Lab 12, Station 1: Pelvic Skeleton and Ligaments

Lab 12 Navigation Introduction Station 1: Pelvic Skeleton and Ligaments Station 2: Pelvic Cavity and Anal Triangle of Perineum Station 3: Female Perineum (Urogenital Triangle) Station 4: Male Perineum (Urogenital Triangle) Station 5: Overview: Pelvic Organs and Vessels Station 1: Pelvic Skeleton and Ligaments Complete anatomy Hip bone Pelvic Skeleton (Pelvic Girdle): Two Hip Bones […]
Protected: Lab 22, Station 2: Pelvic Cavity and Anal Triangle of Perineum

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Lab 22: Prosection lab: Pelvic Skeleton, Pelvic Cavity, and Pelvic Vessels; Perineum

Students: Unlike most lab sessions, which are dissection-based, this session is a “prosection lab.” Assemble in 5 groups, each having ~16 members. There are 5 learning stations situated around the labs. Pick a station to start at. Groups will spend about 25 minutes at each station, rotating around the labs until they have visited all […]
Protected: Lab 22, Station 5: Overview: Pelvic Organs and Vessels

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 22, Station 4: Male Perineum (Urogenital Triangle)

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 22, Station 3: Female Perineum (Urogenital Triangle)

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 6: Carpal Tunnel and Palmar Hand
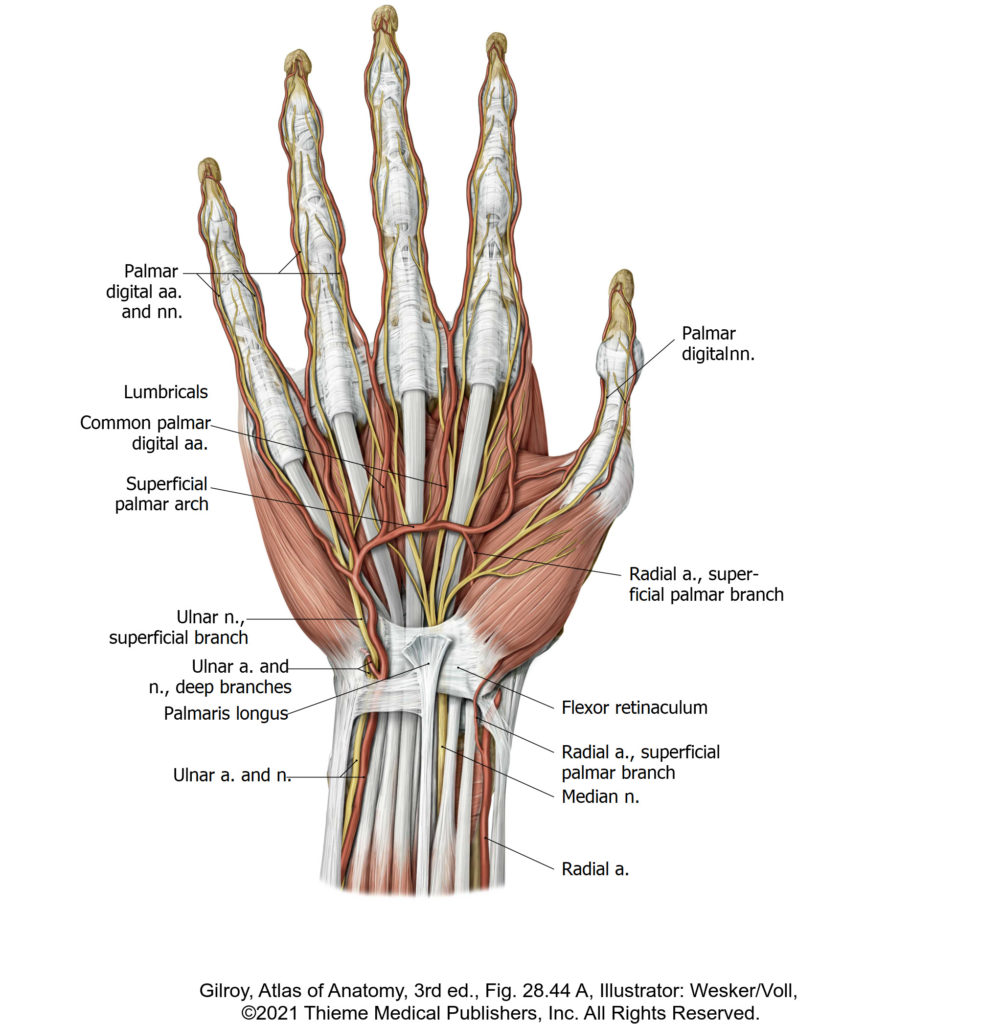
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 4: Dissection: Axilla, Brachial Plexus, and Arm
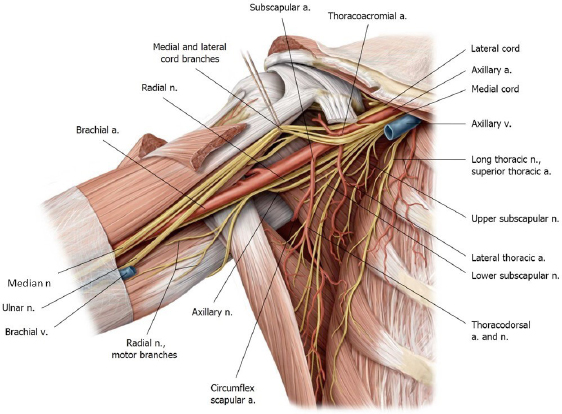
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 5: Cubital Fossa, Elbow, and Anterior Forearm
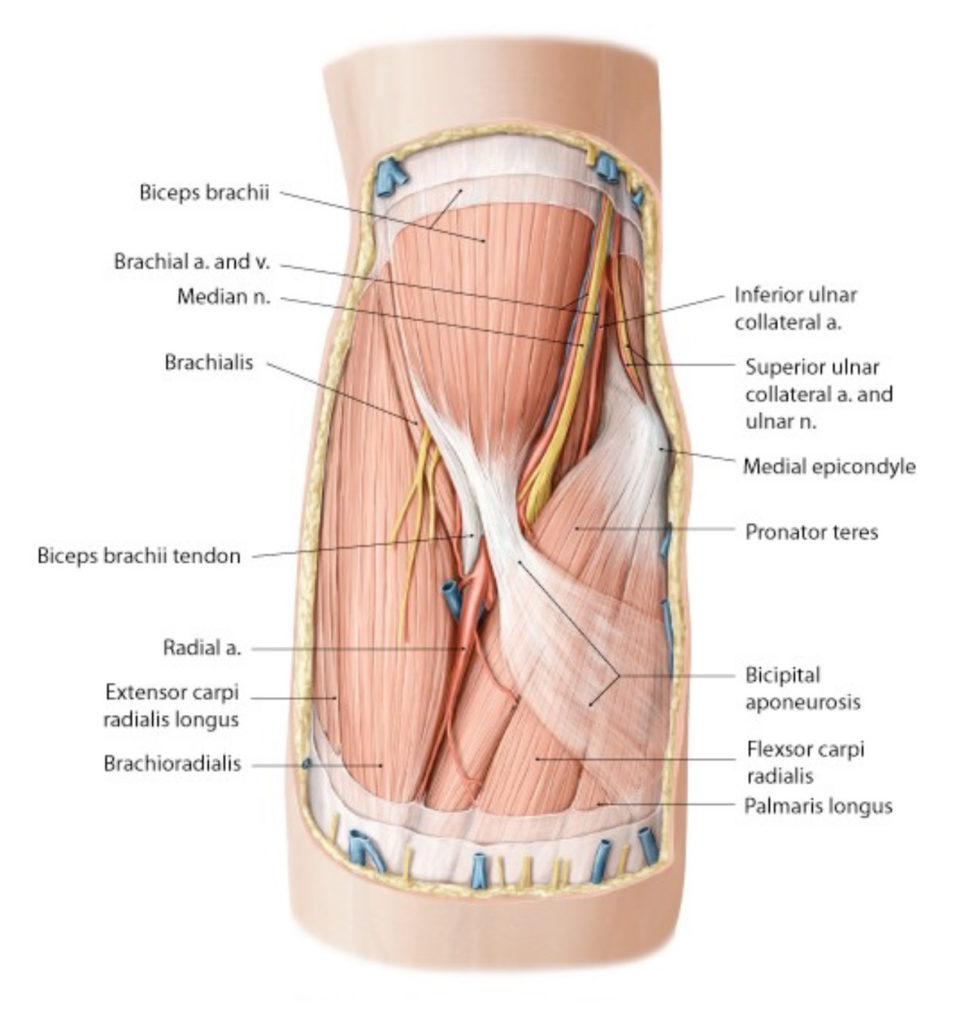
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Head and neck development
Optional reading Langman’s Medical Embryology: Chapter 17, Head and Neck. The relevant sections are: Introduction, Pharyngeal Apparatus, Thyroid Gland, and Face. Most of the events that produce the definitive anatomy of the head and neck are covered in this chapter. The pharyngeal apparatus (the source of the primordial tissues) is discussed first, followed by detailed […]