These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Worksheet 1
Complete the basic measurements, diagnose RVH if the QRS direction is either rightward, anterior, or both, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| SI/QT III pattern |
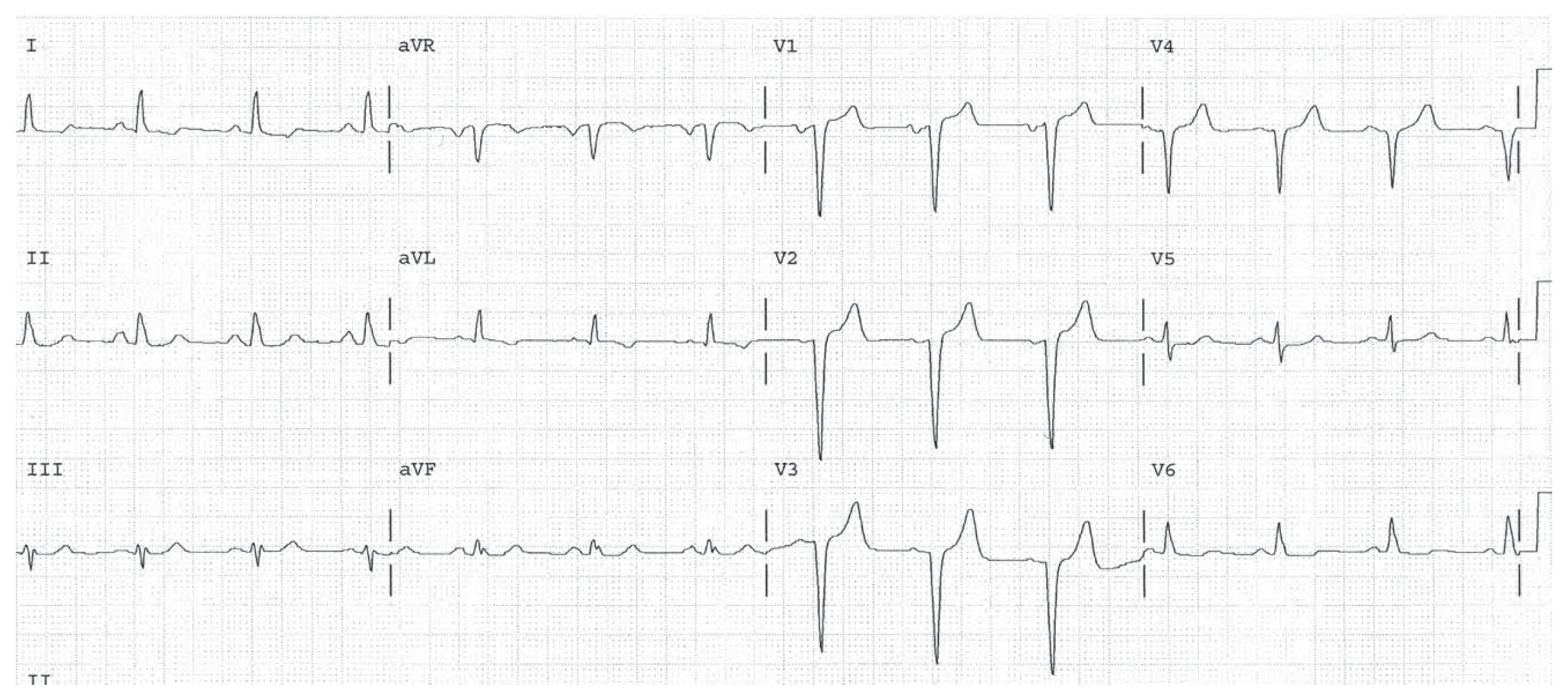
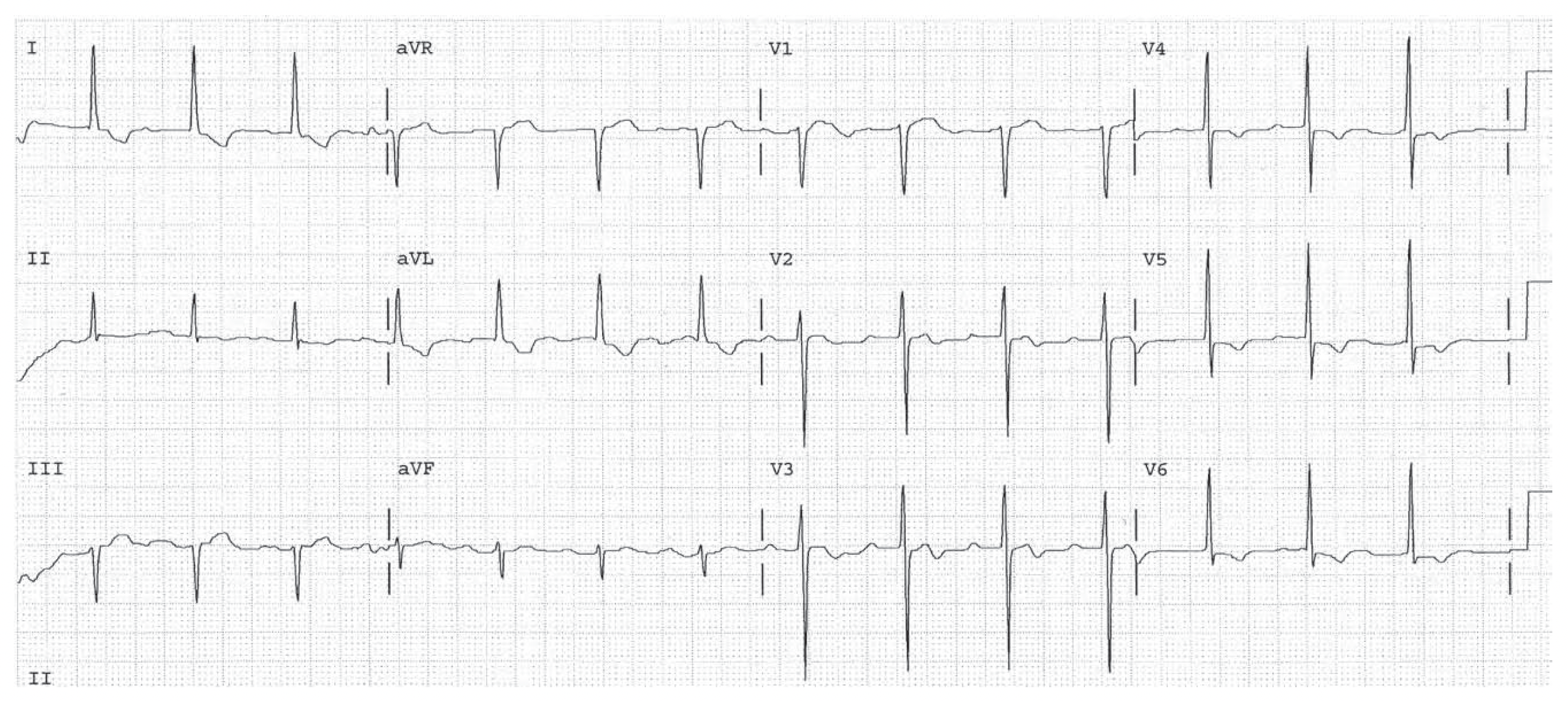
HR 75, sinus. PR normal. QRS 0.09, normal. Normal P and QRS direction. Q waves in leads V1 through V4 consistent with Q wave infarction, possibly old. There is a left atrial abnormality. The QRS voltage is high possibly representing LVH. There are nonspecific ST changes diffusely. (Check with straight edge.)
Worksheet 2
Complete the basic measurements, diagnose RVH if the QRS direction is either rightward, anterior, or both, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| SI/QT III pattern |
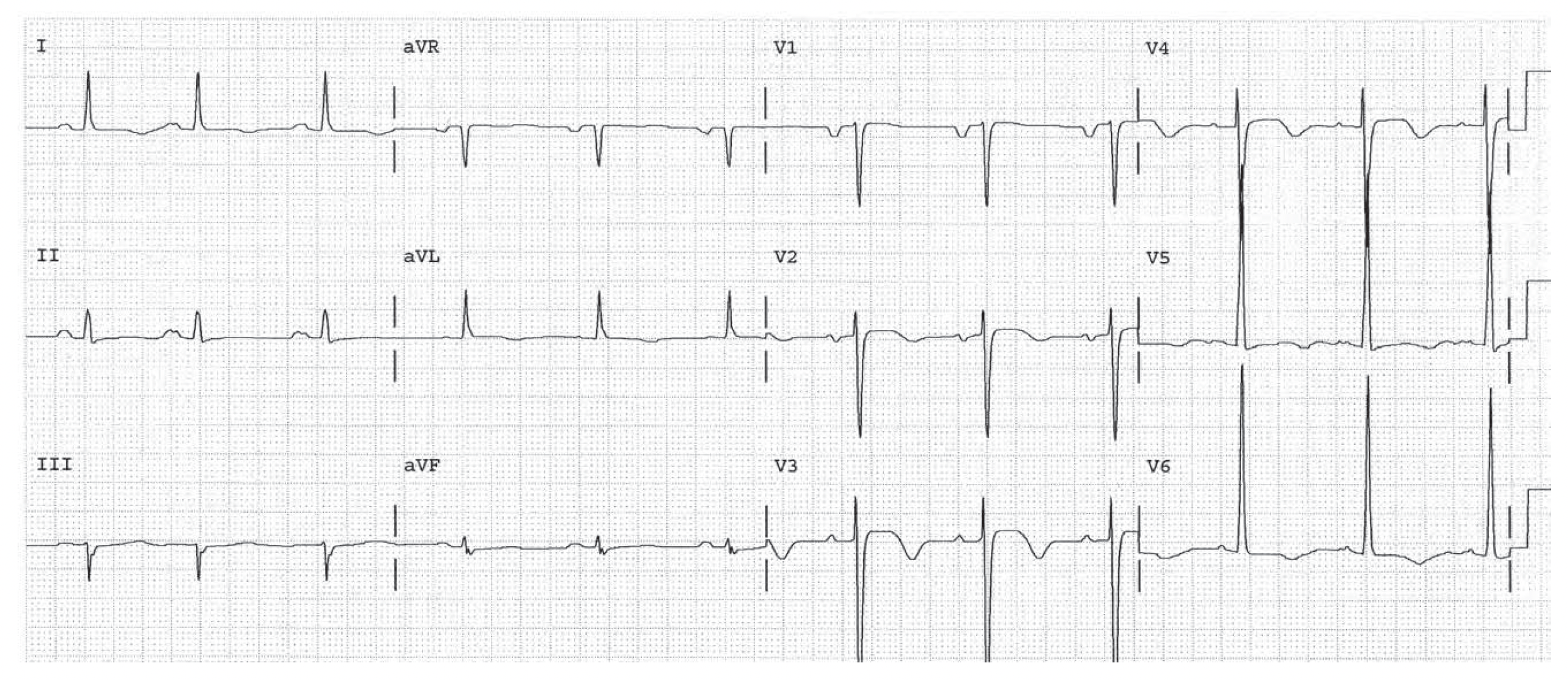
Sinus arrhythmia. Left atrial abnormality. LVH. Diffuse ST segment changes consistent with LVH or ischemia or infarction. ST elevation in V3 and V4 takes precedence (Third Rule of the T Waves).
Worksheet 3
Complete the basic measurements, diagnose RVH if the QRS direction is either rightward, anterior, or both, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| SI/QT III pattern |
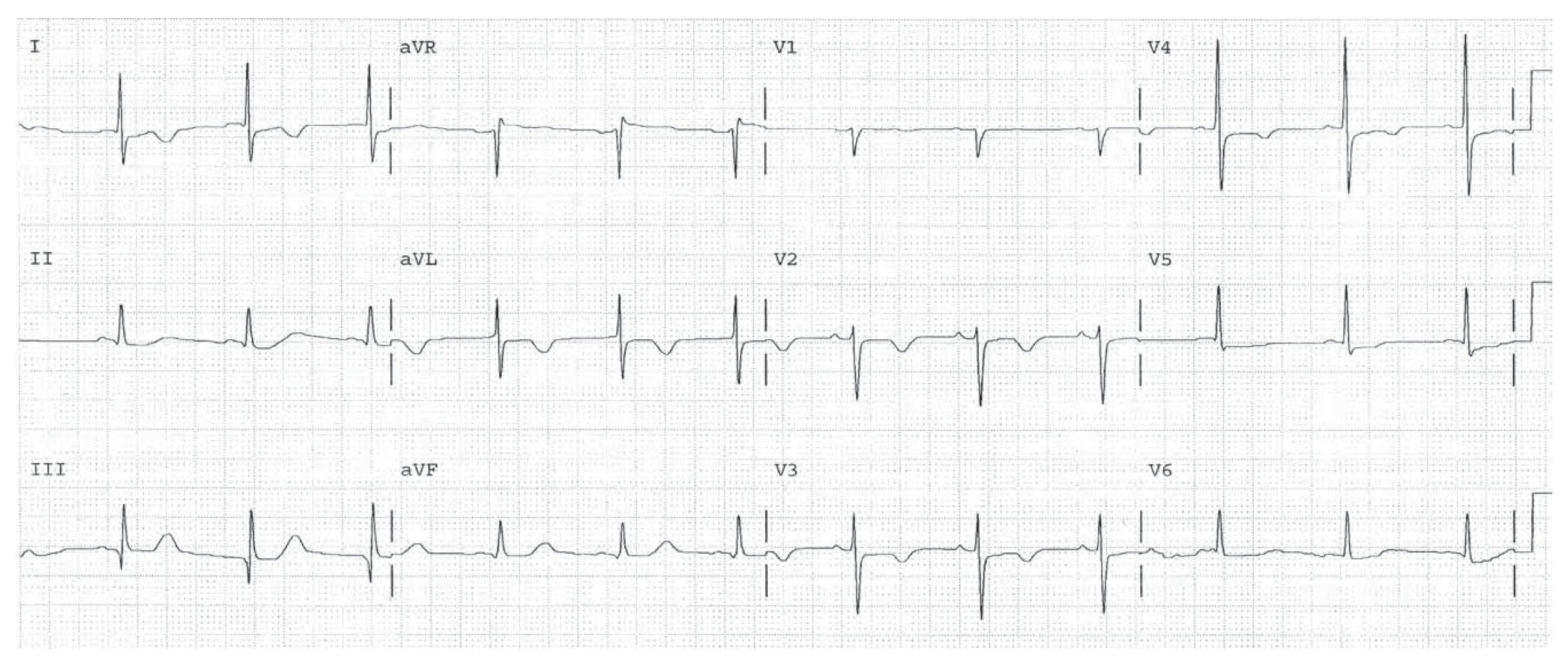
Sinus rhythm at 71. SI Q III pattern suggests possibility of pulmonary embolism. Anterior T wave changes consistent with septal ischemia or infarction (First Rule of the T Waves), or acute pulmonary hypertension. The high QRS voltage in V3 and V4 may represent LVH as well.
Worksheet 4
Complete the basic measurements, diagnose RVH if the QRS direction is either rightward, anterior, or both, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| SI/QT III pattern |
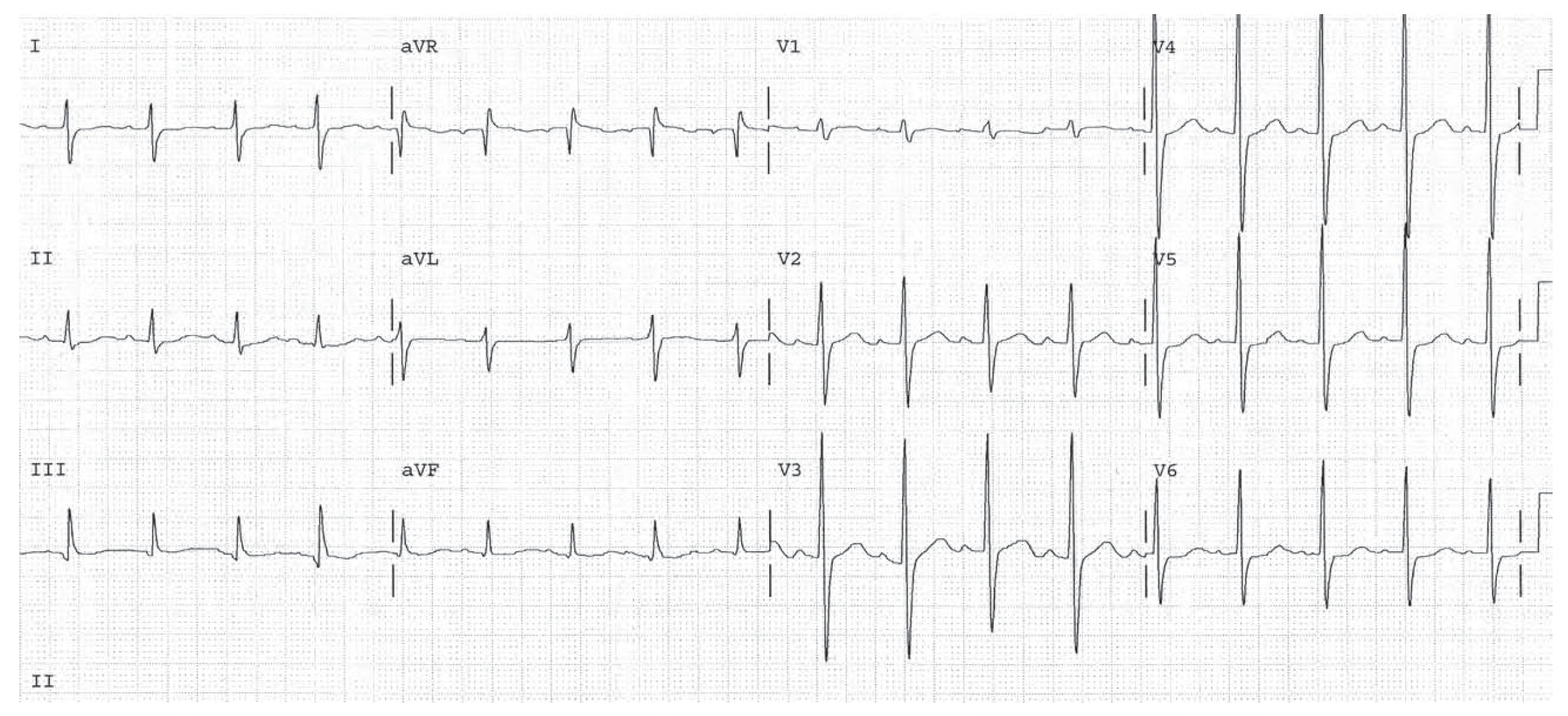
Sinus tachycardia. HR 107. The QRS direction is rightward in lead I indicating RVH or LPHB. The QRS direction is anterior in V1 also indicating RVH. There are also voltage criteria for LVH. Leads V3 and V4 have tall R and S waves, which also suggest biventricular hypertrophy.
Worksheet 5
Complete the basic measurements, diagnose RVH if the QRS direction is either rightward, anterior, or both, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| SI/QT III pattern |
HR 88. Baseline artifact is present, but the rhythm is sinus. The PR interval is long, 1°AV Block. LVH with ST changes consistent with LVH ischemia or infarction.