Mental Health Consequences of Climate Change
Climate change affects mental health through multiple pathways, producing a spectrum of psychological responses ranging from acute trauma to chronic existential distress. Acute mental health impacts: Trauma and stress disorders Extreme weather events—hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and heat waves—can produce immediate and severe psychological trauma. Research evidence Systematic reviews of disaster mental health literature consistently document […]
Temporal and infratemporal regions; temporomandibular joint
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed., Temporomandibular joint section through Arthritis of TMJ. Temporal region Figure 1. Attachments of temporal fascia. GRAY’S ANATOMY FOR STUDENTS, FIGURE 8.138. Figure 2. GRAY’S ANATOMY FOR STUDENTS, FIGURE 8.139. The temporal fossa is the sunken area located on the lateral skull above the zygomatic arch. Boundaries Its floor […]
Hematopoietic System—Draft

Your introduction to the system (it can be written, or you can record a video). It doesn’t need to be very long. In case you need inspiration, here are some suggestions for what to include: How does this system relate to the one that has come before, and the one that follows? Why are certain threads […]
Family Medicine
Welcome to the Family Medicine learning website! At the Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine, much of your learning will include aspects of Family Medicine: the primary care of patients of all ages and all genders. Since Washington State relies on Family Physicians to provide a large component of health care, especially in rural and […]
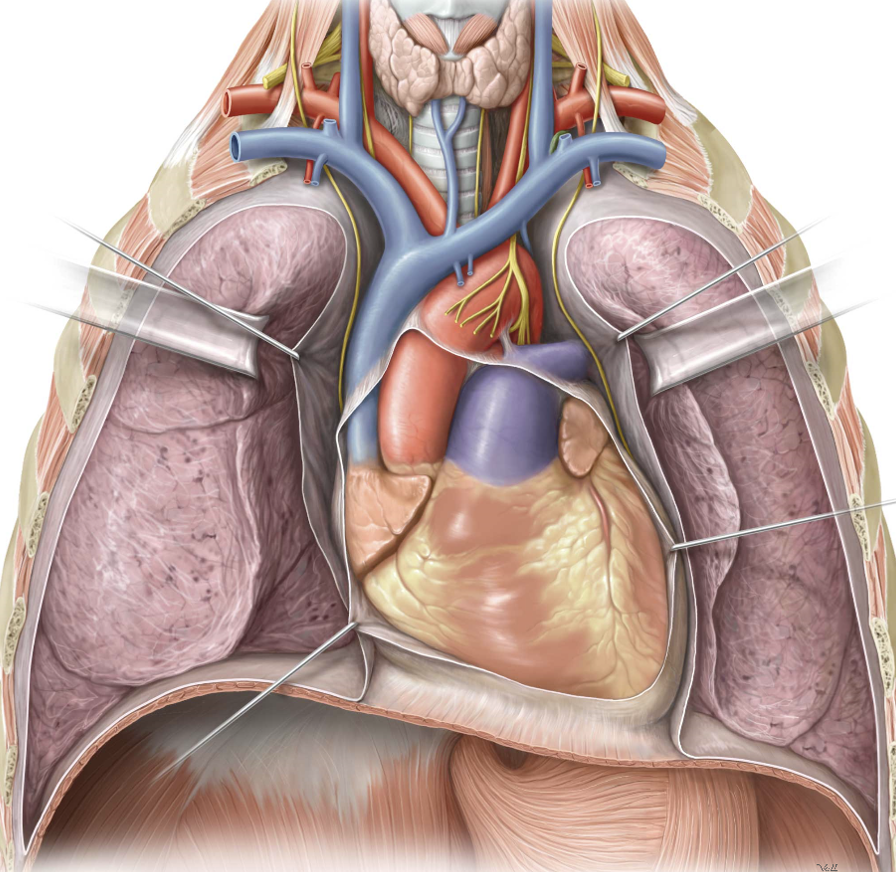
Thoracic cavity
MS1 Complete Physical Examination
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
source: Novan’s notes, by George Novan, MD, and Joanna Breems, MD Last update: September 2023 The terms STIs (sexually transmitted infections) and STDs (sexually transmitted diseases) are nterchangeable. However, more authors now favor using STI because not all “infections” are manifest as “disease”—that is, they are not clinically evident or symptomatic. A note on terminology. […]
Micro-ID topics
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Urethritis, cervicitis, vaginitis, and PID
Learning goals Compare the epidemiology, microbiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentations, and potential complications for Chlamydia trachomatis serovars D-K and Neisseria gonorrhoeae Compare the epidemiology, microbiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentations, and potential complications for yeast vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis, and trichomoniasis Describe the approach to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention in patients presenting with urethritis, cervicitis, vaginitis, and pelvic inflammatory […]
Sexually transmitted Infections (STIs): Genital ulcers and warts
Learning goals For the organisms of interest causing genital ulcer disease and genital warts: Compare the microbiology, pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical presentations, and potential complications for genital herpes (HSV), Treponema pallidum, Haemophilus ducreyi, Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L1-L3, Klebsiella granulomatis, and Human Papilloma virus (HPV) Describe the approach to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention in patients presenting with […]