These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Instructions for Chapter 20 Worksheets
- Make basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy.
- Diagnose clinical conditions based on criteria described in Chapter 20.
- Evaluate clinically.
Clinically-Based Critical Thinking: Interpretation
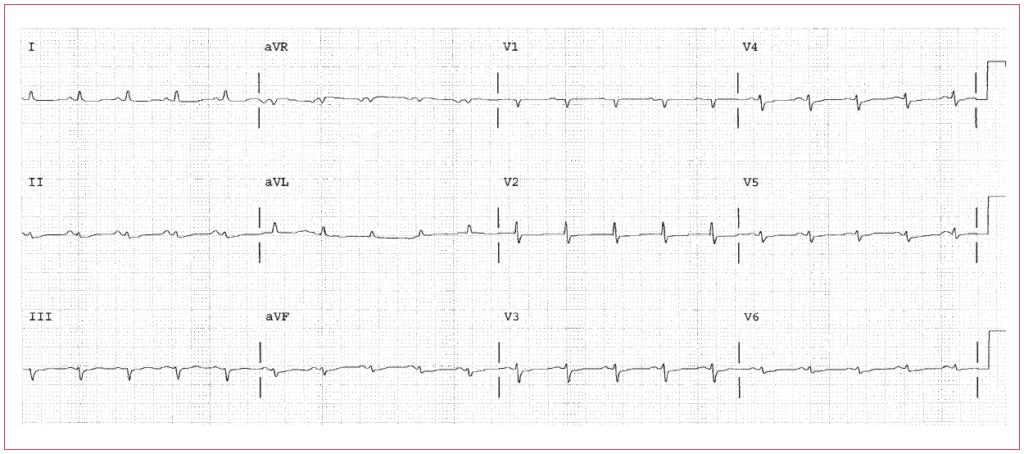
There is sinus tachycardia associated with low voltage. Possibilities include COPD (with sinus tachycardia due to hypoxia or sympathomimetic therapy), or a large pericardial effusion, or tamponade. The presence on an anterior QRS is consistent with pulmonary hypertension. The low amplitude affects the T waves and P waves as well.
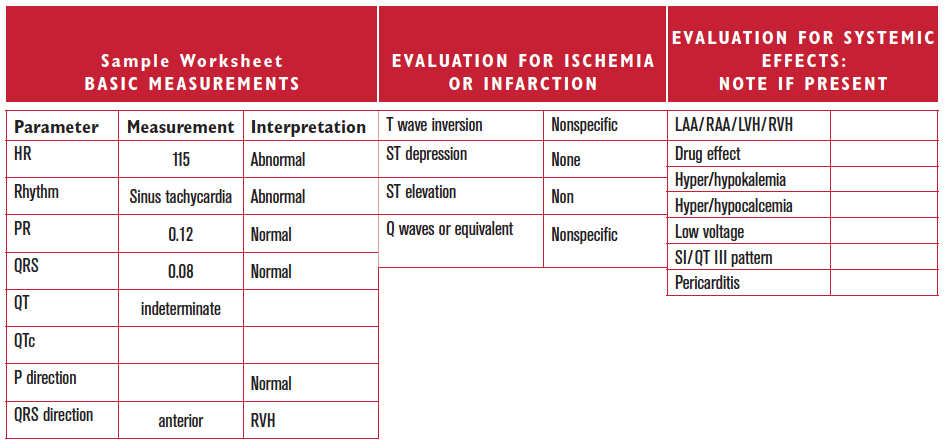
Worksheet 20.1
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose clinical condition, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
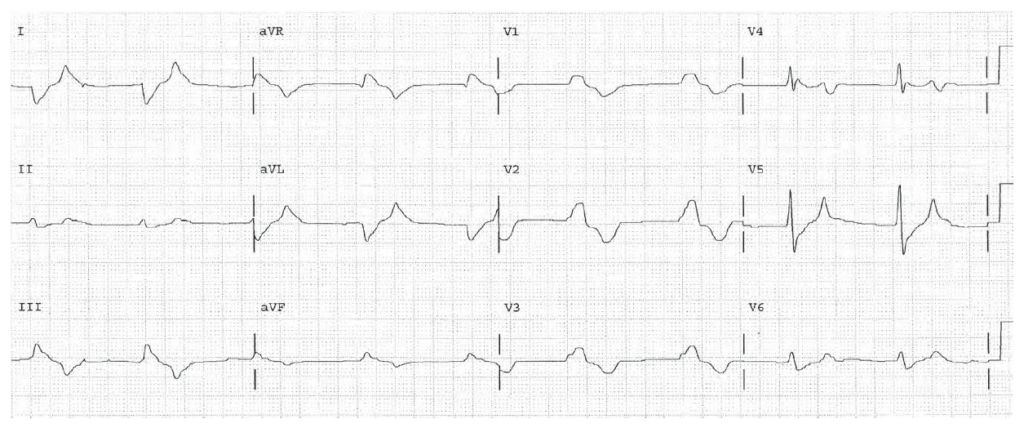
Diffuse wide QRS in sine wave pattern. Hyperkalemia.
Worksheet 20.2
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose clinical condition, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
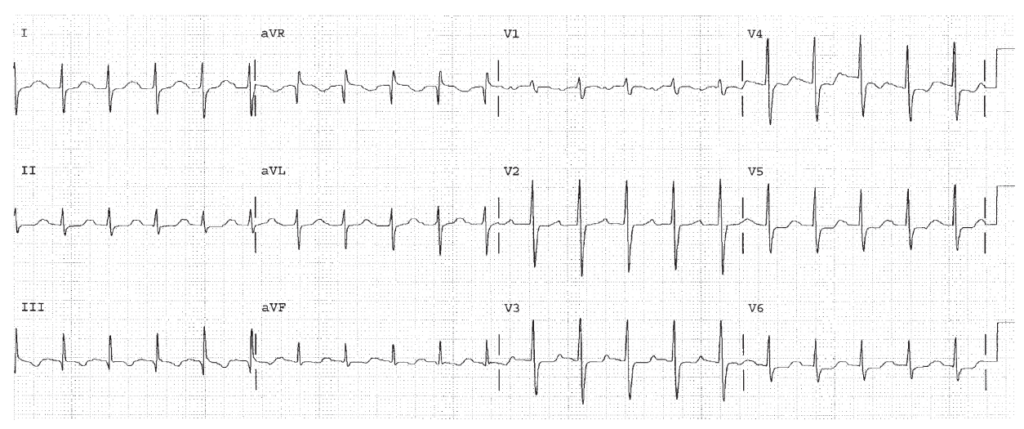
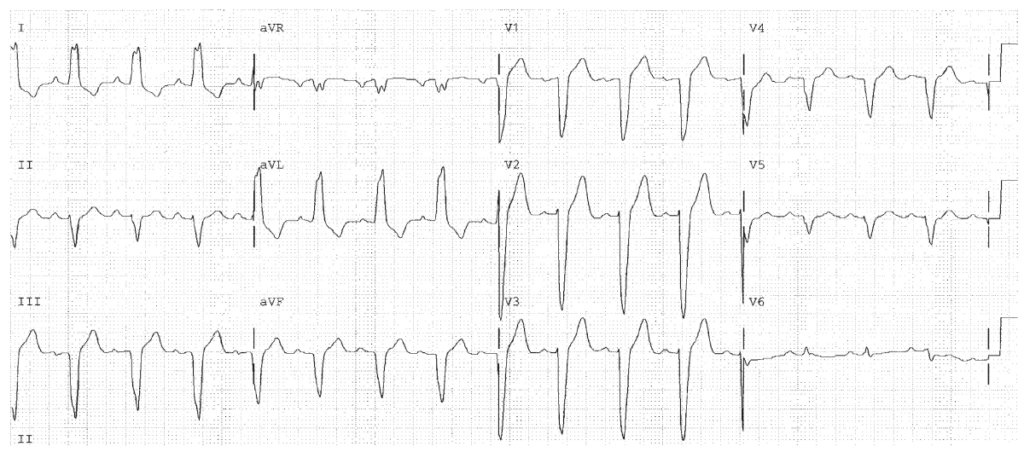
Sinus Tachycardia. RVH. SI QT III pattern. Rule out pulmonary embolism. Diffuse ST segment depression, so First Rule of the T waves also applies.
Worksheet 20.3
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose clinical condition, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
LBBB.