These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Instructions for Chapter 5 Worksheets
- Complete basic measurements.
- Measure the PR, QRS, and QT intervals. Interpret the PR as normal, short, or long. Interpret the QRS as normal (0.09 seconds or less), IVCD (0.10 to 0.11), or BBB (0.12 seconds or more). Assess the QT interval against the HR/QTc chart to estimate normal, long, or short QTc.
- Provide an interpretation.
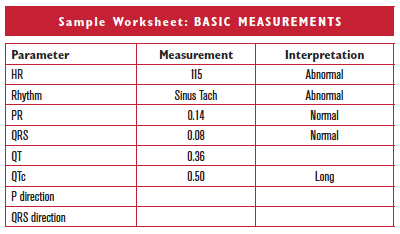
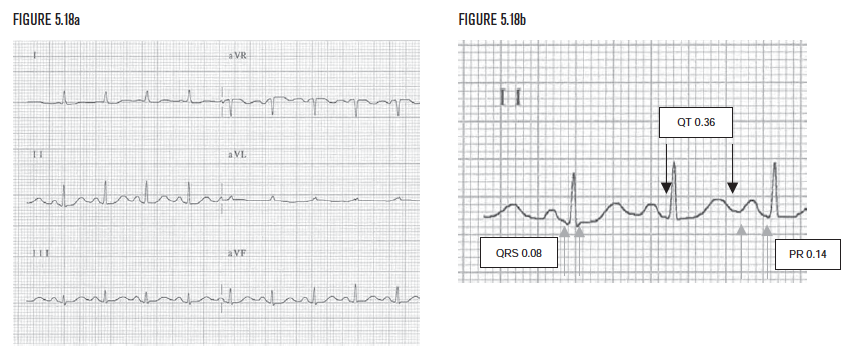
Clinically-Based Critical Thinking: Interpretation
Sinus tachycardia should always be evaluated and explained clinically. Long QTc is present and commonly due to drug toxicity or electrolyte abnormalities. Hypokalemia or hypocalcemia would be common causes and should be evaluated clinically. This patient’s K+ was 3.1. The combination of sinus tachycardia and long QTc suggests the possibility of hypovolemia and hypokalemia due to diuresis, or hypovolemia and hypocalcemia secondary to multiple transfusions.
Worksheet 5.1
Complete the basic measurements, measure the PR, QRS, and QT intervals, and provide an interpretation.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
The HR is 60. This is sinus rhythm. The PR interval is 0.18 to 0.20 seconds and is normal. The QRS interval is 0.10 seconds long, consistent with intraventricular conduction delay (IVCD). The QT interval is 0.40 seconds. The calculated QTc is 0.40, which is normal.
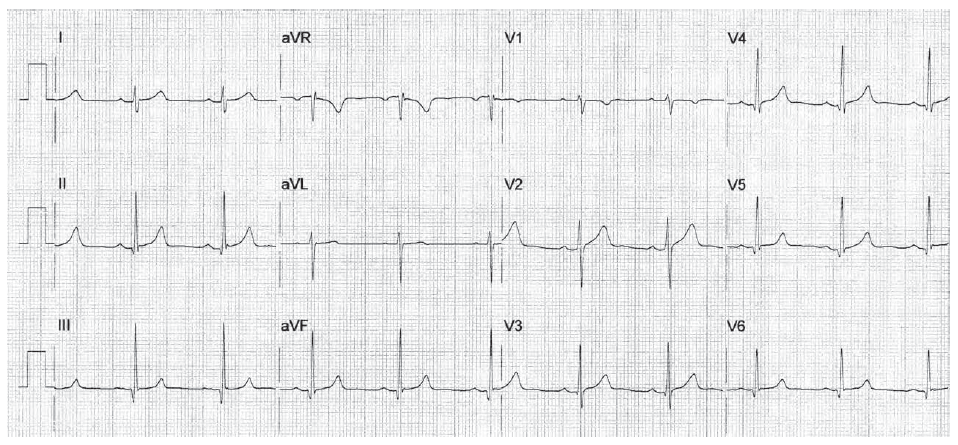
Worksheet 5.2
Complete the basic measurements, measure the PR, QRS, and QT intervals, and provide an interpretation.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
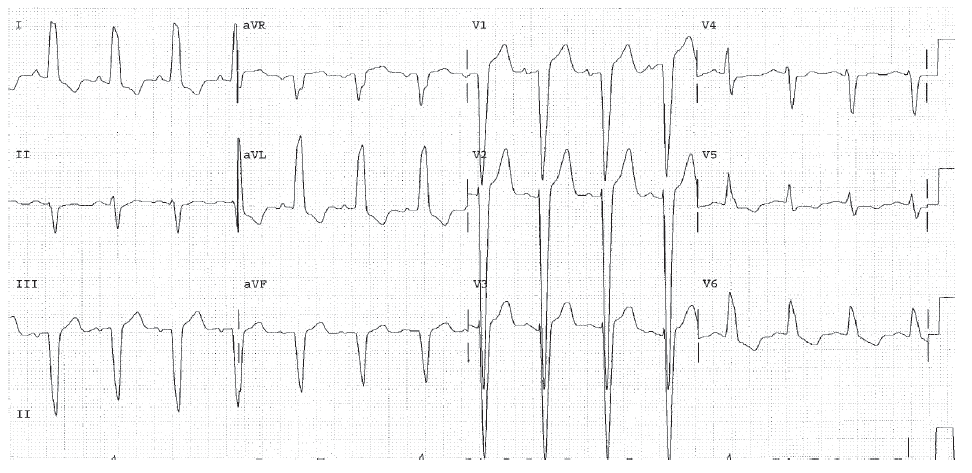
The HR is 71 bpm. This is sinus rhythm. The PR interval is 0.16 seconds and is normal. The QRS interval is 0.12 seconds (in leads I and AVL) and indicates bundle branch block. The QT interval is 0.40 seconds. The calculated QTc is 0.435 which is normal. The clinical significance of bundle branch block is discussed in Chapters 11 and Chapter 12.
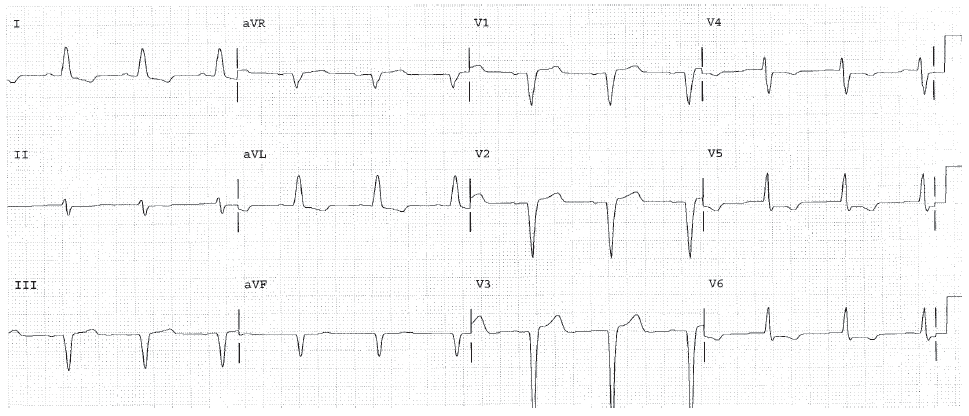
Worksheet 5.3
Complete the basic measurements, measure the PR, QRS, and QT intervals, and provide an interpretation.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
The HR is 88 bpm. The rhythm is sinus. The PR interval is 0.18 and is normal. The QRS interval is 0.14 seconds and is abnormal. This indicates bundle branch block. The QT interval is 0.40 seconds. The calculated QTc is 0.48, which is abnormal and long. Possibilities include drug effects such as sotalol, amiodarone, macrolide antibiotics, antifungal agents, and psychotropics, as well as hypokalemia and hypocalcemia.