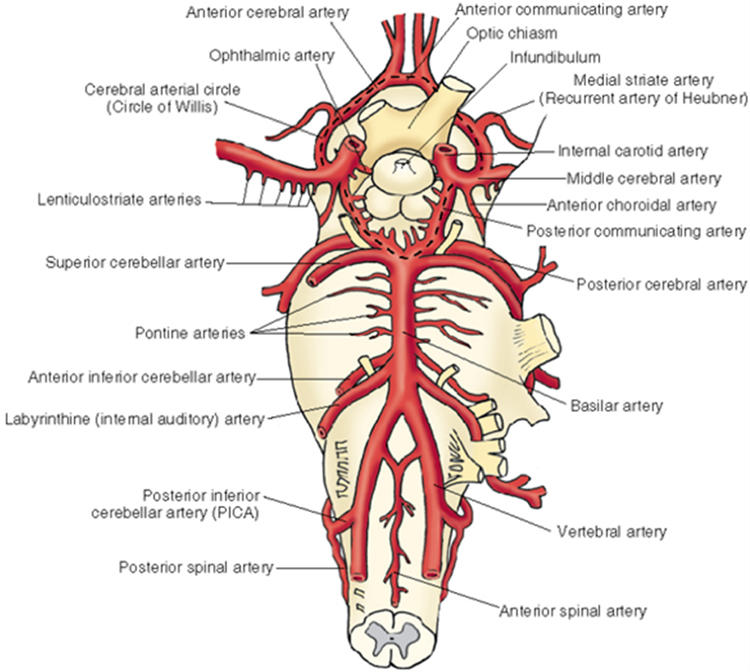
Arterial blood supply Review from FMS 501 Vertebral arteries Read More Supplying the brainstem and cerebellum Anterior and posterior spinal Posterior inferior cerebellar Basilar (unpaired)—multiple pontine branches also come directly off the basilar artery Anterior inferior cerebellar Superior cerebellar Posterior cerebral posterior communicating Internal carotid Read More Supplying the midbrain, thalamus, hypothalamus, and cerebrum Middle […]
Lab 4. Meninges and ventricles
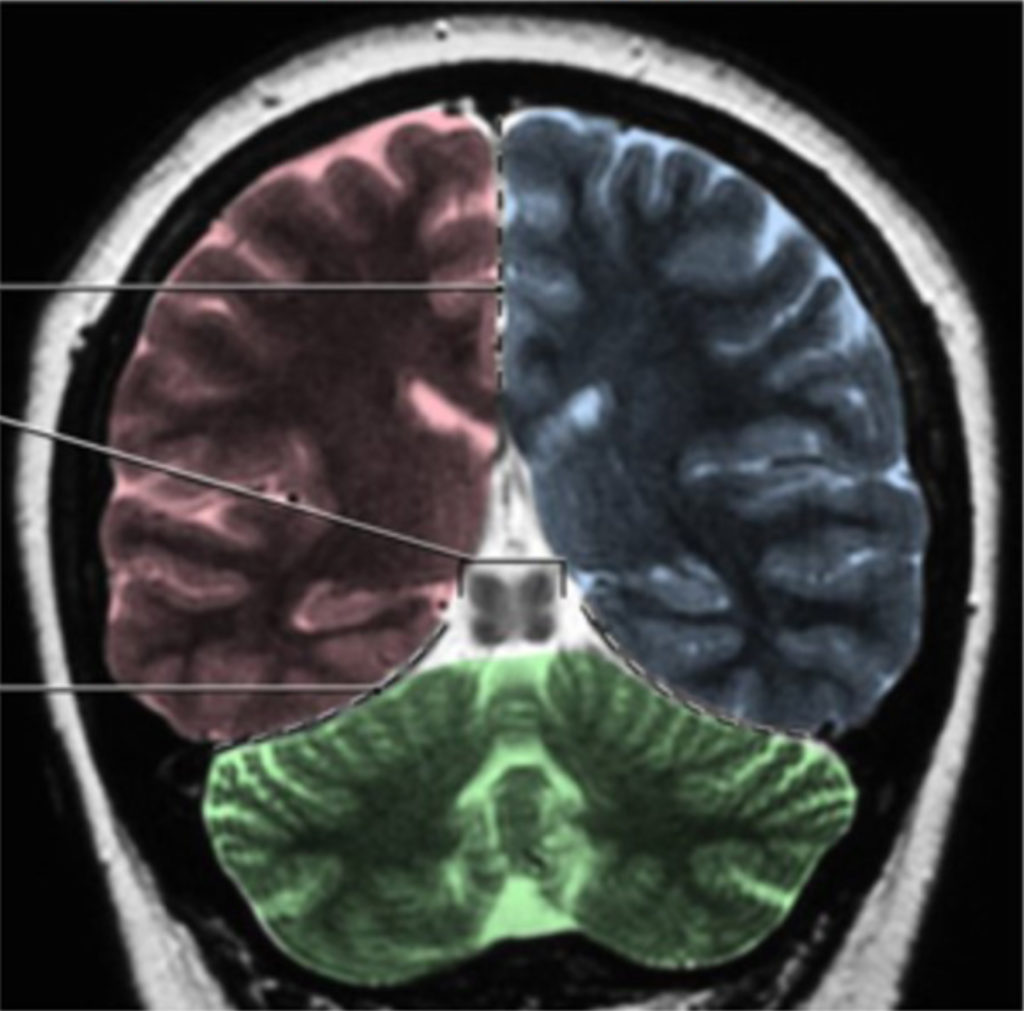
Meninges See Figure 4.1 and Figure 4.2. Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater Falx cerebri: Separating the cerebral hemispheres Tentorium cerebelli: The tentorium cerebelli separates the cranial cavity into two compartment (Figure 4.1), and there is also a prominent tentorial notch that allows for passage of the brainstem The supratentorial compartment contains the cerebrum. The […]
Lab 3: The brainstem
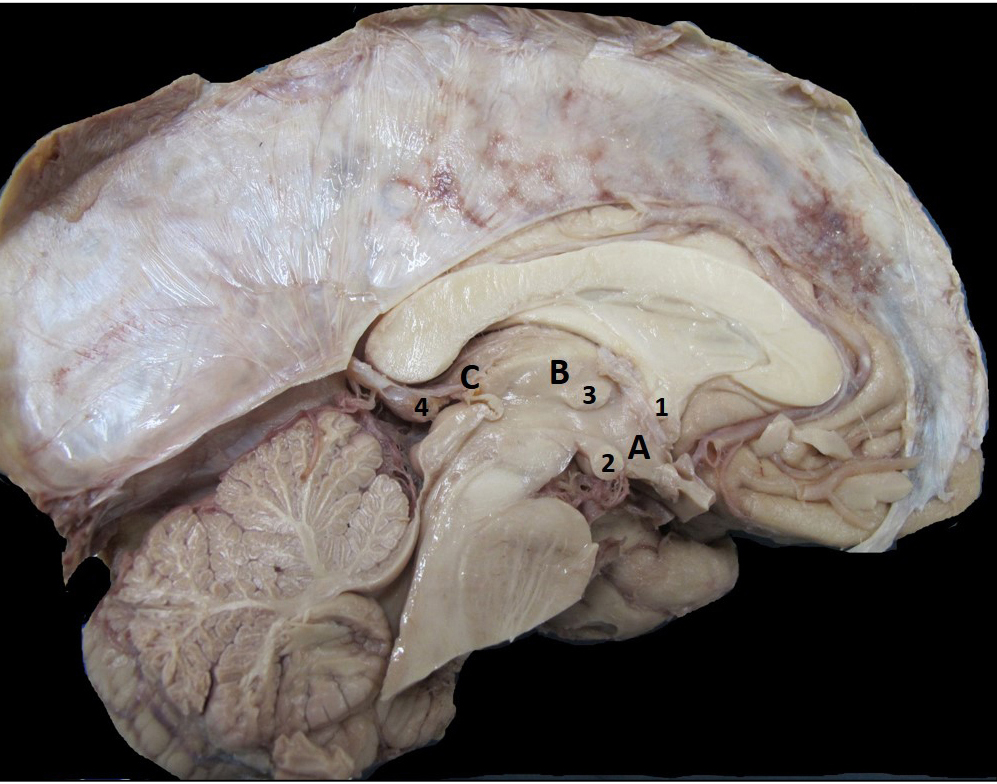
Parts of the brainstem Midbrain Mesencephalon Pons Metencephalon Medulla Myelencephalon See Figure 3.1, Review 3.1, and Review 3.2. The basal subdivision of the brainstem is the most anterior and contains mostly the descending fiber tracts. The tegmentum is the location of the cranial nerve nuclei, ascending fiber tracts, and the reticular formation. In the medulla, […]
Lab 2. Diencephalon
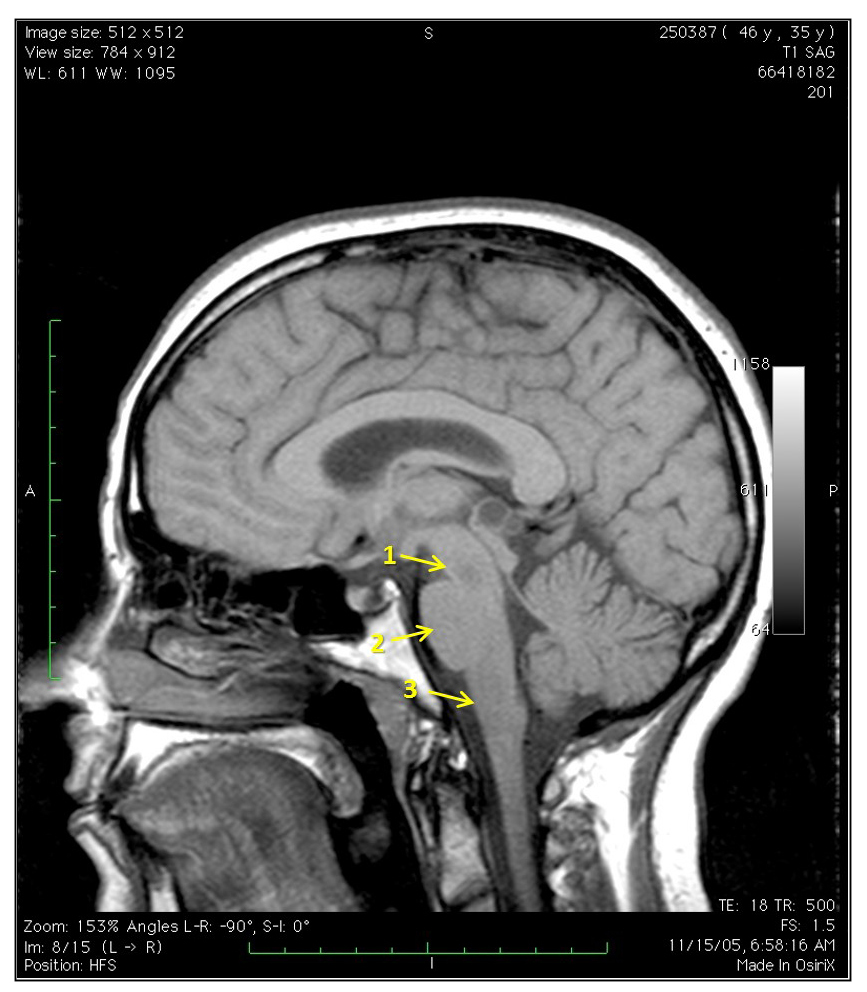
Thalamus See Check Yourself 2.1. The thalamus is key structure that relays information to the cortex associated with motor and sensory information. (These will further be described during the Functional Neuroanatomy lectures.) There are also thalamus nuclei that form the connections in the memory and emotion circuit from the hippocampal formation. This portion of the […]
1. Development of the Nervous System

Neurulation and formation of the Central Nervous System A quick review of neurulation from FMS 501 . . . 1. After migration and patterning, the dorsal layer of ectoderm further differentiates into neuroectoderm. Read More Neuroectoderm begins to invaginate at ~18 days, forming a neural groove between paired neural folds. The neural folds later fuse […]
Lab 1. Cerebrum, sulci, and gyri

Introduction to neuroanatomy Figure 1.1. Anatomic directional terms. From Neuroanatomy: A Laboratory Guide (2e); Jansen and Lampa. Introduction to the Central Nervous System Watch this excellent Introduction to the Central Nervous System from University of British Columbia Neuroanatomy. Cerebrum, sulci, and gyri Lobes of the cerebrum See Interactive 1.1 and Figure 1.2. The limbic (limbus=margin […]
3. Functional neuroanatomy and vasculature, part 2

Long ascending and descending pathways The three major longitudinal pathways the corticospinal tract, posterior column-medial lemniscus, and anterolateral system can be followed systematically to and from the cerebral cortex, through brain stem and to and from spinal cord. A key feature of all these pathways is to note the location where their tracts cross to […]
3. Functional neuroanatomy and vasculature, part 1: The brain stem, cerebellum, cerebrum, and spinal cord
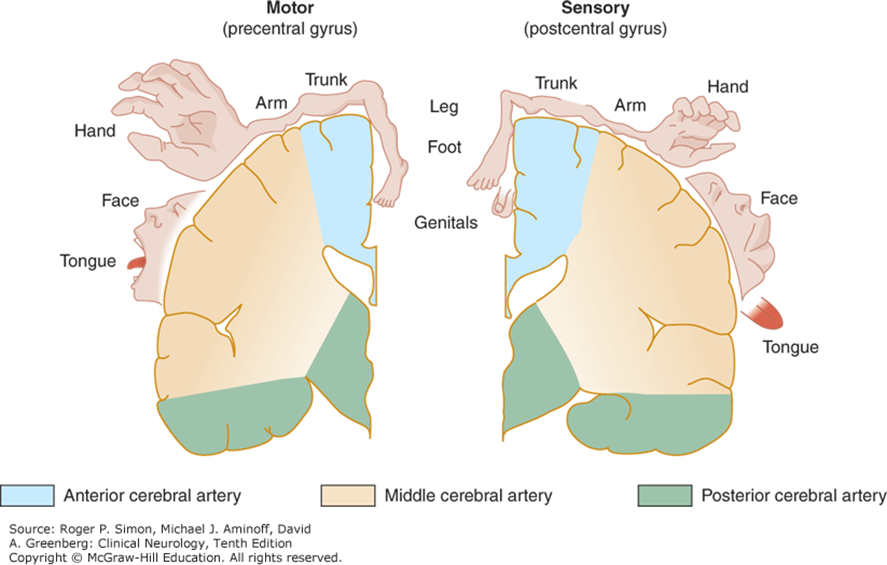
Blood supply to the Central Nervous System An understanding of the brain’s blood supply is crucial to understanding normal CNS function. Conversely, the consequences of cerebrovascular disease affecting the brainstem and cerebrum leading to a loss of function is also vital. Figure 3.3. Schematic of blood supply to brain stem regions (in transverse section). Simon, […]