Lab 12: Dissection: Pelvic Viscera and Pelvic Vessels (Hemisection)
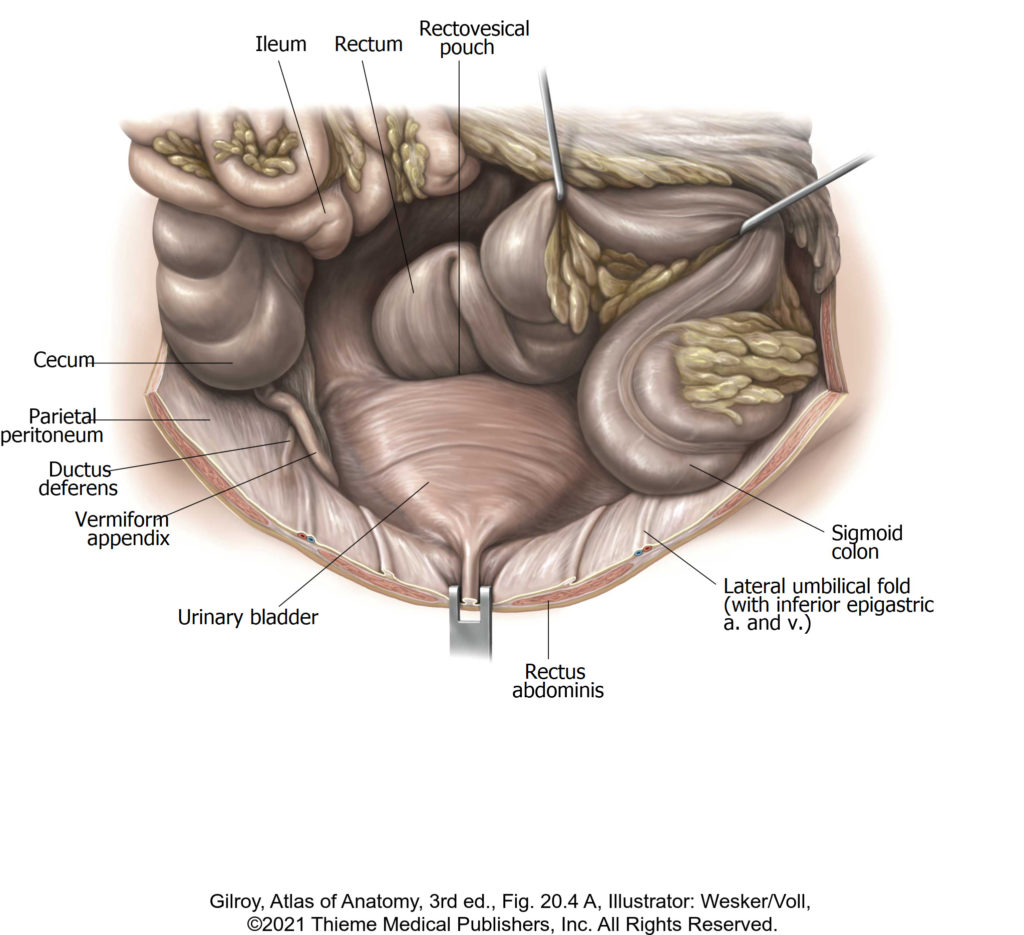
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Understand the general arrangement of pelvic organs in the male and female and identify those organs that can be approached through the pelvic inlet Hemisect the pelvis and remove half with the lower limb Identify pelvic organs and their subparts Identify muscles in the walls and floor of […]
Lab 24: Peritoneal Cavity and Supracolic Region
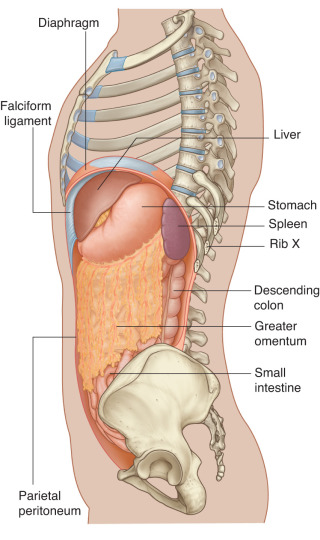
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Survey the GI organs. Examine the peritoneum, peritoneal cavity, mesenteries, omenta, and peritoneal ligaments. Locate the subparts of the greater sac. Study the lesser omentum and demonstrate the lesser sac. Dissect the celiac trunk and demonstrate its branches. Clean and study the organs in the supracolic region: liver; […]
Lab 11, Station 1: Viscera of the Abdominal Cavity
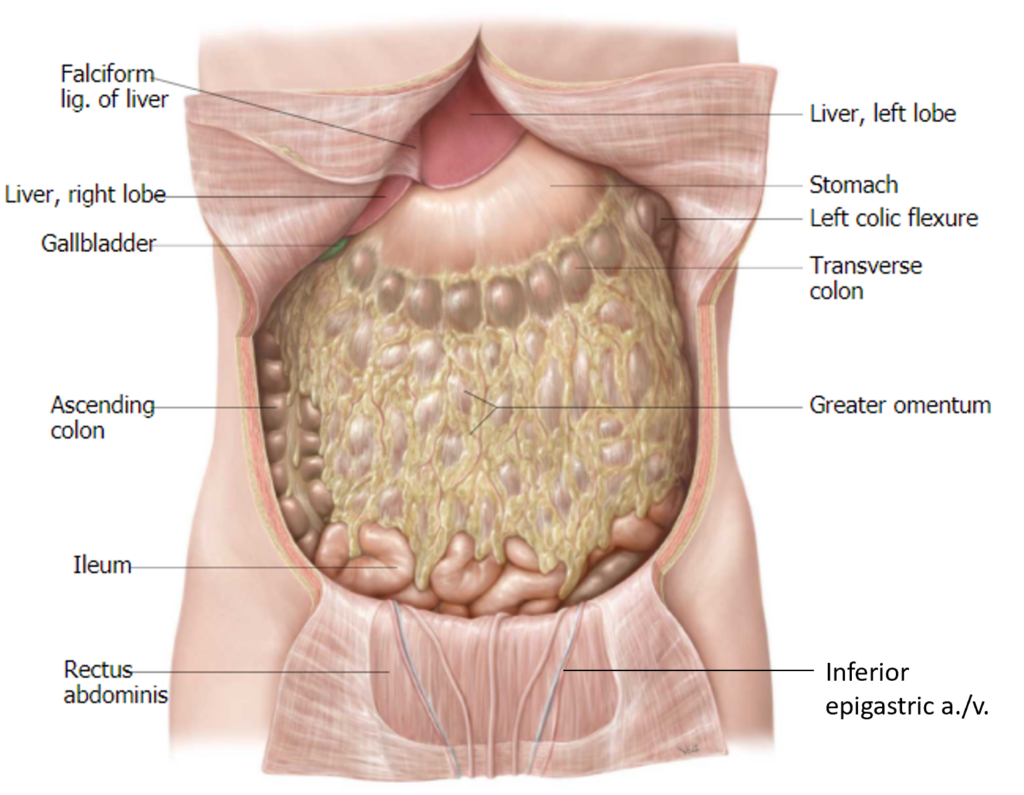
Lab 11 navigation Complete anatomy Abdominal viscera Organs of the Supracolic Region The liver is in the right upper quadrant. The sharp inferior border peeks out under the costal margin; reach under the diaphragm to feel the liver’s diaphragmatic surface. Lift the liver’s inferior border to see the gallbladder (yes, it should be green). Figure […]
Lab 00: Prosection lab: Pelvic Skeleton, Pelvic Cavity, and Pelvic Vessels; Perineum

Need to log in to view the dissector? Tap here for instructions on how to show the keyboard on the displays in the anatomy lab Download this lab as a PDF Students: Unlike most lab sessions, which are dissection-based, this session is a “prosection lab.” Assemble in 5 groups, each having ~16 members. There are […]
Lab 00, Station 4: Male Perineum (Urogenital Triangle)

Lab 12 navigation Station 4: Male Perineum Complete anatomy Male perineum This station covers the male urogenital triangle. The anal triangle has a similar construction in both sexes—it is covered at Station 2. As in the female, the UG triangle contains: (1) the external genitalia and (2) two fascia-lined spaces: superficial and deep perineal pouches. […]
Lab 00, Station 3: Female Perineum (Urogenital Triangle)

Lab 12 navigation Station 3: Female Perineum Complete anatomy Female perineum Question Why is the perineal body a structurally important landmark? It is larger and clinically more important in females. This station covers the female urogenital (UG) triangle. The anal triangle has a similar construction in both sexes—it is covered at Station 2. The UG […]
Lab 00, Station 2: Pelvic Cavity and Anal Triangle of Perineum

Lab 12 navigation Station 2: Pelvic Cavity and Pelvic Floor; Anal Triangle of Perineum Complete anatomy Muscles of the pelvic cavity Pelvic Cavity The pelvic cavity is below the pelvic brim, within the confines of the pelvic skeleton. It is continuous with the abdominal cavity above = the abdominal and pelvic cavities communicate via the […]
Lab 00, Station 1: Pelvic Skeleton and Ligaments

Lab 12 navigation Station 1: Pelvic Skeleton and Ligaments Complete anatomy Hip bone Pelvic Skeleton (Pelvic Girdle): Two Hip Bones + Sacrum Hip bone (coxal bone) = Composed of three fused bones: Ilium + Ischium + Pubis Features of pelvic skeleton as a whole: Greater sciatic notch Lesser sciatic notch Obturator foramen (covered by […]
Protected: Lab 23, Station 4: Oral Cavity and Pharynx—Sagittal View
There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.
Protected: Lab 23, Station 3: Nerves and Vessels Associated with the Oral Cavity

There is no excerpt because this is a protected post.