These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Instructions for Chapter 10 Worksheets
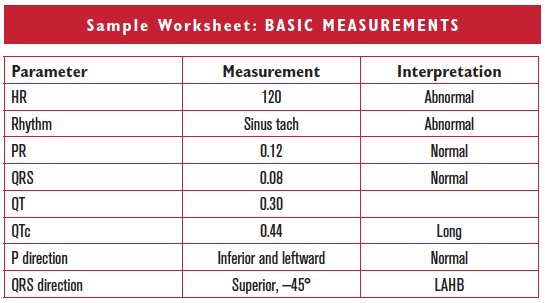
- Complete basic measurements.
- Describe (or calculate!) the QRS direction in the frontal plane as inferior and left, superior, or rightward.
- Clinically diagnose LAHB if the QRS direction is superior. Diagnose LPHB if the QRS direction is inferior and rightward.
Clinically-Based Critical Thinking: Interpretation
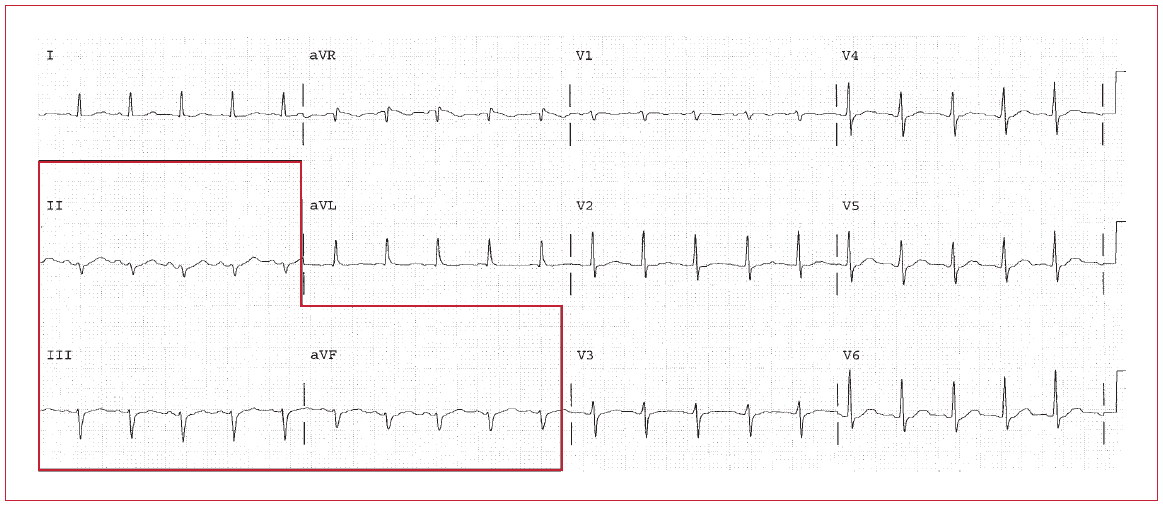
Left anterior hemiblock is present based on the QRS direction pointing superiorly. By itself, LAHB does not have any specific clinical associations other than the presence of conduction disease. Sinus tachycardia is present and should be explained.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
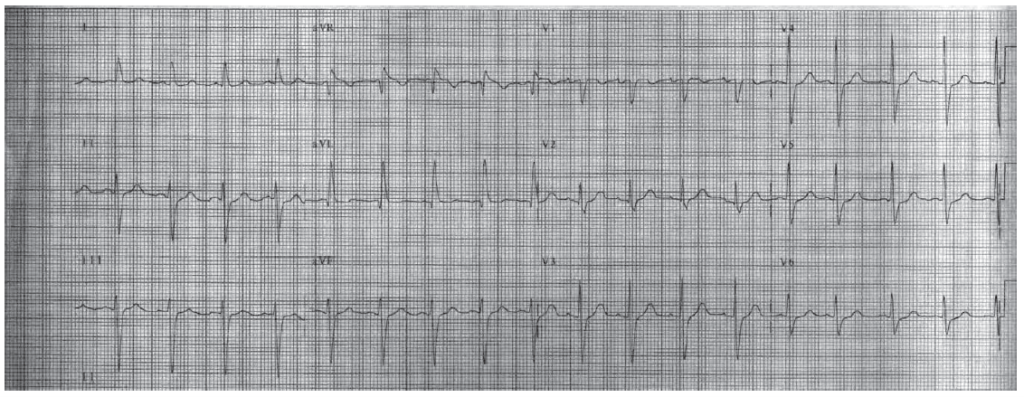
HR 65. Sinus rhythm. PR 0.12 to 0.14, normal. QRS 0.12, bundle branch block. The QT is 0.44. The P direction is normal. The QRS direction is upward at –45°, since it is negative in leads II, III, and AVF. This is LAHB.
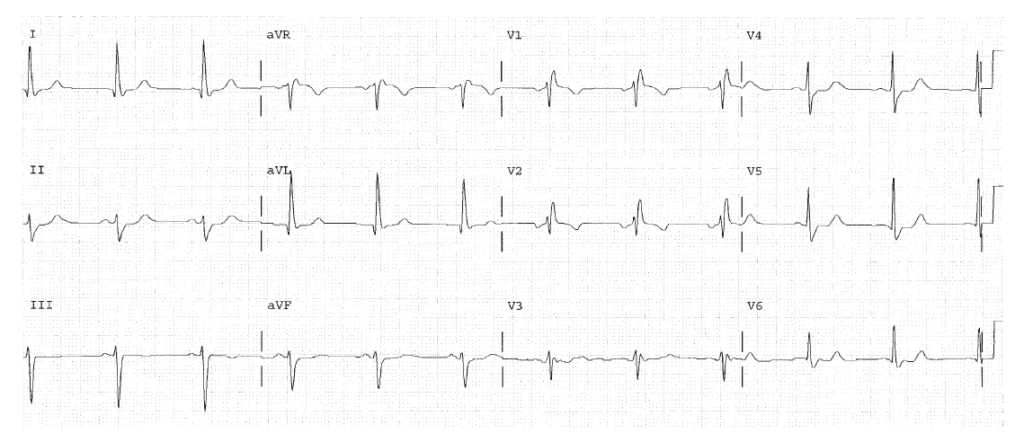
Worksheet 10.2
Complete the basic measurements, describe or calculate the QRS direction, and interpret the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
HR 107. Rhythm sinus tachycardia. PR 0.16. The QRS is 0.12 seconds, consistent with bundle branch block. The QT is 0.36. The P direction is normal.The QRS direction is rightward since it is overall negative in lead I. There is much more area in the S wave than the R wave in lead I, so the QRS is considered negative. This is LPHB.
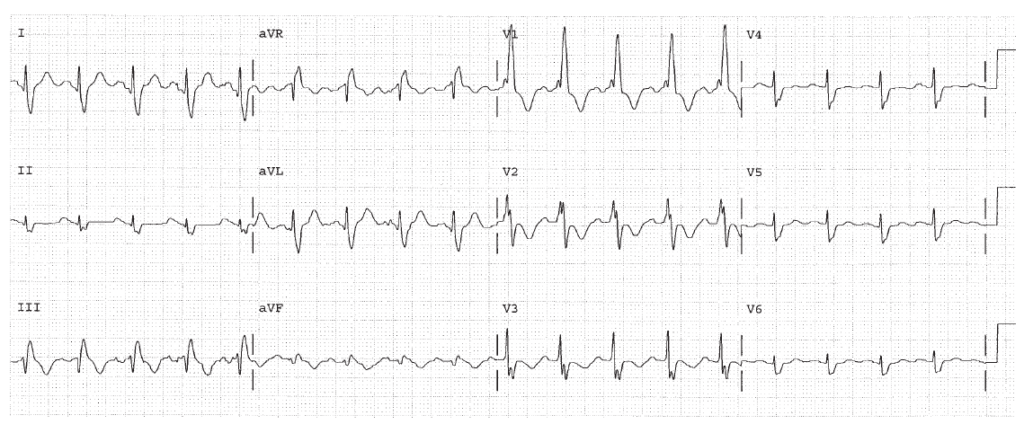
Worksheet 10.3
Complete the basic measurements, describe or calculate the QRS direction, and interpret the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
HR 107. Sinus tachycardia. PR 0.12, normal. QRS 0.11, IVCD. The QT is 0.32. The P direction is normal. The QRS direction is abnormal and points upward since it is negative in leads II, III, and AVF. This is LAHB.