Development of digestive organs
Optional reading The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 12th ed., chapter 11. Introduction As always, understanding the development of the body’s organ systems and parts illuminates their gross anatomy. The definitive anatomy of digestive organs in the abdomen is a perfect example. The embryo starts out with a simple straight tube in the 4th week, […]
old-Lab 24: Peritoneal Cavity and Supracolic Region
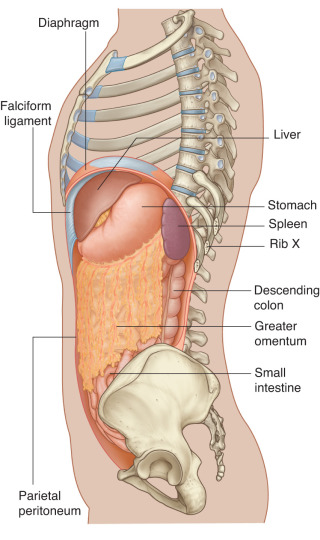
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Survey the GI organs. Examine the peritoneum, peritoneal cavity, mesenteries, omenta, and peritoneal ligaments. Locate the subparts of the greater sac. Study the lesser omentum and demonstrate the lesser sac. Dissect the celiac trunk and demonstrate its branches. Clean and study the organs in the supracolic region: liver; […]
Protected: Lab 7: Posterior Forearm and Dorsal Hand
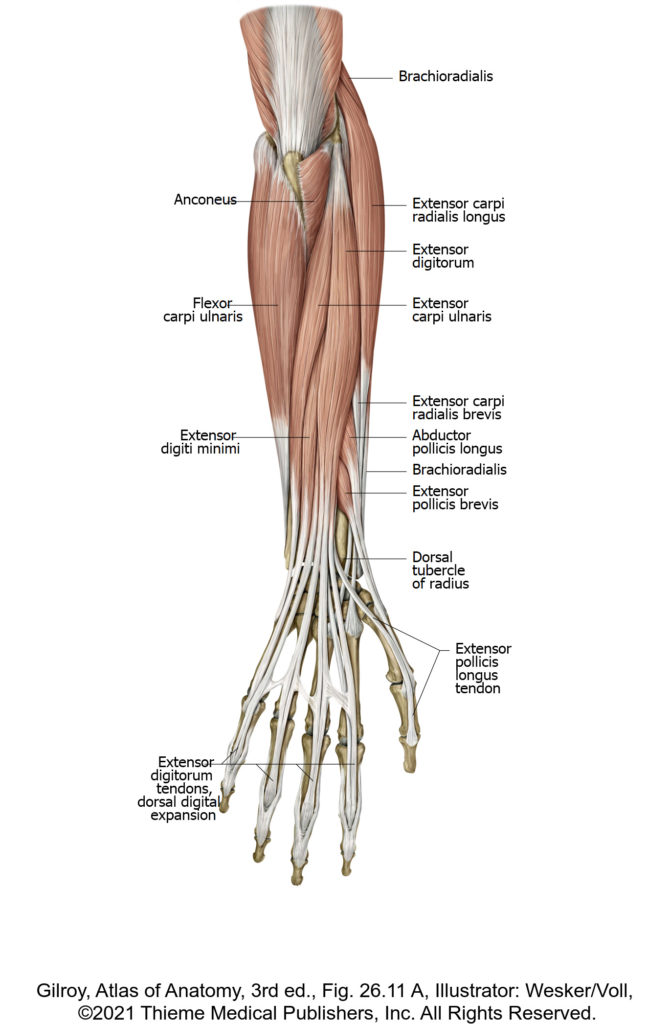
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 22, Station 1: Pelvic Skeleton and Ligaments

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Lab 12, Station 1: Pelvic Skeleton and Ligaments

Lab 12 Navigation Introduction Station 1: Pelvic Skeleton and Ligaments Station 2: Pelvic Cavity and Anal Triangle of Perineum Station 3: Female Perineum (Urogenital Triangle) Station 4: Male Perineum (Urogenital Triangle) Station 5: Overview: Pelvic Organs and Vessels Station 1: Pelvic Skeleton and Ligaments Complete anatomy Hip bone Pelvic Skeleton (Pelvic Girdle): Two Hip Bones […]
Protected: Lab 22, Station 2: Pelvic Cavity and Anal Triangle of Perineum

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 22: Prosection lab: Pelvic Skeleton, Pelvic Cavity, and Pelvic Vessels; Perineum

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 22, Station 5: Overview: Pelvic Organs and Vessels

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 22, Station 4: Male Perineum (Urogenital Triangle)

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 22, Station 3: Female Perineum (Urogenital Triangle)

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.