Cellular Receptors of Relevance to Therapeutics
This table provides a summary of the various types of cellular receptors that are drug targets. Classes Subclasses or families Physiological ligands Transducers, principal effects, or ions G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)a Adhesion Frizzled Glutamate Rhodopsin Secretin Very large number of endocrine and paracrine factors, but other types of ligands as well G proteins Gs: Adenylyl […]
MS2 Combined Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, and Abdominal Exams
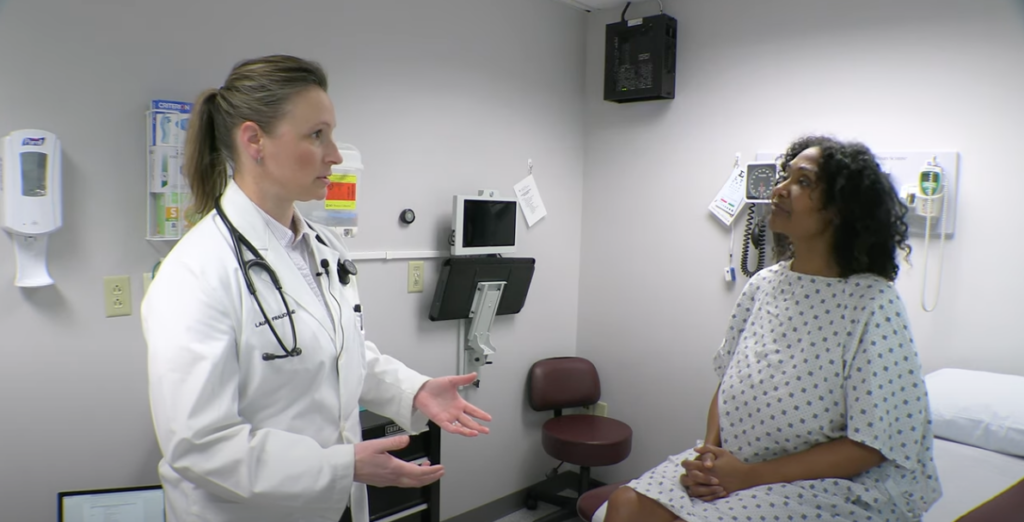

Critical analysis of a case report
In this session, we will assess a paper that is a case report on a patient with episodes of confusion and hypoglycemia. What was the diagnosis? Read the case report to find out! There will also be a short discussion on a case report and where it fits into the evidence-based pyramid. Learning Goals Learning […]
An approach to reading the literature
Learning Goals Demonstrate respectful, constructive, adaptive interactions with peers and/or facilitators, including punctual attendance, advanced preparation, professionalism, and giving and receiving feedback Formulate and critically analyze PICO questions (population/patient/problem, intervention, comparison, outcome) Describe predatory journals and explain how they can be identified Activity 1: Application of PICO The primary purpose of the PICO question is […]
Anatomy of a case report

Writing case reports: A balanced perspective As educators, we often encounter students eager to write case reports. Dr. Coidado fielded so many queries and requests for assistance that she reached out to me to help her create this resource. While I have many reservations about this effort and my own personal biases, it’s important that […]
Office of Research

Student-led workshop series
Tachyarrhythmias and ectopy
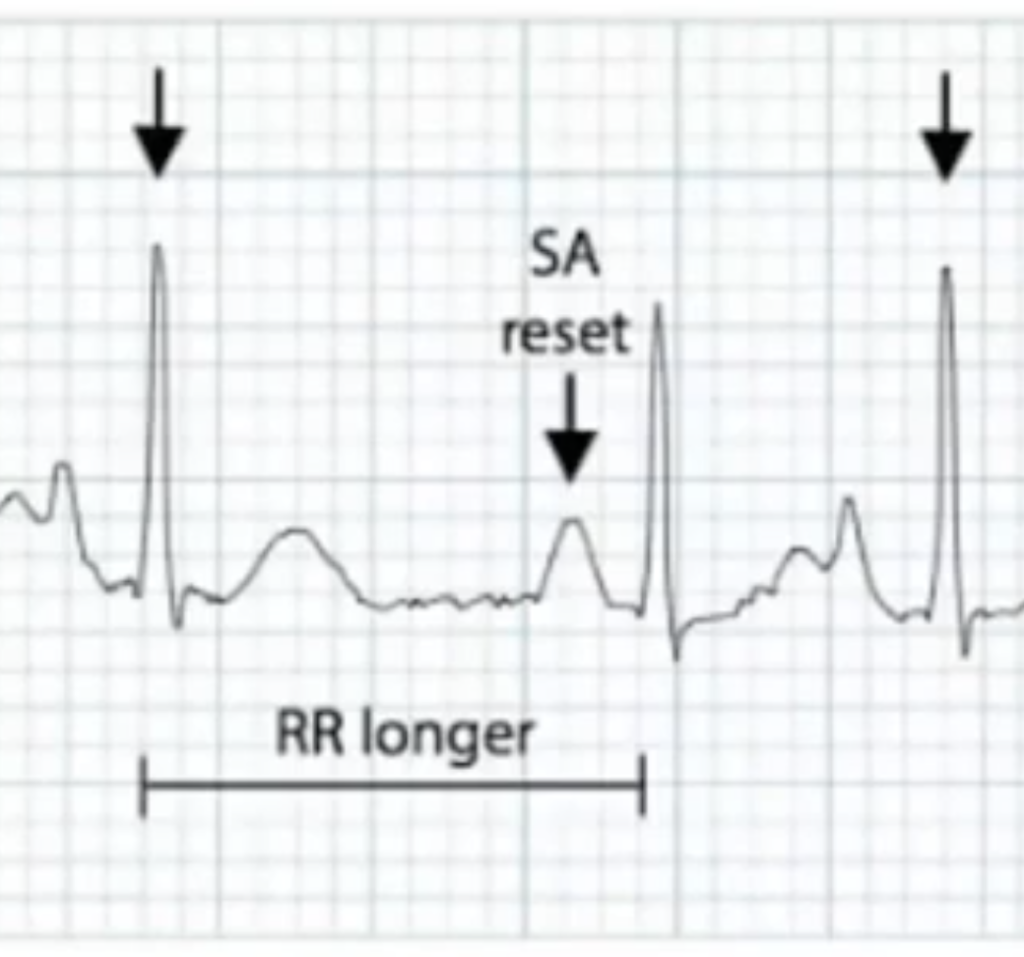
https://youtu.be/fL5pOiHdunI In this video (scrub through the video to see chapters) 00:41 Review of basic principles 02:01 Practical arrhythmia summary 03:13 Normal HR, regular, and narrow QRS 06:18 Normal HR, irregular, and narrow QRS 09:55 Atrial flutter 12:58 Atrial fibrillation 15:23 Fast HR, regular, and narrow QRS 27:45 Fast HR, irregular, and narrow QRS 33:24 Normal HR, regular, and wide QRS 35:17 Normal HR, irregular, […]
Bradyarrhythmias
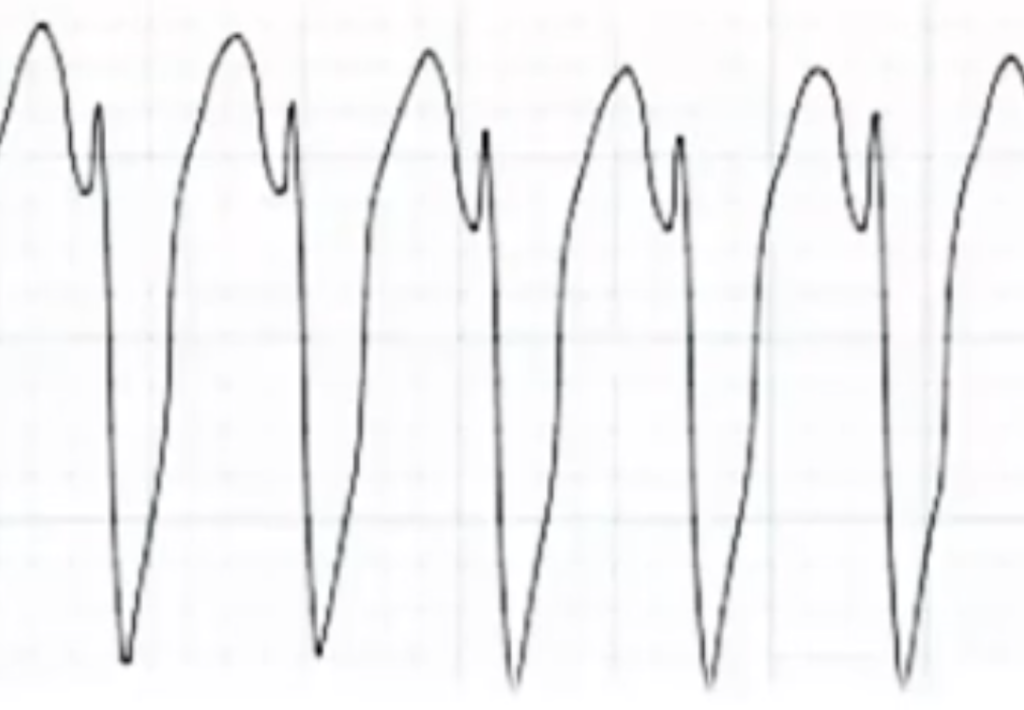
https://youtu.be/PQ4TtOWgvZ8 In this video (scrub through the video to see chapters) 00:32 Analyze, synthesize, manage 05:51 Fast? Slow? Irregular? 06:14 QRS Narrow? Wide? 06:38 Where are my P waves? 08:50 Normal HR, regular, and narrow QRS 09:55 Normal HR, irregular, and narrow QRS 14:32 Slow HR, regular, and narrow QRS 21:29 Slow HR, irregular, and narrow QRS 25:19 Normal HR, regular, and wide QRS […]
Basic principles of arrhythmias
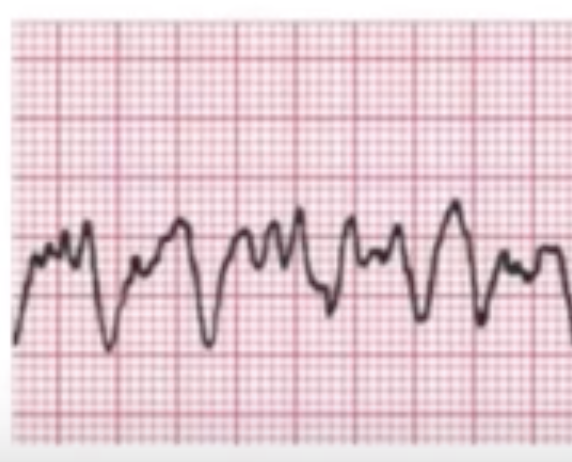
https://youtu.be/9KfVgX35wTE In this video (scrub through the video to see chapters) 03:45 Basic principles of arrhythmias 07:33 Conduction block and arrhythmias 08:35 Abnormal automaticity 10:28 Triggered activity 12:08 Summary of basic principles so far 14:05 Reentry 18:18 Rhythm strips
History of research misconduct and resulting codes of research ethics
Required reading JAMA Network Emanuel EJ, Wendler D, Grady C. What Makes Clinical Research Ethical? JAMA. 2000;283(20):2701–2711. doi:10.1001/jama.283.20.2701