Overview of the neck viscera; thyroid and parathyroid glands
Optional reading Moore, Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed., Viscera of neck section through Nerves of parathyroid glands. In thinking about the overall architecture of the neck, it can be organized into 4 units: 1. Visceral unit The visceral unit contains the neck’s visceral organs (the focus of this chapter). It is located anteriorly. 2. Vertebral […]
Protected: Lab 3: Dissection: Shoulder and Pectoral Region
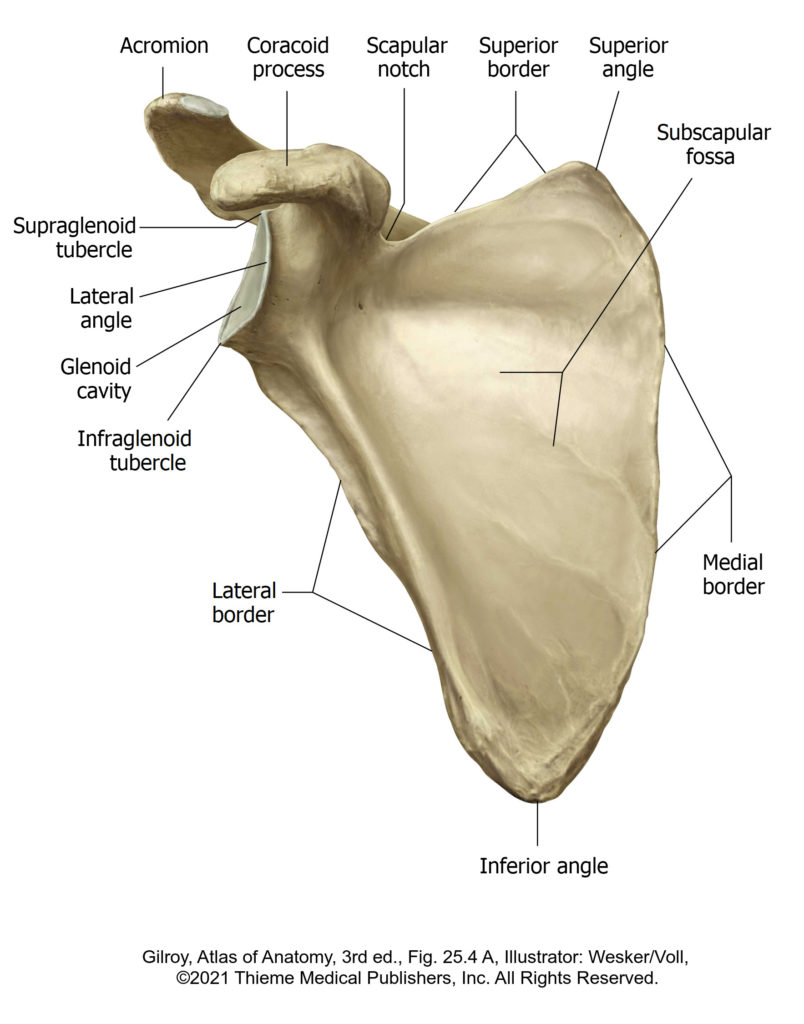
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 2 Introduction: Vertebral Column; Spinal Cord; Spinal Nerves; Back Muscles
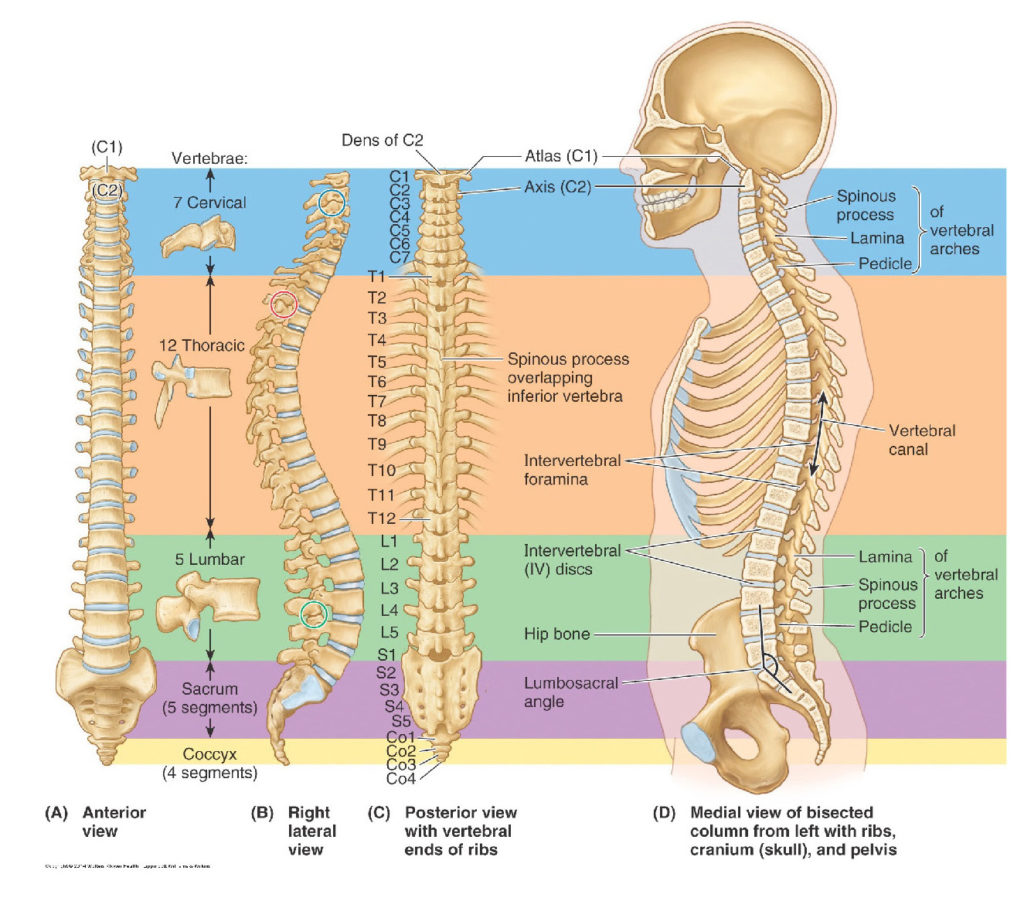
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 2, Station 4: Spinal Cord
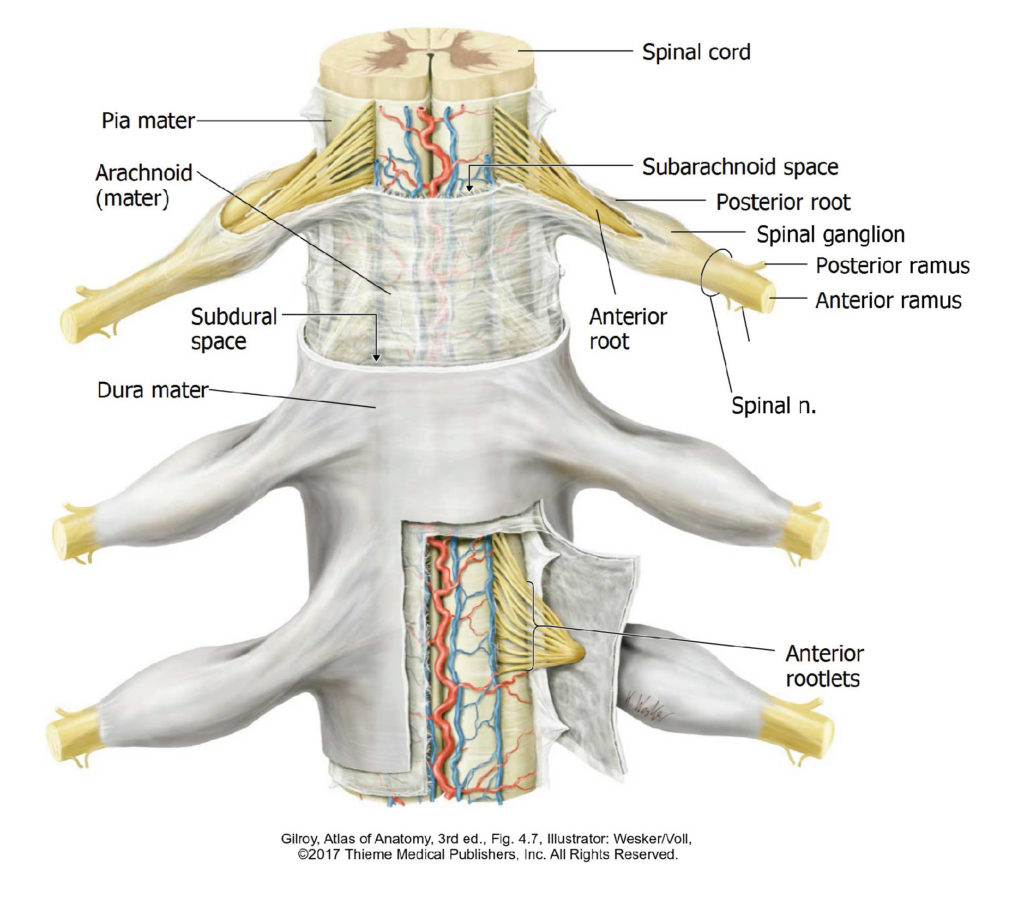
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 2, Station 5: Spinal Nerves
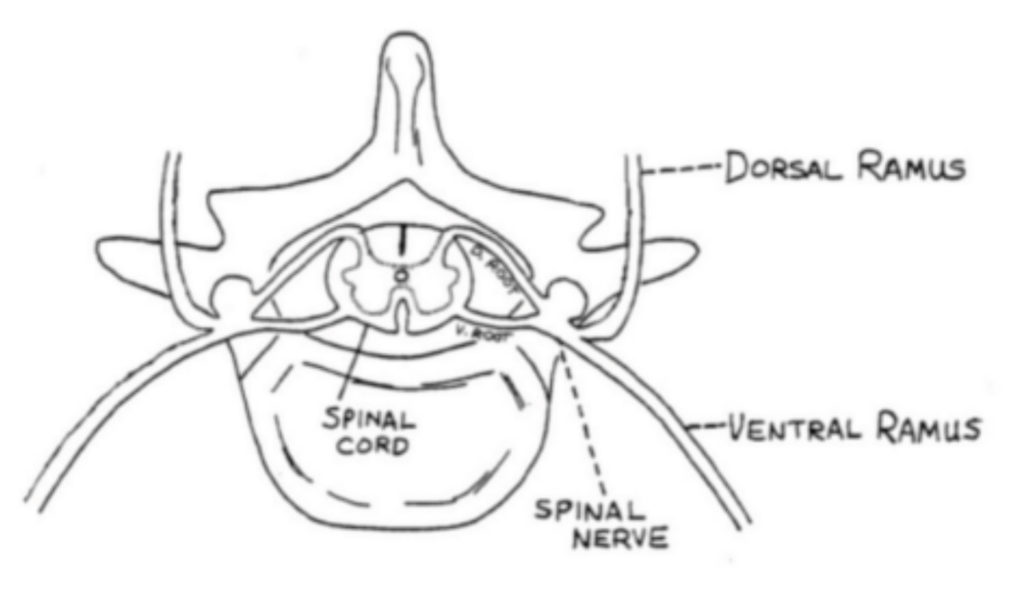
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 2, Station 6: Muscles of the Back and Posterior Shoulder
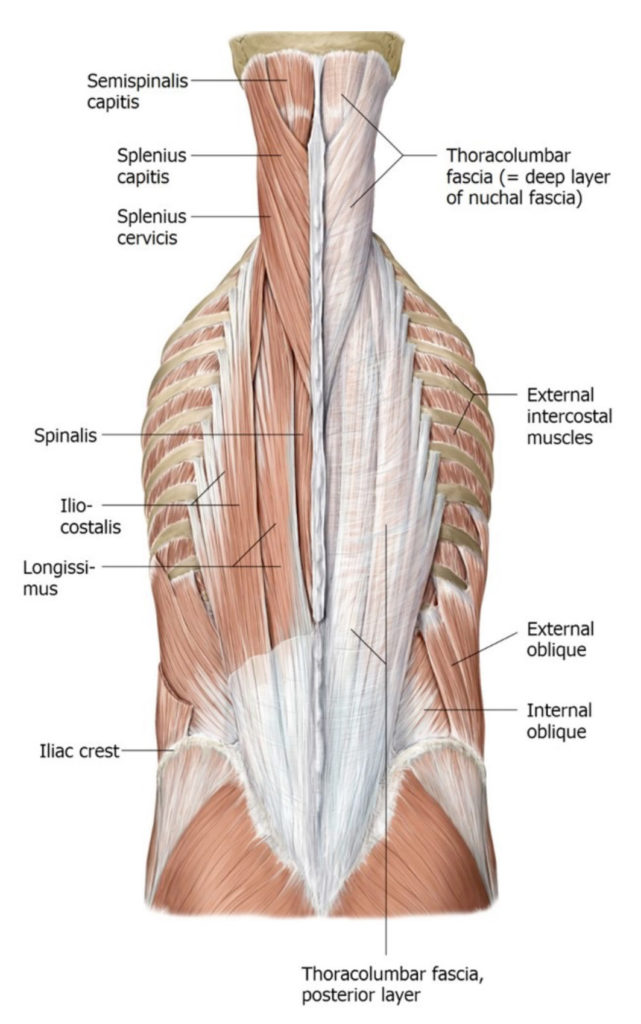
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 2, Station 3: Imaging of the Vertebral Column

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 2, Station 1: Vertebral Column
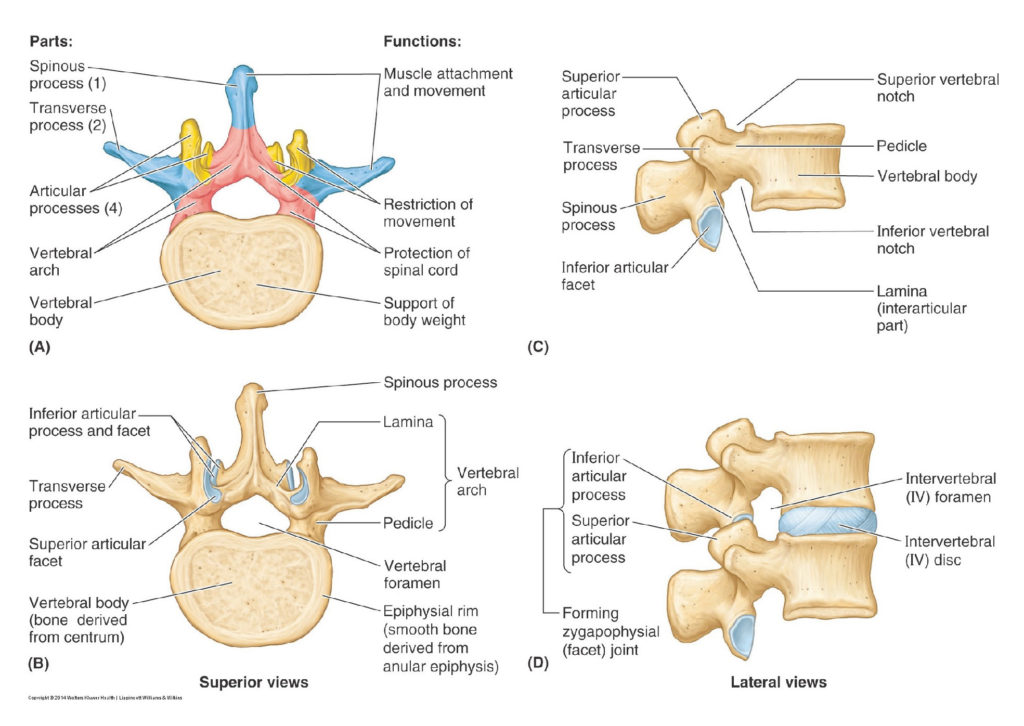
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 2, Station 2: Vertebral Column 2
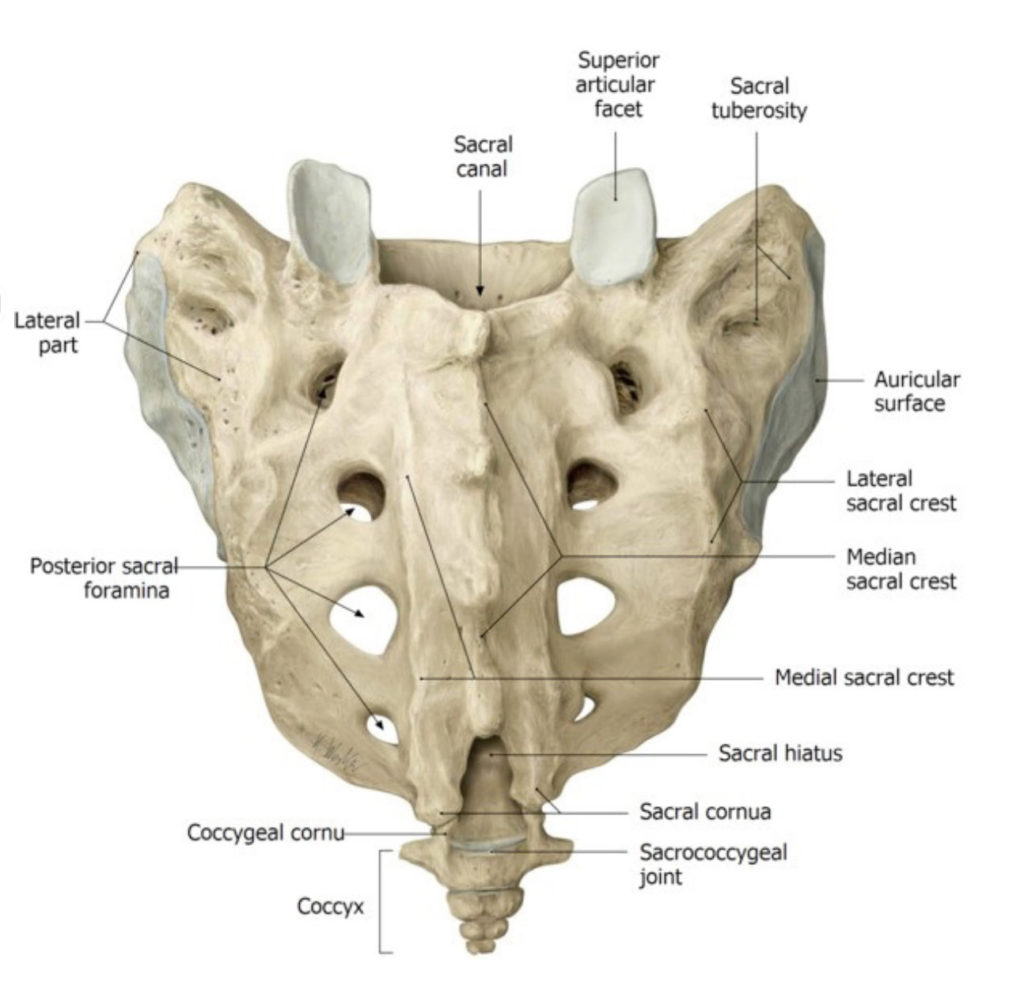
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 1: Introduction to Anatomy
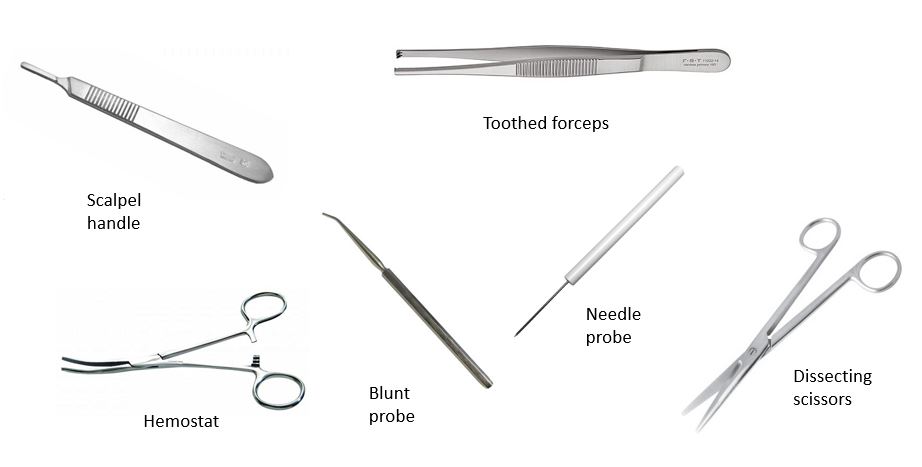
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.