Case 1: Hyperkalemia progression and reversal
Figure 19.6b demonstrates very wide QRS complexes that measure 0.20 seconds. This is not a typical bundle branch block because it is so wide. The T wave is tall wide and bizarre as well. Any QRS of 0.20 seconds suggests hyperkalemia until it is ruled out.
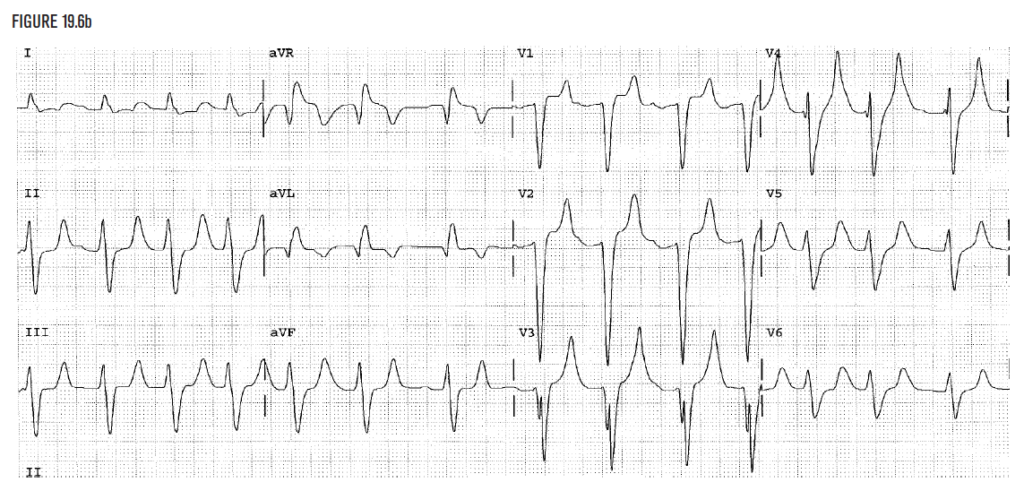
Figure 19.6c was taken in the same patient as Figure 19.6b, but it was taken when the potassium level later rose to 9.8 mEq/L. The wide QRS complexes at the beginning of the strip may be confused with ventricular flutter, but the clear wide QRS complexes in V4 and V5 confirm the presence of hyperkalemia as the diagnosis. Recognition of Figure 19.6b as hyperkalemia can help prevent the occurrence of Figure 19.6c.
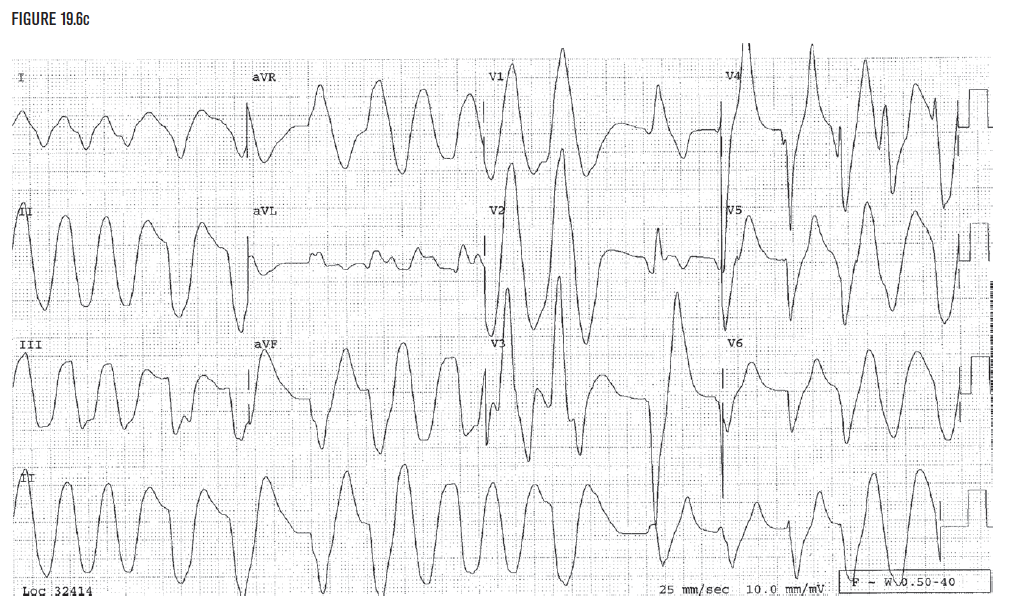
Figure 19.6d demonstrates the normalization of the EKG to baseline for this patient after correction of the potassium level. The QRS now measures 0.11 seconds.
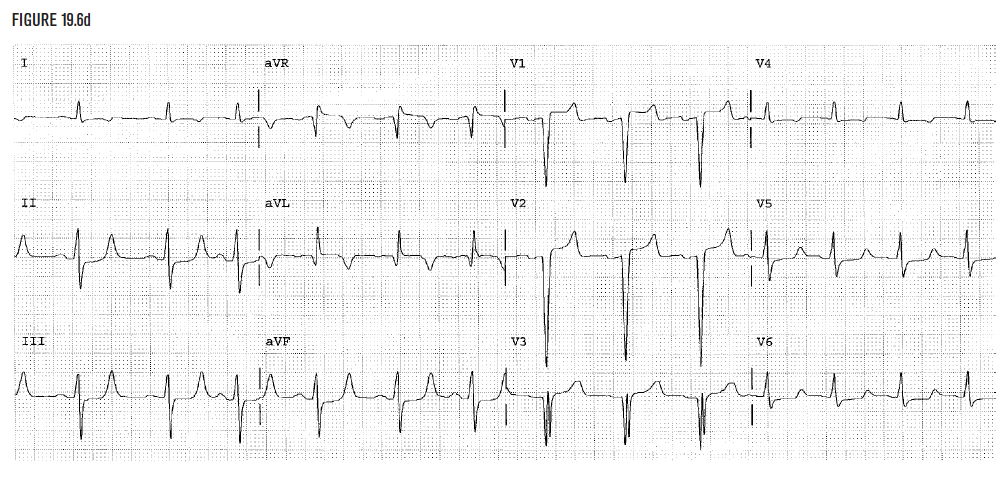
Image credits
Unless otherwise noted, images are from Adobe Stock.


