These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Instructions for Chapter 19 Worksheets
- Make basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia and infarction, evaluate for hypertrophy.
- Diagnose drug and electrolyte abnormalities as appropriate based on the heart rate, QRS, QTc, and ST segments.
- Evaluate clinically.
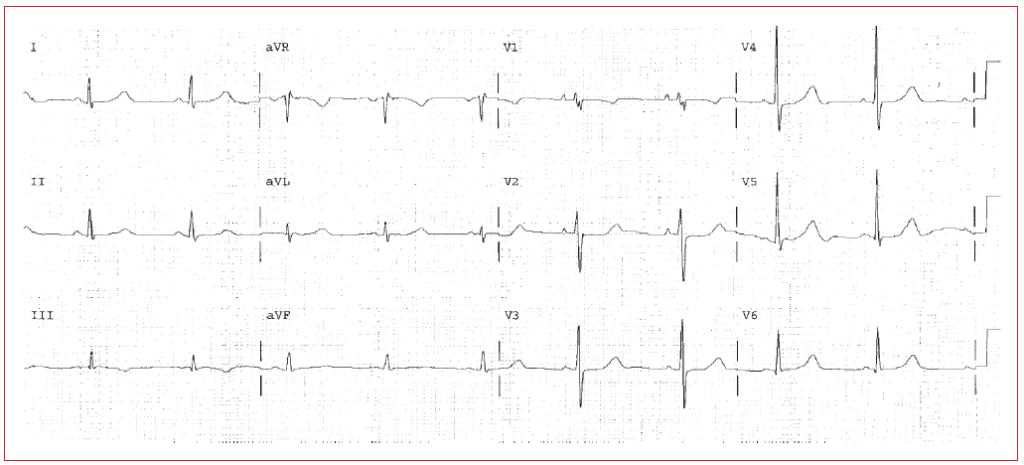
Clinically-Based Critical Thinking: Interpretation
Sinus bradycardia is present. There is an abnormally long QTc. This suggests a drug toxicity or electrolyte abnormality. Antiarrhythmic therapy, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and so on, should be considered and ruled out as causes. The offending agent should be removed if at all possible.
Worksheet 19.1
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose drug and electrolyte abnormalities, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
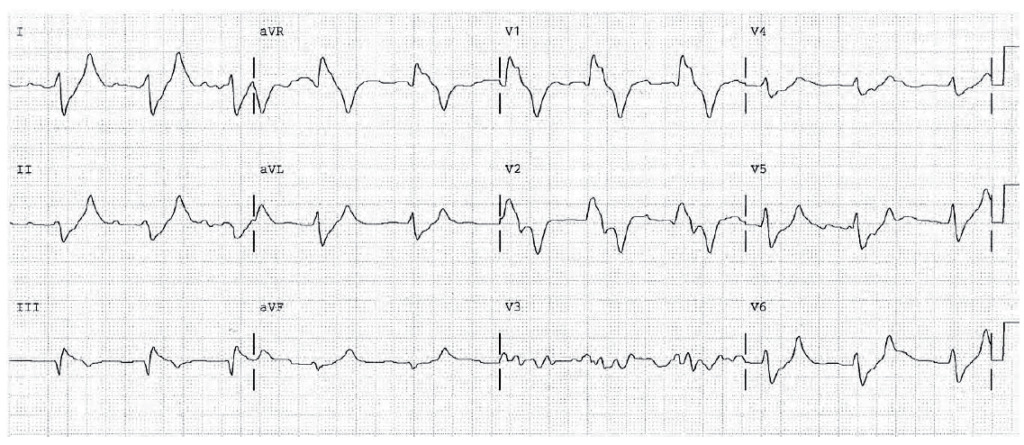
Atrial fibrillation. Low voltage. Low amplitude T waves. QT 0.44 QTc high. Diffuse nonspecific ST changes. Suggestive of hypokalemia. Serum potassium was 2.3 mEq/L.
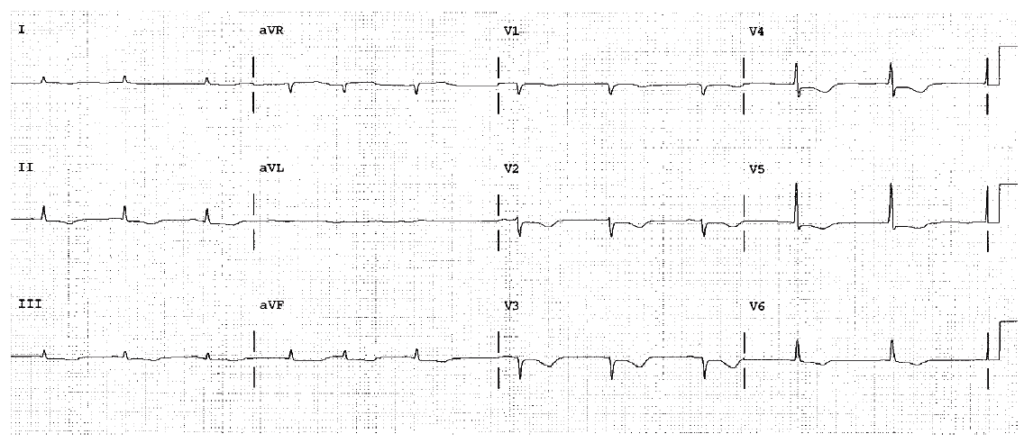
Worksheet 19.2
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose drug and electrolyte abnormalities, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
HR 65. QT 0.50. The QTc is 0.52 and dangerously long. Diffuse ST segment changes, possibly secondary to drug or electrolyte effects. Hypokalemia and hypocalcemia should be ruled out immediately. The cause, drug or electrolyte should be identified and corrected.
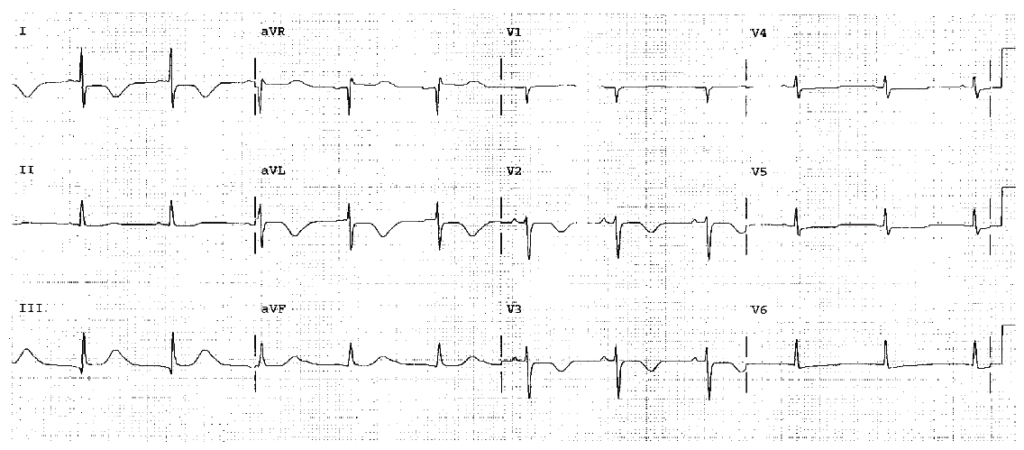
Worksheet 19.3
Complete the basic measurements, evaluate for ischemia, infarction, and hypertrophy, diagnose drug and electrolyte abnormalities, and evaluate clinically.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
| Systemic effects | If present, note |
| LAA/RAA/LVH/RVH | |
| Drug effect | |
| Hyper/hypokalemia | |
| Hyper/hypocalcemia | |
| Low voltage | |
| SI/QT III pattern | |
| Pericarditis |
Hyperkalemia. Sine wave pattern. Diagnostic and requires immediate therapy to lower the serum potassium level.