These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Instructions for Chapter 6 Worksheets
- Complete basic measurements.
- Describe or calculate the P direction in the frontal plane as inferior or superior, leftward, or rightward. Diagnose the P direction as normal if it is inferior and leftward. Diagnose junctional rhythm if the P direction is superior. Diagnose as possible arm lead reversal or dextrocardia if the P wave direction is rightward.
- Provide an interpretation.
Clinically-Based Critical Thinking: Interpretation
Sinus rhythm indicates a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic influences on the sinus node. A normal P direction demonstrates that the EKG was taken with the leads correctly placed and can be further interpreted.
Worksheet 6.1
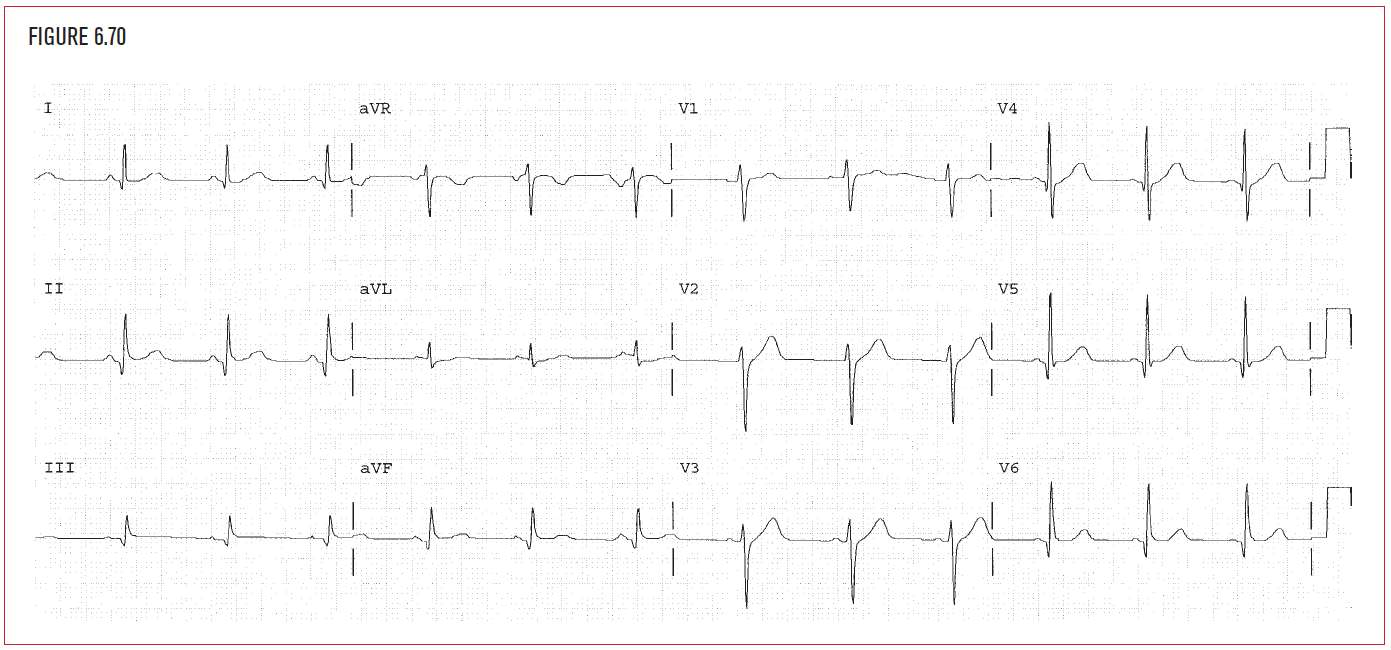
Complete the basic measurements, evaluation, and interpretation for the EKG below.
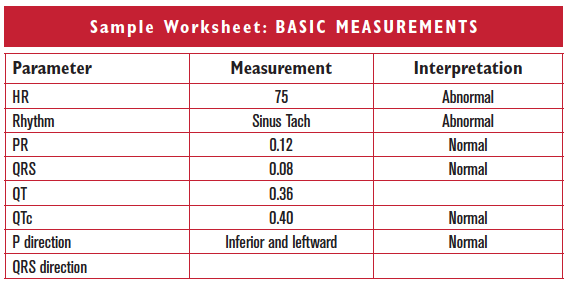
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
The HR is 75. This is sinus rhythm. The PR is 0.12 seconds, normal. The QRS is 0.08 seconds, and normal. The QT is 0.36 seconds. The QTc is normal. The P direction is inferior and leftward which is normal. The normal P axis confirms that the EKG was taken correctly, and may be interpreted normally.
Worksheet 6.2
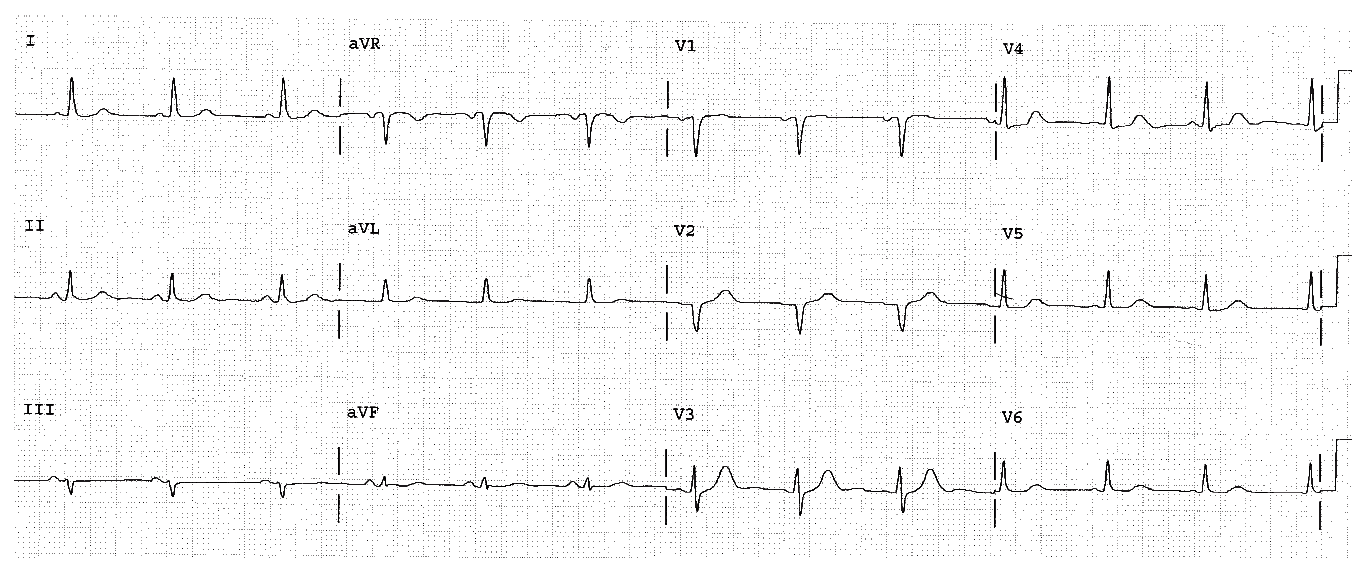
Complete the basic measurements, evaluation, and interpretation for the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
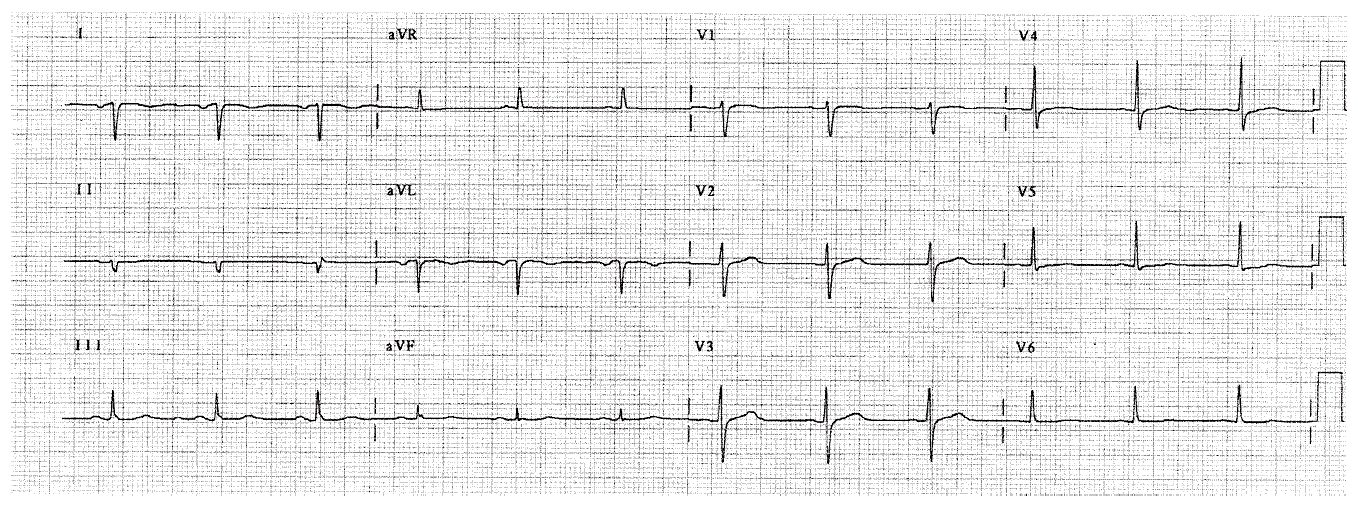
The HR is 65. The P direction is very abnormal and points upward (it’s negative in AVF) and to the patient’s right side (it’s negative in lead I). Possibilities for an upward pointing P wave include junctional rhythm. Possibilities for a rightward P include dextrocardia and arm lead misplacement. The patient should be examined, and a repeat EKG done carefully to determine which diagnosis is correct.
Worksheet 6.3
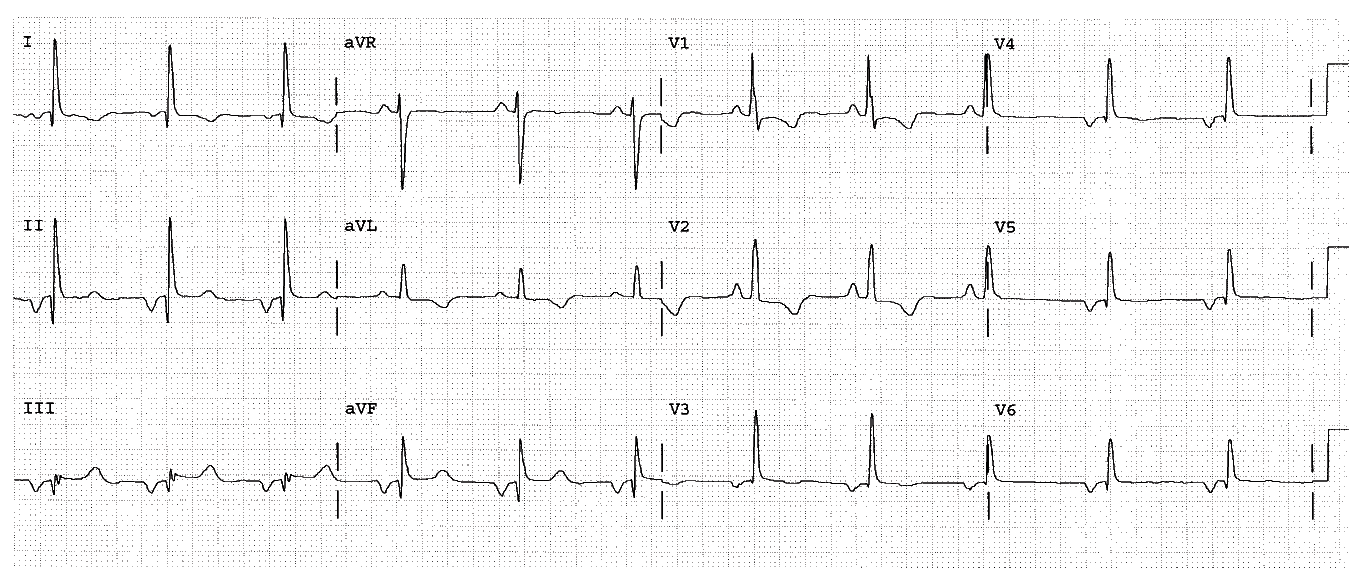
Complete the basic measurements, evaluation, and interpretation for the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
The HR is 71 bpm and is normal. The P axis is abnormal. It is negative in lead I, so it is pointing to the patient’s right side. This indicates dextrocardia or arm lead misplacement. The patient should be examined and a repeat EKG done carefully to determine which is correct.