Posterior leg
Posterior compartment of the leg 7 muscles arranged in a superficial layer (darker green in Figure 27.1) and deep layer (yellow in Figure 27.1) Superficial muscles: powerful plantar flexors because they support and move body weight All muscles in the posterior leg are innervated by the tibial nerve and supplied with blood by the posterior […]
Anterior and lateral leg: Ankle joint
Bones and fascia The deep fascia of the thigh (fascia lata) continues on to the leg, forming a dense, snug-fitting layer called the crural fascia The crural fascia, intermuscular septa, bones of the leg,and interosseous membrane separate the leg into anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments Figure 26.1 Clinical correlation: Compartment syndrome The deep fascia in […]
Lab 15: Anterior and Lateral Leg, Knee and Ankle Joints, and Dorsum of Foot
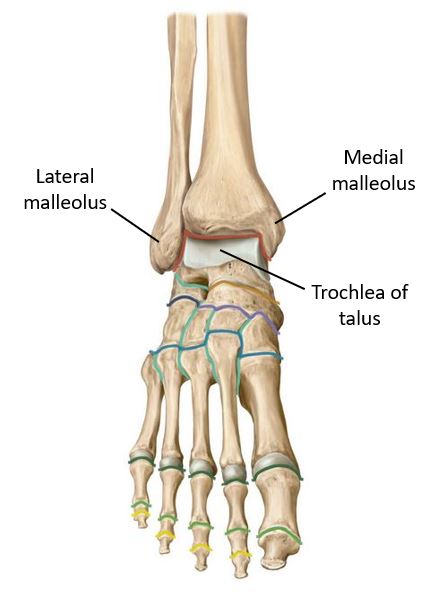
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Identify bony features associated with the knee, leg, and ankle. Identify the muscles in the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg and discuss their actions, innervations, and blood supply. Identify the muscles, nerves, and vessels on the dorsum of the foot. Identify the bones, ligaments, and cartilages […]
Lab 14: Gluteal Region, Posterior Thigh, and Popliteal Fossa
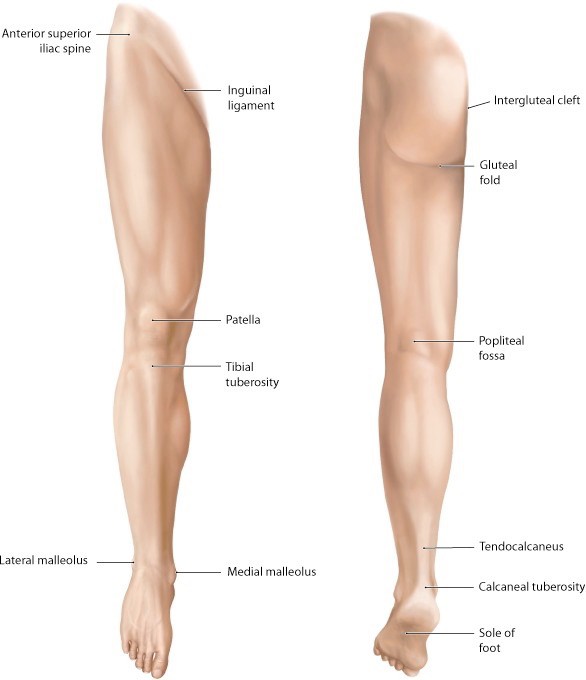
Download this lab as a PDF (Updated 28 October 2024, 8:42 a.m.) Goals Clean and identify the muscles, nerves, and vessels of the gluteal region. Identify the greater sciatic foramen and the structures that traverse it. Clean and identify the muscles, nerve, and vessels of the posterior compartment of the thigh. Identify the boundaries and […]
The knee joint
The knee is a modified hinge joint There are three articulations within the knee joint complex: Lateral and medial tibiofemoral and patellofemoral joints Movements can occur along two axes: The primary movements are flexion and extension Because the radii and lengths of the articular surfaces of the femur and tibia differ, there is a small […]
Gluteal region, posterior thigh, and popliteal fossa
Pertinent osteology Please review the anatomy of the acetabulum, posterior hip bone, sciatic notches, and femur. Figure 24.1 Osteology of the os coxae. Figure 24.2 Sciatic foramina. Figure 24.3 Osteology of the femur. Gluteal region Physically, the gluteal region is part of the trunk, but functionally, it is clearly part of the limb. The gluteal […]
The hip joint
Figure 23.1 The hip joint is the articulation between the round femoral head and the concave acetabulum (“little vinegar cup”). The lunate surface is the articular surface of the acetabulum, forming an arc that fills ¾ of the acetabular cup. It is covered with articular cartilage. The acetabulum is deepened by the acetabular labrum, a […]
Lab 13: Anterior and Medial Compartments of Thigh; Hip Joint
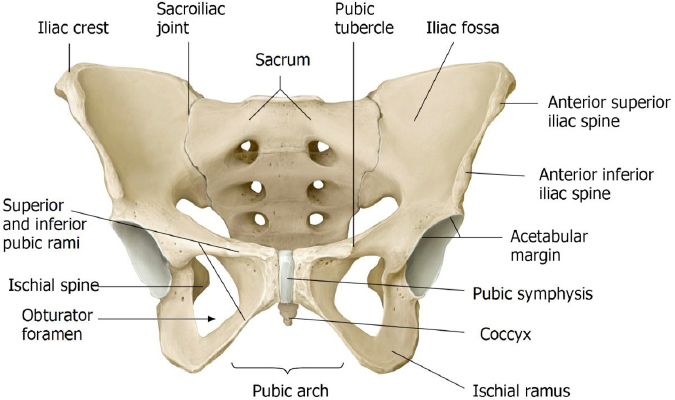
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Identify the parts of the hip bones, femur, patella, and tibia that are associated with the anterior and medial thigh. Identify the femoral triangle, its boundaries, and contents, including the structures passing through the subinguinal space. Identify the adductor canal and its contents. Identify the muscles, nerves, and […]
Lab 25: Infracolic Region
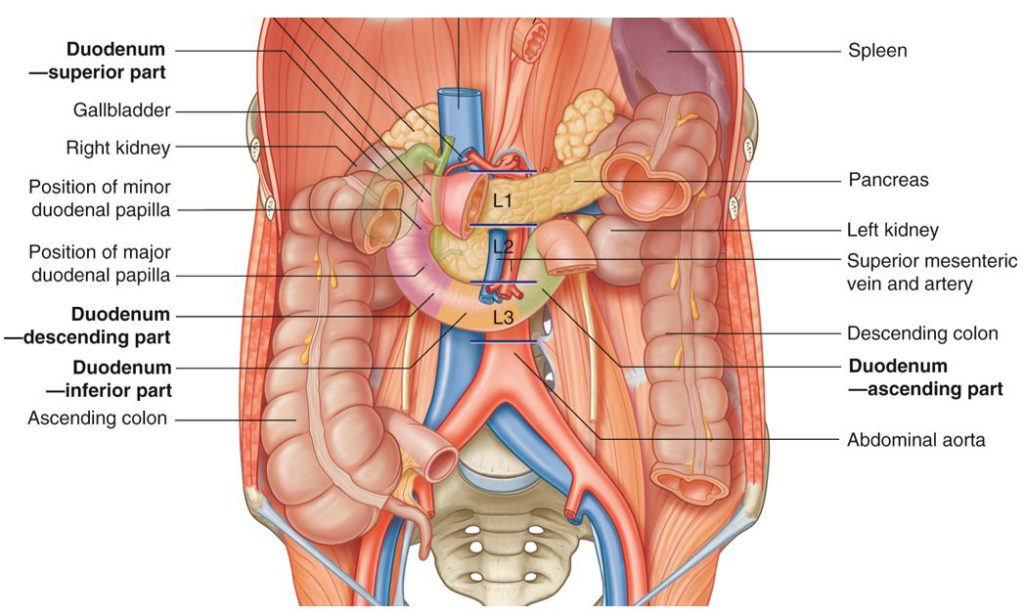
Download this lab as a PDF Goals Identify the parts of the small and large intestines. Dissect the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries and their branches. Identify the hepatic portal vein and its major tributaries. Open the jejunum, ileum, and cecum to view their internal features. Before you cut: Review the parts of the Small […]
Anterior and medial compartments of the thigh
Optional Reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 8th ed., Anterior and medial regions of thigh section through Surface anatomy of anterior and medial regions of thigh. Compartmentalization of the thigh The deep fascia, intermuscular septa, and femur together define anterior and posterior compartments in the thigh. The anterior compartment contains muscles that flex the hip and extend […]