Protected: Lab 28: Dissection: Orbit and Ear
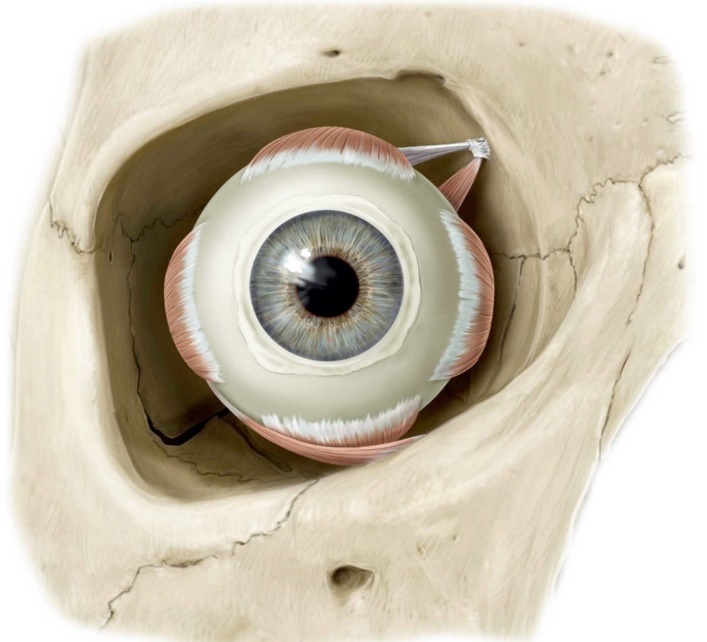
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 19: Posterior Leg and Plantar Foot
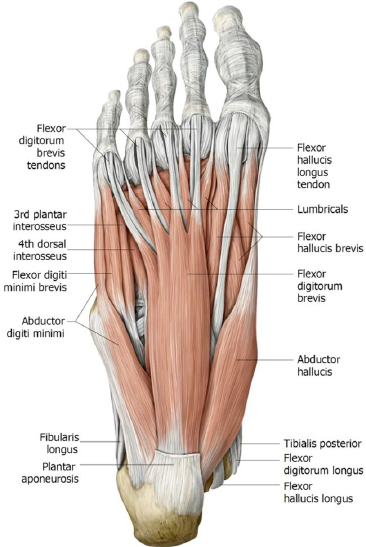
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 18: Anterior and Lateral Leg, Knee and Ankle Joints, and Dorsum of Foot
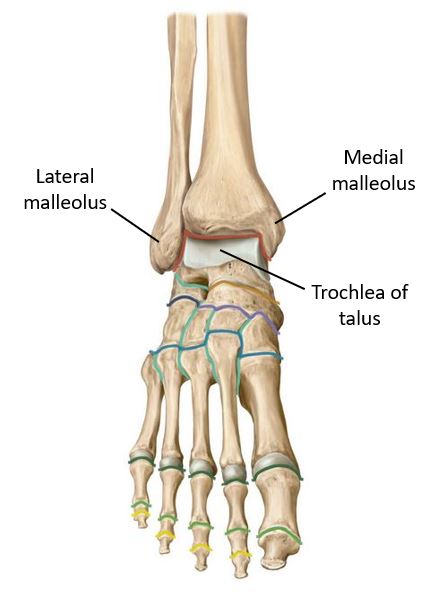
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 27: Face, Parotid Gland, and Superficial Neck
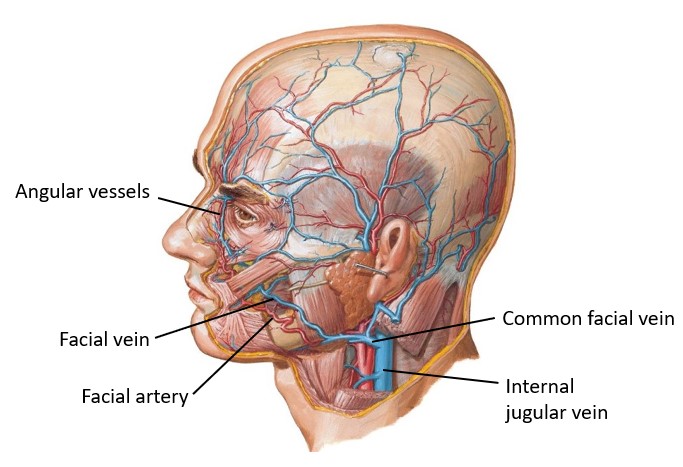
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 26: Scalp, Cranial Cavity, and Meninges
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 17: Gluteal Region, Posterior Thigh, and Popliteal Fossa
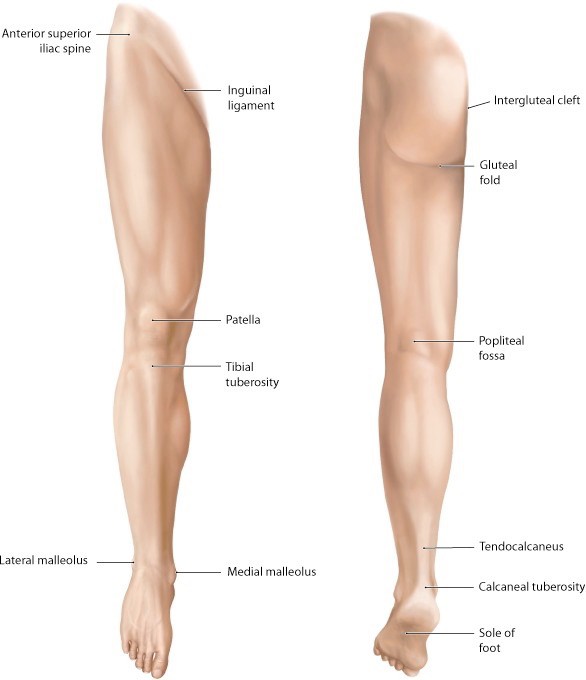
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Station 1. Meninges and ventricles
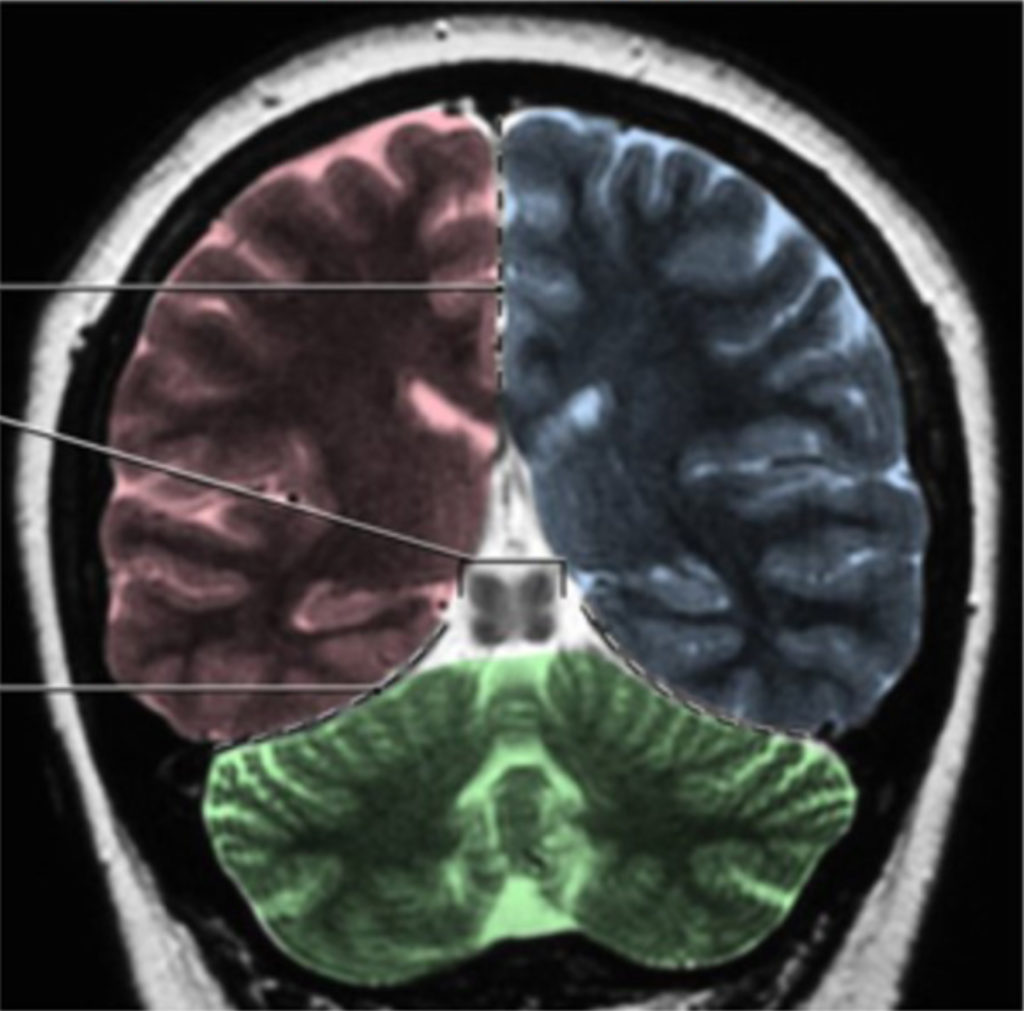
Neuroanatomy lab navigation Identify the parts of the ventricular system on a mid-sagittal brain, coronal sections, and model. The formation of the ventricular system, as it relates to development, was discussed in the Neuroembryology session. Review the clinical significance of the flow and blockage of CSF For further reference Figure 1. Figure 2. Lateral ventricles […]
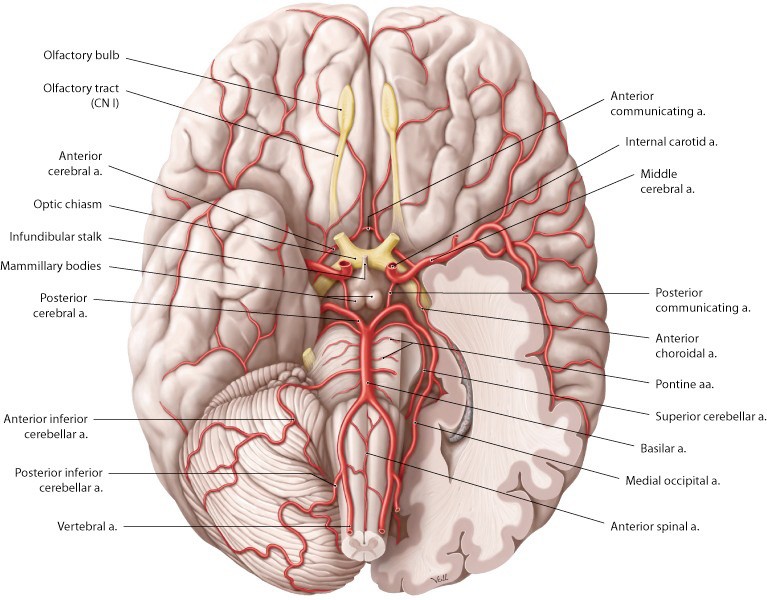
Station 5. Blood supply and circulation
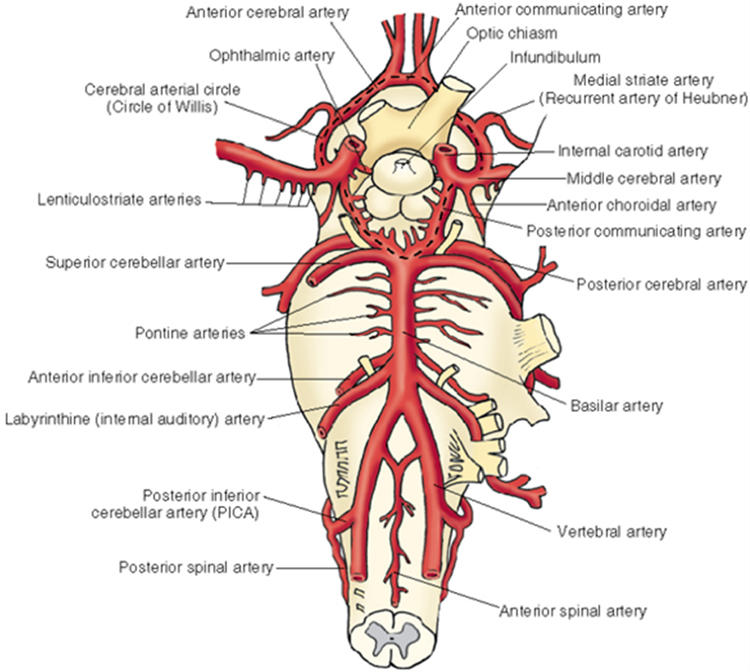
Neuroanatomy lab navigation Arterial blood supply Review and identify the arterial supply. Vertebral arteries supplying the brainstem and cerebellum Anterior and posterior spinal Posterior inferior cerebellar Basilar (unpaired)—multiple pontine branches also come directly off the basilar artery Anterior inferior cerebellar Superior cerebellar Posterior cerebral Posterior communicating Internal carotid supplying the midbrain, thalamus, hypothalamus, and cerebrum […]
Station 3. Diencephalon
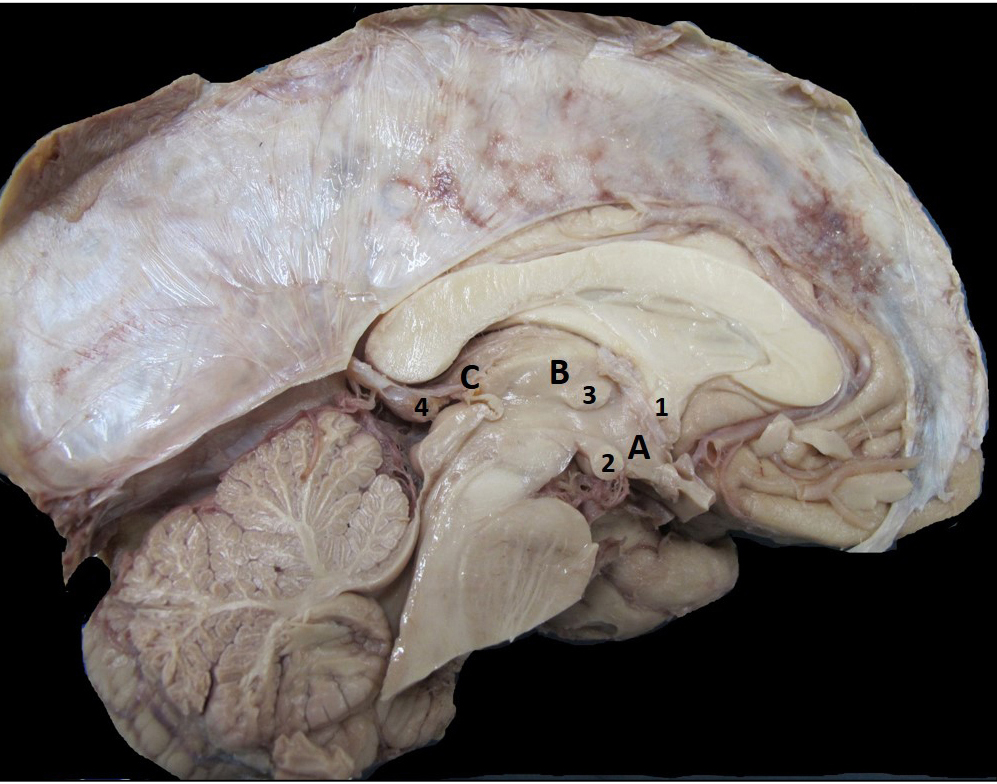
Neuroanatomy lab navigation The diencephalon is composed of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus. Thalamus The thalamus is key structure that relays information to the cortex associated with motor and sensory information. There are also thalamus nuclei that form the connections in the memory and emotion circuit from the hippocampal formation. This portion of the thalamus […]
Station 2. Cerebrum, sulci, and gyri

Neuroanatomy lab navigation Introduction to neuroanatomy Figure 1. Anatomic directional terms. From Neuroanatomy: A Laboratory Guide (2e); Jansen and Lampa. Introduction to the Central Nervous System Watch this excellent Introduction to the Central Nervous System from University of British Columbia Neuroanatomy. Cerebrum, sulci, and gyri Lobes of the cerebrum Recall that the surfaces of the […]