Labs
Cultures
Cytology
- Results
- Additional information
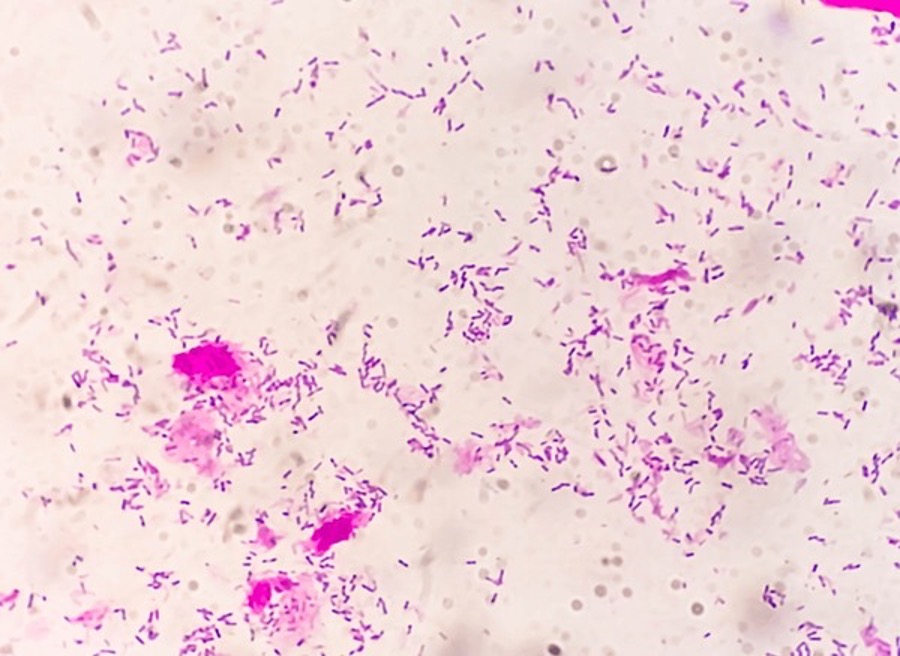
Moderate afb.
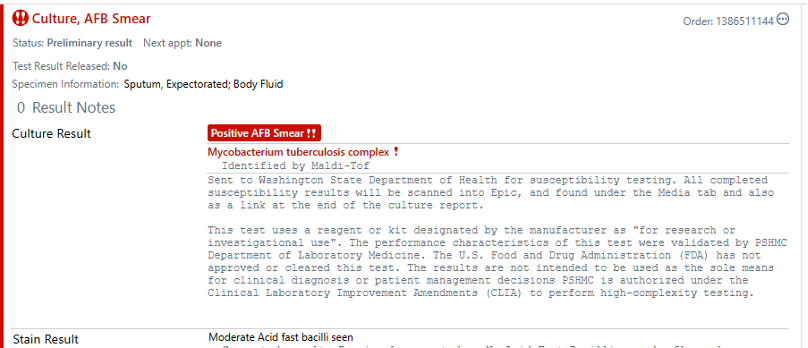
- NAAT positive for M. tb complex.
- GenExpert negative for rifampin resistance.
- Subsequent smears are same results,
- All should be sent for culture.
Two days after admission
Ray has been in the hospital for two days. In an abundance of caution, given his H&P and findings on the chest CT, Ray is empirically placed on RIPE (rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol). A chest tube is placed to drain the empyema. Although it is uncomfortable, Ray finds breathing easier. The first sputum results return, and you are called by the ID consultant to look at the slides.
Your differential
With TB on your differential now confirmed, you review DOH’s Notifiable Conditions, which requires communication within 24 hours. You notify the Yakima Health Department TB nurse.
She thanks you for contacting her and tells you she will review the hospitalization notes. Unfortunately, her local health officer does not treat tuberculosis. She will need you, in consultation with the ID doctors, to continue treating Ray when he is discharged.
Think about this
Discuss in the Slack channel.
Based on your understanding of tuberculosis, and given Ray’s history (see Background), who would you consider for this contact tracing? Why?
Over the past week
-
Temperature
Ray has occasional fevers (high 102.1°F), but gradual improvement is noted.
-
Lungs
After drainage of the empyema, Ray finds it easier to breathe.
-
X-ray
CXRs are performed daily, but no significant changes are noted.
-
Chest tube
The chest tube is removed on Day 5 of hospitalization.
-
Discharge
- You offer to see Ray in your continuity of care clinic because the local health officer does not treat tuberculosis. Per the Washington state statutes, regulations, and reporting, the health officer will need to be made aware of his treatment.
think about this
What does TB contact tracing entail? Given what you know of Ray’s background who would be of greatest concern? Why? Share your answer in the Slack channel.
After being discharged

You are now doing your primary care rotation with your preceptor, Dr. Williams, at the Yakima Valley Farm Workers’ Clinic. Ray follows up with you and Dr. Williams three weeks after his hospital discharge. He tells you (through the interpreter) that he is feeling much better—cough is less, and he is less tired. Your evaluation finds he has gained four pounds since his discharge. The chest tube scar looks good, but Ray’s examination worries you because there are no significant changes in what you hear when you listen to his lungs.
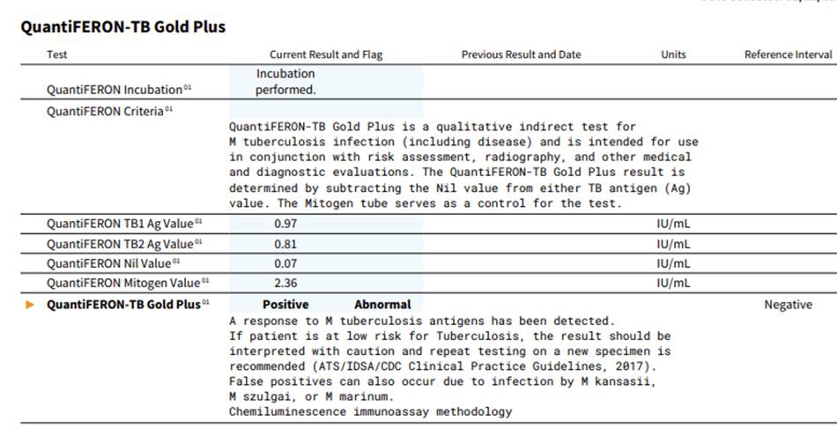
Dr. Williams reassures you that this is not unusual, especially given the severity of Ray’s disease. In your review of labs that have returned after he was discharged, his diagnosis of M. Tb has been confirmed with culture results that came back positive a few days ago. Drug-susceptibility testing determines his TB is sensitive to all medications.
think about this
If AST/ALT tests during Ray's hospitalization were normal, and he has no symptoms to suggest hepatotoxicity (refer to IDSA guidelines 2016 Figure 2), write what studies are indicated today in the Slack channel.
think about this
In the Slack channel, discuss how you would explain the course of treatment to Ray.
think about this
In the Slack channel, share your thoughts on what other considerations you should discuss with Ray.
Clinical correlation
You thank Ray for the opportunity of caring for him, both in the hospital and in the clinic, and reassure him TB can be treated with medications. You let him know the health department TB nurse will be providing his treatment, and as you are on a four-week rotation, he will be seen by Dr. Williams in the Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) along with other medical students on their rotations. Ray will be able to continue to work in the orchards.
Public Health correlation
Access to care and healthcare utilization
- What barriers to accessing timely, continuous, and appropriate healthcare did Ray face?
Economic instability and health
- What are the trade-offs Ray faced between earning income and seeking healthcare?
- How does income insecurity affect treatment adherence and follow-up?
- What public health or social safety net programs could help mitigate these conflicts?
Resource: TB101 for Health Care Workers. CDC.
Image credits
Unless otherwise noted, images are from Adobe Stock.