Portions of this site are undergoing maintenance, which will be concluded the week of 11 August. Please check back then, and if you have questions in the meantime, get in touch with the Digital Publishing team.
Happy summer!
501
- See all threads with blue symbols below.
- You will “meet” ~80 simulated patients, in digital format across two years. Their stories will provide opportunities to apply scientific and clinical knowledge and skills that you are learning across the rest of the pre-clerkship curriculum. You will learn from and “care for” these patients using a team approach throughout CBL.
- Peer Evaluation and Communication Skills
- The Medical Interview
- Review of Systems and Introduction to Clinical Reasoning
- Applied Professionalism and Ethics in Medicine
- Embryology
- Musculoskeletal System
- Back/Spine
- Shoulder
- Upper Limb
- Thorax
- Abdomen
- Pelvis
- Biochemistry
- The Cell: Structure and Function
- Carbohydrate Metabolism
- Lipid Metabolism
- Nitrogen Metabolism
- Biochemistry and Nutrition
- Red Blood Cell Metabolism
- Cell Physiology
- Nervous Tissue
- Connective Tissue
- Muscle Tissue
- Epithelial Tissue
- Cartilage and Bone
- Lymphatic Tissue
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Microbes
- Microbiome and Antimicrobial Stewardship
- Principles of Laboratory Diagnosis
- Antibiotics
- Diseases that Target Red Blood Cells
- Vaccines
- Viruses
- Homeostasis and Cell Adaptation
- Cell Injury and Repair
- Neoplasia
- Inflammation
- Cell Injury from Ischemia
- Blood Smears
- Genetic and Molecular Basis for Cancer
- Pharmacokinetics
- Drug Targets
- Pharmacodynamics
- Antibiotics
- Anti-inflammatories
- Introduction to Imaging
- Red Blood Cells
- Coagulation
- White Blood Cells
- Hematopoietic Neoplasms
- Values of Leadership
- Personal and Professional Development
- Competing Goods
- Complexity
- Theories and Styles
- Personality Types
- Growth and Development
- Service Learning
- Professional Development
- Clinical Medicine Exposure
- Building Relationships at Your Clinical Campus
- Developing Professional Identity
- Focus on a Societal Theme
502
- You will “meet” ~80 simulated patients, in digital format across two years. Their stories will provide opportunities to apply scientific and clinical knowledge and skills that you are learning across the rest of the pre-clerkship curriculum. You will learn from and “care for” these patients using a team approach throughout CBL.
- Trauma-Informed Care and Physical Exam
- Clinical Reasoning and Physical Exam
- Abdominal
- Cardiovascular
- Pulmonary
- HEENT
- Musculoskeletal
- Neurologic
- Doctoring Friends and Family
- Clinical Reasoning and the Assessment and Plan
- Introduction to Common Laboratory Evaluations
- Geriatric Interviewing
- Patient Confidentiality and Medical Professionalism
- Introduction to Evidence-Based Medicine
- Defining Scholarship
- Databases and Literature
- Statistics for the Health Sciences
- Qualitative Research
- Critical Analyses/Appraisal
- Quantitative Methods
- Expanded Definitions of Scholarship
- Research Ethics
- Structure and Function (Physiology) of Kidneys
- Electrolyte and Acid-Base Homeostasis
- Pathophysiology
- Renal Failure
- Glomerulonephritis
- Interstitial Kidney Disease
- Nephrolithiasis
- Cystic Disorders
- Endocrine Disease
- Neoplasia
- Structure and Function (Physiology) of the Heart and Vasculature
- Electrocardiograms (ECG)
- Pathophysiology
- Arrhythmias
- Hypertension
- Ischemic Heart Disease
- Valvular Disease
- Heart Failure
- Cardiomyopathy
- Pericardial Disease
- Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Congenital Heart Disease
The Respiratory System begins in 502, but it is primarily delivered in 503. See below for details.
- Lower Leg
- Heart
- Respiratory System
- Cellular Physiology of the Renal/Urinary System
- Cellular Physiology of the Cardiovascular System
- Racism in Medicine
- Nephrology
- Cardiology
- Bias and Cultural Humility in Medicine
- Microanatomy of the:
- Renal/Urinary System
- Cardiovascular System
- Respiratory System
- In the Clinical Setting
- Gram-Negative Bacteria
- Urinary Tract Infections
- Gram-Positive Bacteria
- Endocarditis
- Antibiotics
- Upper Respiratory Infections
- Therapy for Chronic Kidney Disease
- Nutrition for Cardiovascular Disease
- Urothelial Neoplasia
- Diuretics
- Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Drugs
- Drugs for Dysrhythmias
- Drugs for Dyslipidemia
- Drugs for Coronary Artery Disease
- Thrombolytics and Anti-platelet drugs
- Planetary Health
- Genitourinary Imaging
- Chest X-ray Interpretation
- Cardiovascular Imaging
- Dysfunctions of Teams
- Building a Team
- Forming
- Storming
- Norming
- Performing
- Service Learning
- Professional Development
- Clinical Medicine Exposure
- Building Relationships at Your Clinical Campus
- Developing Professional Identity
- Focus on a Societal Theme
503
- You will “meet” ~80 simulated patients, in digital format across two years. Their stories will provide opportunities to apply scientific and clinical knowledge and skills that you are learning across the rest of the pre-clerkship curriculum. You will learn from and “care for” these patients using a team approach throughout CBL.
- Physical Examination
- Musculoskeletal
- Neurologic
- Testicular and Prostate
- Breast and Pelvic
- Geriatric Interviewing
- Interpretation of Chest Radiography
- Oral Presentation
- Ethics
- End of Life
- Defining and Determining Death
- Transplant
- Sexism in Medicine
- Clinical Skills Workshops
- Community Patient Experiences
- Anatomy Capstone
- IRB
- Qualitative Methods
- Mixed Methods
- Survey Design
- Epidemiology and Biostatistics
- Research Ethics
- Community-Based Participatory Inquiry Methods
- Individual Project Planning
- Learning Plan
- Structure and Function (Physiology) of the Lungs
- Pulmonary Function Tests
- Pathophysiology
- Airway Disorders
- Infections
- Hypoxemia
- Pleural Disease
- Thromboembolic Disease
- Idiopathic Disorders
- Mediastinal Disorders
- Structure and Function (Physiology) of the Skin
- Pathophysiology
- Inflammatory Disorders
- Immune-Mediated
- Infectious
- Infestations and Bites
- Skin Disorders Due to Environment
- Neoplastic Disorders
- Cutaneous Drug Reactions
- Inflammatory Disorders
- Structure and Function (Physiology) of the Musculoskeletal System
- This was covered in 501 during Anatomy.
- Pathophysiology
- Osteoarthritis
- The Spine
- The Arm
- The Hip, Pelvis, and Knee
- The Foot, Ankle, and Lower Extremity Injuries
- Exercise Physiology
- Aging and Falls
- Pediatric Musculoskeletal Injuries
- Genetic and Neoplastic Disorders of Bone
- Muscular Dystrophies
- Respiratory
- Reproductive
- Racism in Medicine
- Pulmonology
- Dermatology
- Respiratory System
- Extrapulmonary
- Intrapulmonary
- Integument
- Female Reproductive System
- Regulation of the Airway
- Hypersensitivities
- Literature Search Strategies
- Error Disclosure
- Upper Respiratory Infections
- Lower Respiratory Infections
- Pneumonia
- Fungal Infections
- Tuberculosis
- Bioterrorism and Other Zoonoses
- Antibiotics
- Childhood Exanthems
- Rickettsia and Arthropod-Borne Viruses
- Spirochetes
- HIV
- Atypical Skin Infections
- Anaerobes
- Osteomyelitis
- Joint Infections
- Pregnancy and Lactation
- Coagulation and Thrombosis
- Histopathology of Lung Disease
- Drugs for Allergy
- Drugs for Asthma and COPD
- Anticoagulant Drugs
- Pharmacology in Pregnancy
- Planetary Health
- Cardiovascular Imaging
- Imaging of Congenital Heart Disease
- Chest X-ray Interpretation
- Musculoskeletal Imaging
- Emotional Intelligence
- Lexicon of our Emotions
- Environments We Create
- Immediate Self-Management
- Lifelong Strategies
- Implications of Self-Management
- Empathy
- Empathy Killers
- Organizational Awareness
- Influence
- Development of Others
- Purpose and Vision
- Service Learning
- Professional Development
- Step 1 Preparation
- Clinical Medicine Exposure
- Building Relationships at Your Clinical Campus
- Developing Professional Identity
- Focus on a Societal Theme
511
- You will “meet” ~80 simulated patients, in digital format across two years. Their stories will provide opportunities to apply scientific and clinical knowledge and skills that you are learning across the rest of the pre-clerkship curriculum. You will learn from and “care for” these patients using a team approach throughout CBL.
- Review of General Adult Physical Exam
- Diabetes Workshop
- Ethics
- Abortion
- Conscientious Refusal
- Genitourinary Exam
- Telehealth
- Point-of-Care Ultrasound
- Clinical Skills Workshops
- Community Patient Experiences
- Structure and Function (Physiology) of
- Endocrine Glands
- Pancreas
- Thyroid
- Parathyroids
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary
- Adrenals
- Gonads
- Pathophysiology
- Diabetes Mellitus and Hypoglycemia
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Hypo- and Hyperthyroidism
- Thyroid Nodules
- Hypo- and Hyperparathyroidism
- Osteoporosis
- Diabetes Insipidus and SIADH
- Acromegaly
- Hypercortisolism and Cortisol Deficiency
- Adrenal Hyperplasia
- Hypopituitarism
- Neoplasia, MEN, and Polyglandular Syndrome
- Female Reproductive System Pathophysiology
- Breast Conditions
- High-Risk Obstetric Conditions
- Pregnancy Loss
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
- Dysmenorrhea and Endometriosis
- Pelvic Organ Prolapse
- Neoplasia
- Male Reproductive System
- Structure and Function Physiology
- Pathophysiology
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Neoplasia
- Structure and Function (Physiology) of the Digestive System
- Vitamins
- Pathophysiology
- Disorders of the Oropharynx
- Disorders of the Esophagus
- Disorders of the Stomach
- Disorders of the Small Bowel
- Disorders of the Large Bowel
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Anorectal Disorders
- Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas
- Congenital Anomalies
- Neoplasia
- Digestive System
- Glucose Metabolism
- Racism in Medicine
- Endocrinology
- LGBTQ+ Health and Disparities
- Endocrine Glands
- Male Reproductive System
- Digestive System
- Further Developing Search Strategies
- Sexually Transmitted Infections
- Parasitology
- Infectious Diarrhea
- Hepatitis
- Values and Ethics
- Nutrition Therapy for Diabetes
- Obesity and Weight Management
- Lifestyle Interventions for Osteopenia and Osteoporosis
- Dysphagia and Enteral Nutrition
- Diarrhea, Constipation, and GERD
- Nutrition Therapy for Cancer
- Drugs for Diabetes
- Pharmacology of Bone
- Corticosteroids
- Pharmacology in Gynecology
- Male Reproduction Drugs
- Drugs for Diarrhea and Constipation
- Drugs and the Liver
- Planetary Health
- Female Reproductive Imaging
- Male Reproductive Imaging
- Gastrointestinal Imaging
- Comparing Health Outcomes
- History of U.S. Health Systems
- Models of Health Provision/ Insurance
- Healthcare Finance
- The Triple Aim
- The Legislative Process
- The Regulation of Medicine
- Models of Healthcare Delivery
- Documentation and Billing
- Informatics
- Medicolegal Issues
- Ethics of Health Systems
- Service Learning
- Professional Development
- Completion of Medschlr 520 and 540
- Step 1 Preparation
- Clinical Medicine Exposure
- Building Relationships at Your Clinical Campus
- Developing Professional Identity
- Focus on a Societal Theme
512
- You will “meet” ~80 simulated patients, in digital format across two years. Their stories will provide opportunities to apply scientific and clinical knowledge and skills that you are learning across the rest of the pre-clerkship curriculum. You will learn from and “care for” these patients using a team approach throughout CBL.
- Mental Status Exam
- Adolescent Interviewing
- Trauma Informed Care
- Ethics
- Physician-Assisted Suicide
- Mental Health
- Contested Therapies
- Neurology Workshop
- Ophthalmology Workshop
- Writing Orders
- Point-of-Care Ultrasound
- Urogenital Exams
- Telemedicine
- Clinical Skills Workshops
- Community Patient Experiences
- Function (Physiology) of the Behavioral System
- Functional Neurocircuitry
- Development
- Sleep-Wake Cycles
- The Biopsychosocial Model
- Stress and Adaptation
- Pathophysiology
- Neurodevelopmental Disorders
- Sleep-Wake Disorders
- Eating Disorders
- Anxiety Disorders
- Depression
- Suicide
- Trauma and Stress-related Disorders
- Substance Use Disorders
- Psychotic Disorders
- Bipolar and Related Disorders
- Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders
- Somatic Symptom and Related Disorders
- Personality Disorders
- Dementia
- Structure and Function (Physiology) of the Neurologic System
- Clinical Localization
- Neuroanatomy
- Brain Circulation
- Special Senses
- Ophthalmology
- Pathophysiology
- Spinal Cord Disorders
- Delirium and Encephalopathy
- Seizures and Epilepsy
- Headaches
- Stroke
- Movement Disorders
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Neuromuscular Junction Disorders
- Central Demyelinating Disorders
- Infections
- Neoplasia
- Structure and Function (Physiology) of the Musculoskeletal System was covered in 501 during Anatomy
- Exercise Physiology
- Aging
- Non-rheumatologic Pathophysiology
- Genetic and Neoplastic Disorders
- Muscular Dystrophies
- Infections
- Injuries
- Osteoarthritis
- Immunology Related to Joints
- Rheumatologic Pathophysiology
- Crystalopathies
- Spondyloarthropathies
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Pediatric Inflammatory Arthritis
- Viral and Other Arthritides
- Cytokine Storms
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Sjogren’s Syndrome and Mixed
- Connective Tissue Disease
- Systemic Sclerosis and Raynaud’s Phenomenon
- Vasculitides
- Myopathies
- Infections
- Head and Neck
- Neuroanatomy
- Sensory Transduction
- Age-Related Sensory Decline
- Health Literacy/Interpreters
- Special Senses
- Interprofessional Communication
- Teams and Teamwork
- Nervous System Infections
- Eye and Orbital Infections
- Joint Infections
- Infections in Immunocompromised Hosts
- Nutrition-Focused Physical Exam
- Drugs for Epilepsy
- Drugs for Headache
- Drugs for Alzheimer’s Disease
- Drugs for Insomnia
- Drugs for Pain
- Behavioral Health Drugs
- Rheumatology Drugs
- Planetary Health
- Vector-borne Disease
- Climate Change and Mental Health
- Neuroimaging
- Culture Building
- Recruiting/Hiring/Retention
- Discipline
- Bias in the Workplace
- Generational Differences
- Economics
- Finance
- Business Strategy
- Running a Meeting
- Negotiation
- Marketing/Communication
- Service Learning
- Professional Development
- Completion of Medschlr 520 and 540
- Step 1 Preparation
- Observed Structured Clinical Exam (OSCE)
- Clinical Medicine Exposure
- Building Relationships at Your Clinical Campus
- Developing Professional Identity
- Focus on a Societal Theme
513
- Step 1 Prep
- Take Step 1
- Transition to Clerkship Course
- Anatomy of Change/ Leading Change
- Urgency and a Guiding Coalition
- Communicate a Vision
- Empower Wins
- Consolidate and Institutionalize
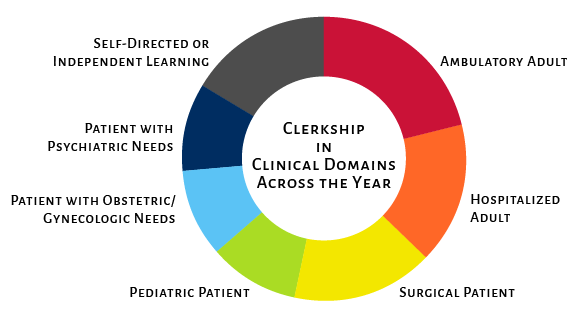
LIC
All students complete a 46-week LIC to gain the clinical skills, knowledge, and empathy necessary to succeed as residents and practicing physicians.
Students are exposed to multiple disciplines simultaneously for the duration of the year, with each discipline integrated into students’ weekly schedule. This enables students to form and maintain relationships with patients and clinicians, develop clinical competencies over time and across specialties, and experience a continuity of care that more closely mirrors what they will experience as residents and practicing physicians.
Ambulatory Adult
- Supervised care of adult patients over the age of 18. Learning will occur in affiliate clinics and ambulatory care centers and the supervising faculty preceptors will be internal medicine physicians, family medicine physicians, or specialist physicians.
Hospitalized Adult
- Supervised care of adult patients over the age of 18. Learning will occur in affiliate hospitals and the supervising faculty preceptors will be internal medicine physicians, family medicine physicians, or specialist physicians.
Surgical Patient
- Supervised care of adult or pediatric patients presenting with surgical needs. Learning will occur in affiliate clinics, ambulatory care centers, hospitals, emergency rooms, and surgery suites or centers. The supervising faculty will be surgeons or surgery sub-specialists or anesthesiologists.
Pediatric Patient
- Supervised care of pediatric patients under the age of 18. Learning will occur in affiliate clinics, ambulatory care centers, and hospitals. The supervising faculty preceptors will be pediatricians, family medicine physicians, or pediatric specialist physicians, with opportunities in select circumstances to engage in care with interprofessional preceptors and in community care sites.
Patient with Obstetric/Gynecologic Needs
- Supervised care of patients seeking Obstetrics or Gynecological care. Learning will occur in affiliate clinics, ambulatory care centers, hospitals, emergency rooms, labor suites, and surgery suites or centers. The supervising faculty are obstetricians, gynecologists, internal medicine physicians, family physicians, midwives, or OB/GYN sub-specialists.
Patient with Psychiatric Needs
- Supervised care of patients with behavioral or psychiatric needs. Learning will occur in affiliate clinics, ambulatory care centers, or hospitals. The supervising faculty will be psychiatrists, internal medicine physicians, family medicine physicians, and/or other faculty behavioral health providers [e.g., psychologists, social workers (e.g., LCSW), etc.].
Self-Directed or Independent Learning
- Value Based Care
- Patient Safety Tools and Practice
- Continuous Quality Improvement
- Health and Power
- Health Equity and Improvement
- Social Determinants in Clinical Care and Populations
- Structural Competency
- Local Determinants of Health
- Organization of Local Services
- Innovations in Clinical Care
- Social Determinants of Health Simulation
- Learning in the Workplace
- Teaching
- Spectrums of Advocacy
- Advocacy in Action
- Possible completion of Medschlr 520 or 540, if not yet completed
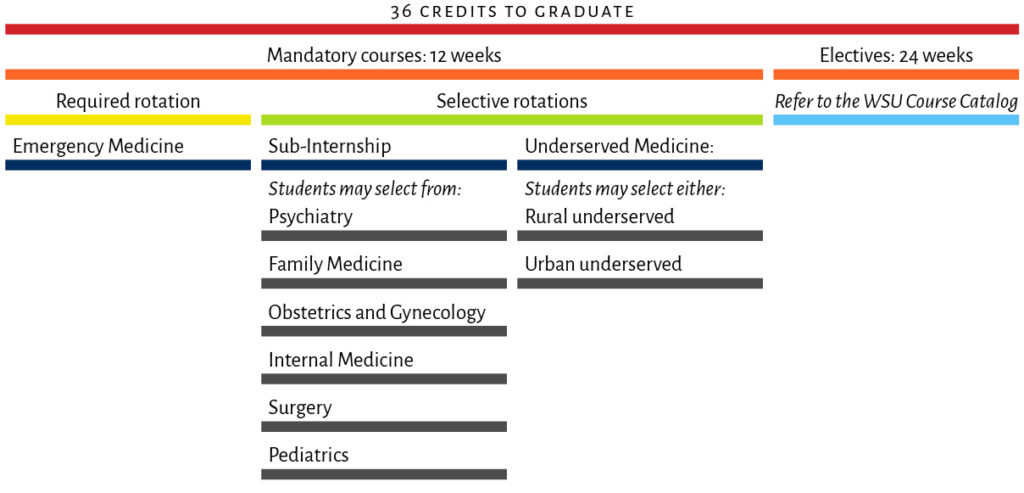
Year 4
Required rotation
-
Emergency Medicine
Selective rotations
-
Sub-Internship:
-
Students may select from:
-
Psychiatry
-
Family Medicine
-
Obstetrics and Gynecology
-
Internal Medicine
-
Surgery
-
Pediatrics
-
-
-
Underserved Medicine:
-
Students may select either:
-
A rural underserved or
-
An urban underserved rotation.
-
-
An elective rotation is a rotation a student can choose—either clinical, non-clinical, or research—that when added to mandatory courses make up the total body of study required to complete the MD degree program requirements. In order to graduate, students must complete 36 credits (1 week = 1 credit) in their 4th year. Twelve of those credits will be fulfilled with required courses listed in the mandatory course drop-down menu. The other 24 credits provide flexibility for students to bolster their residency applications, gauge interest in subspecialties, and complete away rotations. Only 12 credits maximum of the 24 credit electives required to graduate can be completed in a virtual or non-patient care rotation.
See the WSU Catalog for elective options.
- Identify a Community Challenge
- Examine Needs and Develop a Plan
- Create an Intervention
- Implement an Intervention
- Examine an Intervention
- Disseminate an Intervention
- Participate in synchronous and asynchronous learning sessions about:
- Licensure and Certification
- Professional Societies
- Personal Finance
- CVs, Interviewing, and Contracts
- Personal Development
- Wellness
- Possible completion of Medschlr 540, if not yet completed