Pterygopalatine fossa
Optional reading Moore, Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Pterygopalatine fossa section through The bottom line: Pterygopalatine fossa. The pterygopalatine fossa (PPF) is a small, bilateral bony space immediately behind the maxilla. Shaped like an inverted teardrop, it is about the size of a thumbnail. Bony borders Anterior: Posterior surface of maxilla. Posterior: Anterior surface of […]
Root of the neck
Optional reading Moore, Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Deep structures of neck section through Nerves in root of neck. The root of the neck (base of the neck, cervicothoracic region) is important because it is the region of continuity between the neck and thorax, and the neck and upper limbs. It can be somewhat confusing […]
Orbit, eyelids, and lacrimal apparatus
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Head chapter, Orbits, eyeball, and accessory visual structures section through Lacrimal apparatus; Extra-ocular muscles of orbit section through Surface anatomy of eye and lacrimal apparatus. The orbit is the bony “eye socket” that contains the eyeball, extra-ocular muscles, nerves and vessels, and the lacrimal gland. It is protected […]
The ear
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Head chapter, Ear section through Auditory ossicles. The ear is the part of the head that contains the structures associated with the special sensations of hearing and balance. For descriptive and functional purposes, anatomists and clinicians organize the ear into three parts: external, middle, and internal. Figure 1. […]
Neck fascia and triangles
Optional reading Moore, Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Fascia of neck section through Surface anatomy of cervical regions and triangles of neck. Surface features and landmarks The anterior neck (“neck proper” or cervix): Extends from the inferior border of the mandible superiorly to the clavicles and sternum inferiorly. The posterior neck (nucha or “nape”): Extends […]
Face and parotid gland
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Head chapter, Face and scalp section through Surface anatomy of face; Parotid and temporal regions, infratemporal fossa, and temporomandibular joint section through Infratemporal fossa. The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 12th ed., Development of salivary glands section through Atresia of the nasolacrimal duct. The face is the anterior part […]
Scalp and cranial cavity
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 9th ed., Head chapter, Internal surface of cranial base section through Posterior cranial fossa; Face and scalp section through Lymphatic drainage of face and scalp; Cranial meninges section through Arachnoid mater and pia mater; Cerebral arterial circle section and Venous drainage of brain section. Scalp The scalp covers the skull and […]
Temporal and infratemporal regions; temporomandibular joint
Optional reading Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed., Temporomandibular joint section through Arthritis of TMJ. Temporal region Figure 1. Attachments of temporal fascia. GRAY’S ANATOMY FOR STUDENTS, FIGURE 8.138. Figure 2. GRAY’S ANATOMY FOR STUDENTS, FIGURE 8.139. The temporal fossa is the sunken area located on the lateral skull above the zygomatic arch. Boundaries Its floor […]
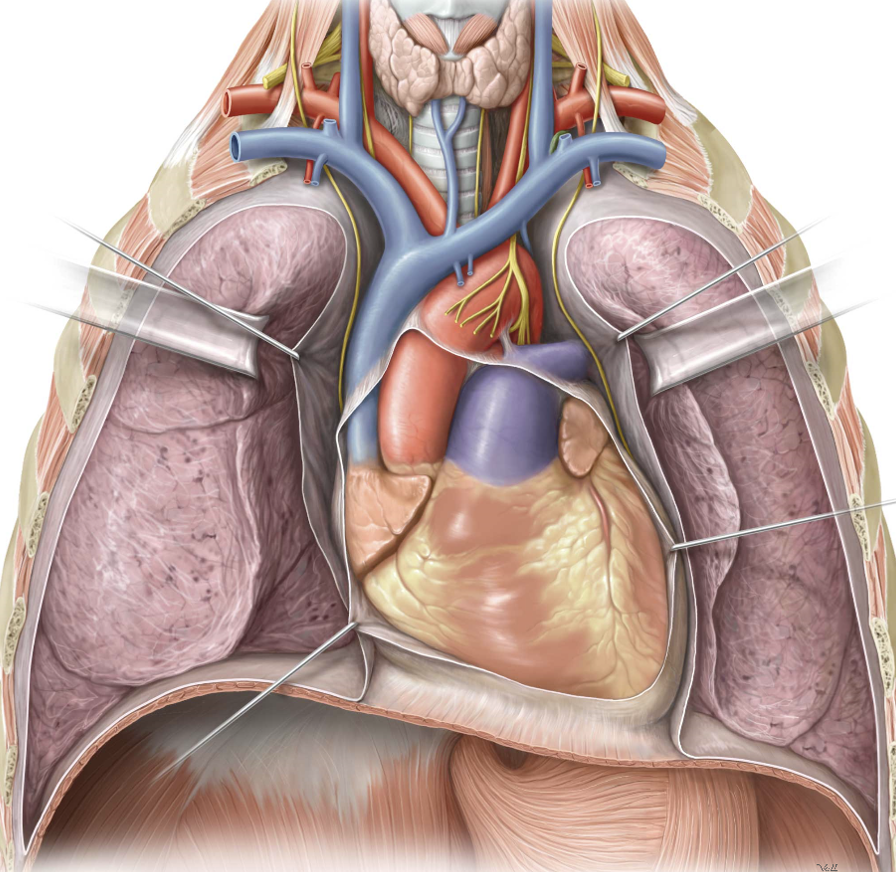
Thoracic cavity
Development of digestive organs
Optional reading The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 12th ed., chapter 11. Introduction As always, understanding the development of the body’s organ systems and parts illuminates their gross anatomy. The definitive anatomy of digestive organs in the abdomen is a perfect example. The embryo starts out with a simple straight tube in the 4th week, […]