These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Instructions for Chapter 4 Worksheets
- Count the number of small boxes between two QRS complexes. Divide that number into 1500 to accurately determine the HR.
- Use the HR to classify the rhythm as sinus rhythm (60 to 100), sinus tachycardia (greater than 100), or sinus bradycardia (less than 60).
- Provide an interpretation.
Clinically-Based Critical Thinking: Interpretation
Sinus tachycardia should always be evaluated and explained clinically. It is a vital sign, and always has clinical relevance. Relative predominance of the sympathetic nervous system or relative inhibition of the parasympathetic nervous system typically causes sinus tachycardia.
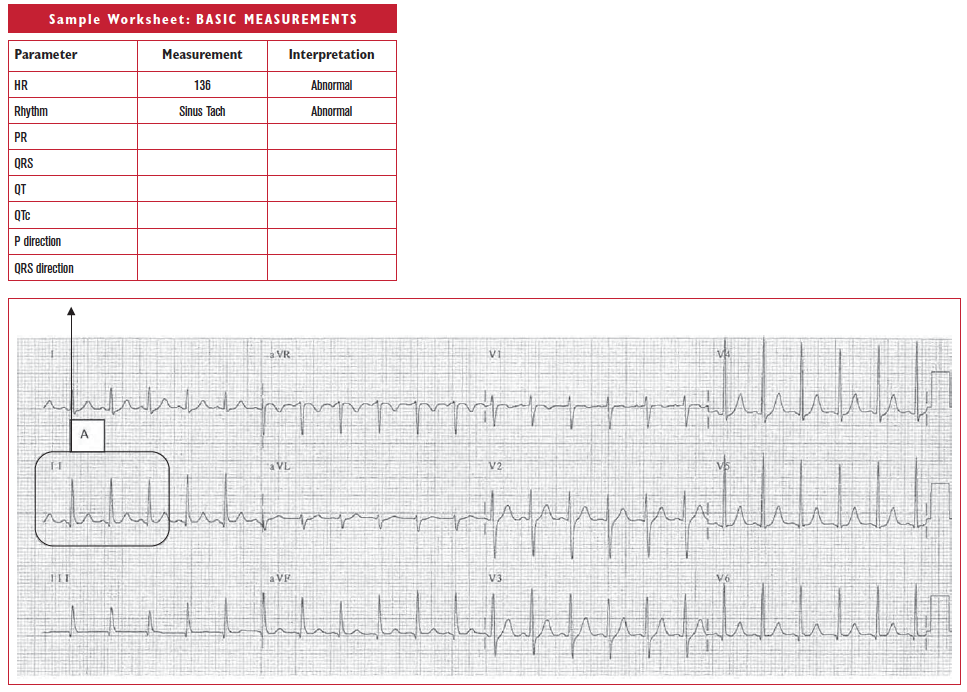
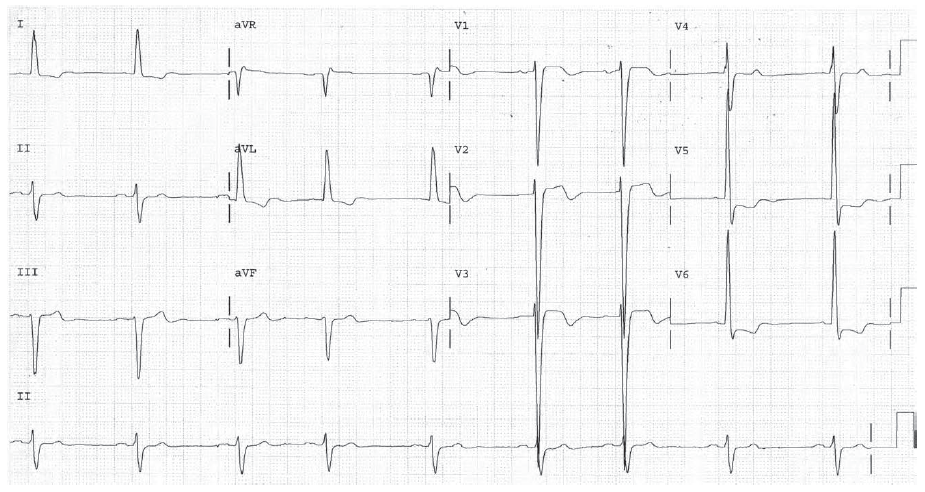
Worksheet 4.1
Complete the basic measurements, evaluation, and interpretation for the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
The HR is 83 bpm. The rhythm is sinus. Sinus rhythm indicates relative balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic effects on the heart.
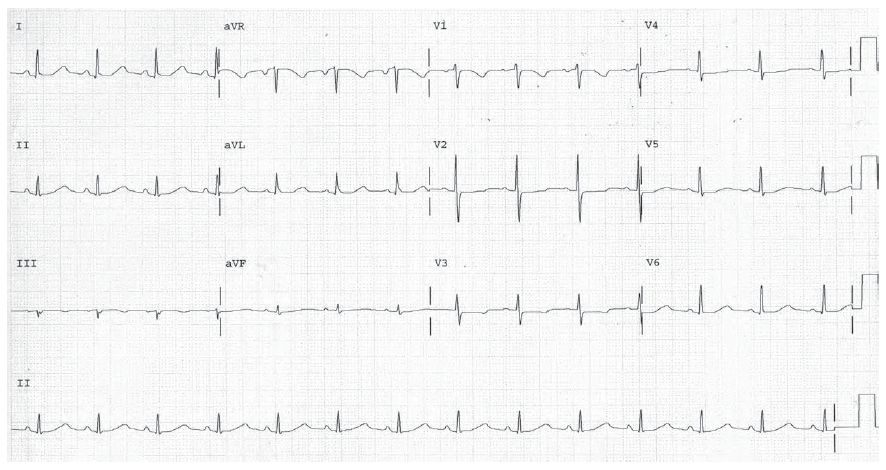
Worksheet 4.2
Complete the basic measurements, evaluation, and interpretation for the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
The HR is 125. The rhythm is sinus tachycardia. Sinus tachycardia indicates sympathetic predominance. Shock, heart failure, sepsis, hyperthyroidism, and hypovolemia should be considered.
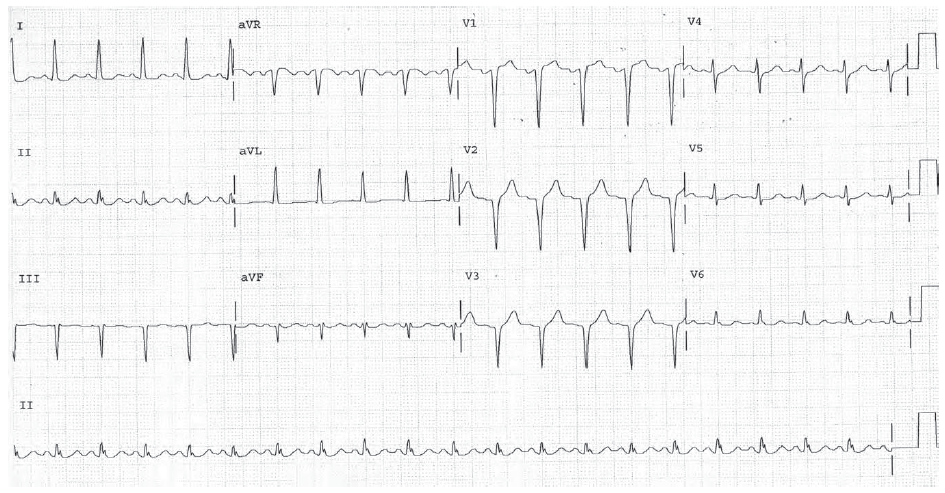
Worksheet 4.3
Complete the basic measurements, evaluation, and interpretation for the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
The HR is 50. The rhythm is sinus bradycardia. The fourth and seventh beats are nonspecific PACs. The presence of sinus bradycardia indicates relative inhibition of the sympathetic nervous system. Most commonly this is due to medications such as beta blockers.