These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Worksheet 1
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose clinical condition, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
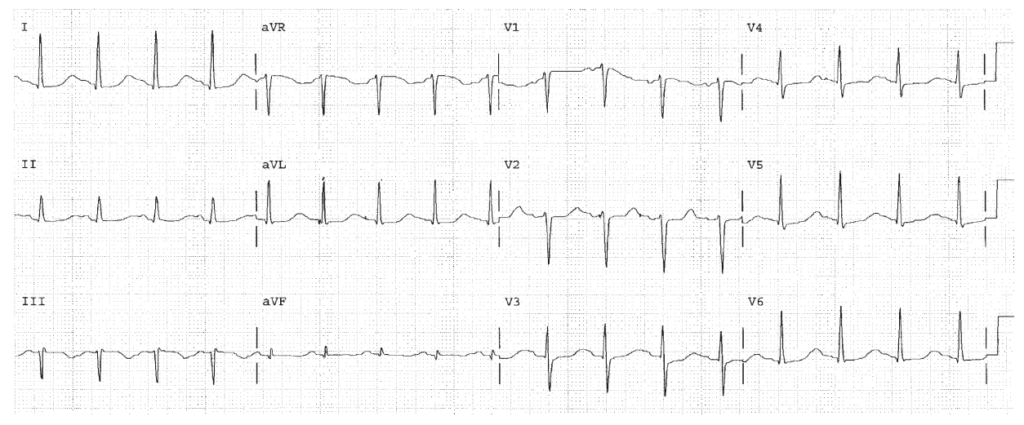
HR 100, sinus rhythm. QT 0.44. The QTc is 0.57 which is dangerously long. Drug and electrolyte abnormalities must be identified immediately and corrected. Diffuse ST changes present (First Rule of the T Waves also applies).
Worksheet 2
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose clinical condition, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
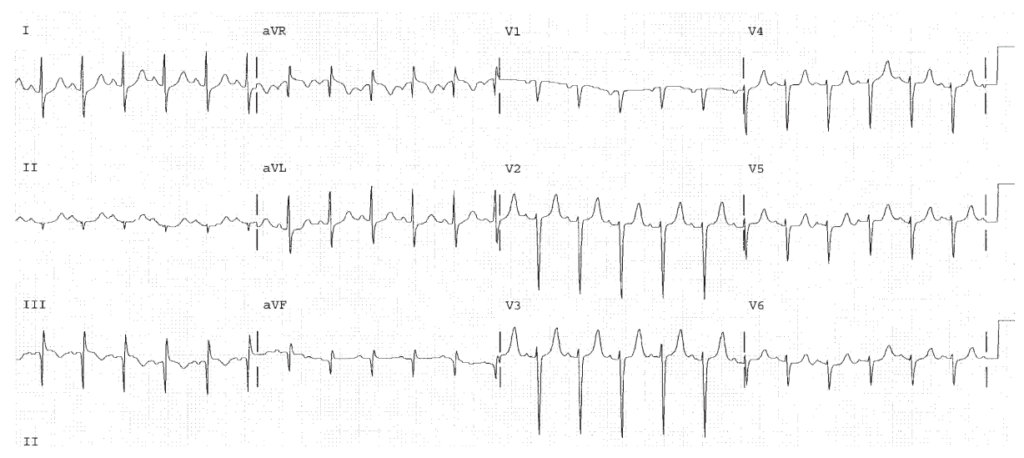
Sinus tachycardia. RVH. Inferior Q waves. SI QT III pattern. Acute pulmonary embolism should be ruled out. Peaked T waves, rule out hyperkalemia.
Worksheet 3
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose clinical condition, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
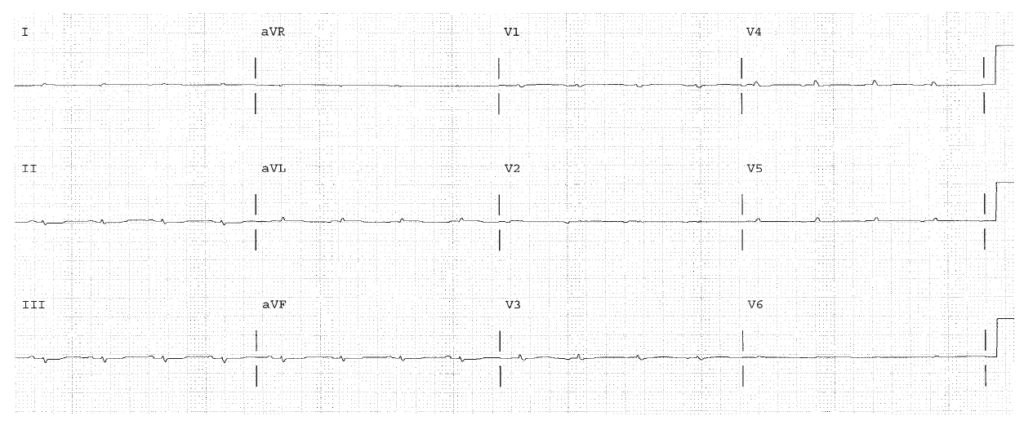
Low voltage. There is dramatic reduction of voltage. Pneumothorax, COPD, pericardial effusion, pleural effusion, should be considered. This patient had infiltrative cardiomyopathy.
Worksheet 4
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose clinical condition, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
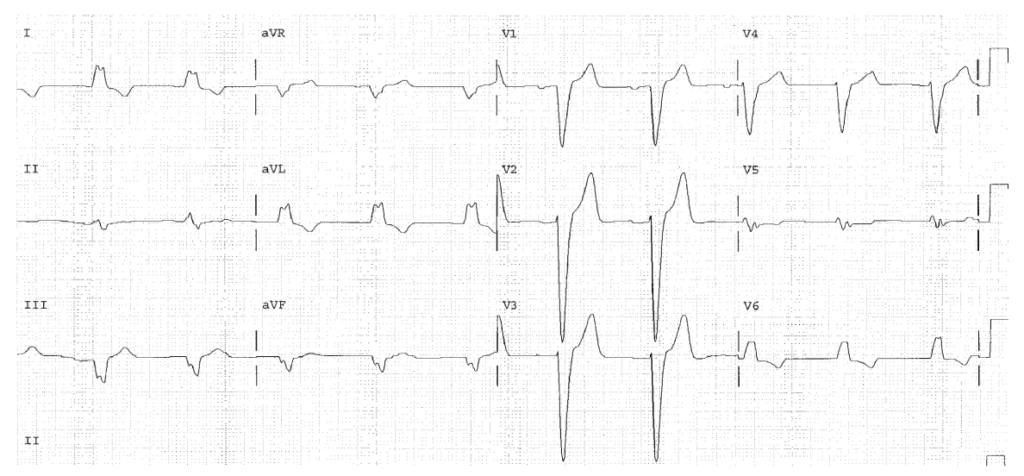
Peaked T waves in V2 and V3. Hyperkalemia.
Worksheet 5
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose clinical condition, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
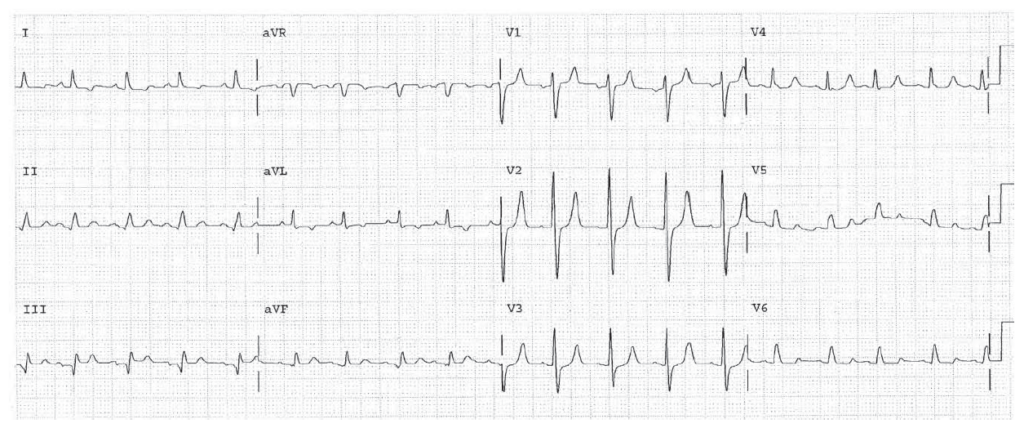
LBBB with a very wide QRS. This combination suggests additional conduction depression from drug or electrolyte effect.