These worksheets are for self-study only. Answers will not be evaluated.
Instructions for Chapter 15 Worksheets
- Complete basic measurements.
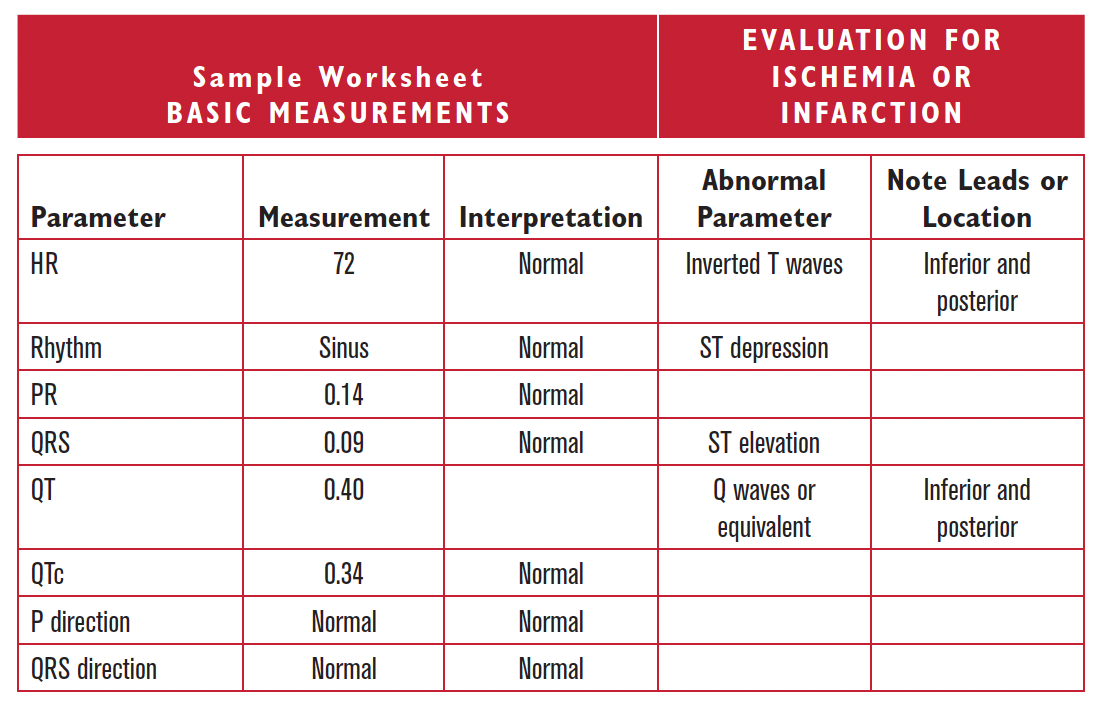
- Note if inverted T waves or ST segment depression is present. Note the presence of Q waves or Q wave equivalents as described in columns A, B, and E in Figure 15.12. Diagnose Q wave infarction according to the patterns in Table 15.2. Next, attempt to estimate timing of the infarction according to the T and ST abnormalities by using Table 15.1. Lastly, interpret T or ST abnormality according to the three Rules of the T Waves.
- Provide an interpretation.
Clinically-Based Critical Thinking: Interpretation
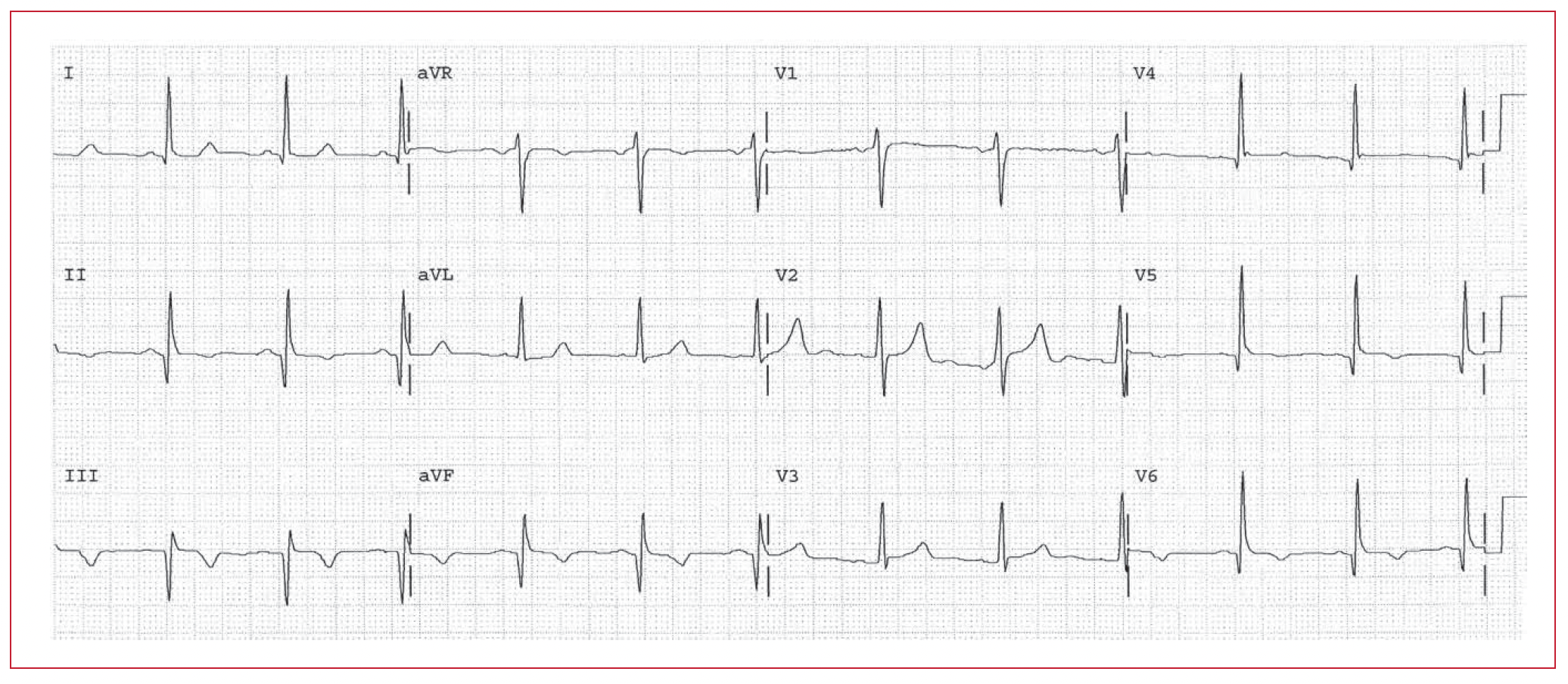
Diagnose inferior infarction based on the Q waves in the inferior leads. There is a wide R wave in leads V1 and V2, which is equivalent to a posterior wall Q wave. The inverted T waves in the inferior leads suggest that the infarction may have been recent. However if this is the only EKG, First Rule of the T Waves is in effect. The T inversion may be due to the previous Q wave infarction, but it may also be a new event! More information is necessary.
Worksheet 15.1
Complete the basic measurements, evaluation, and interpretation for the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
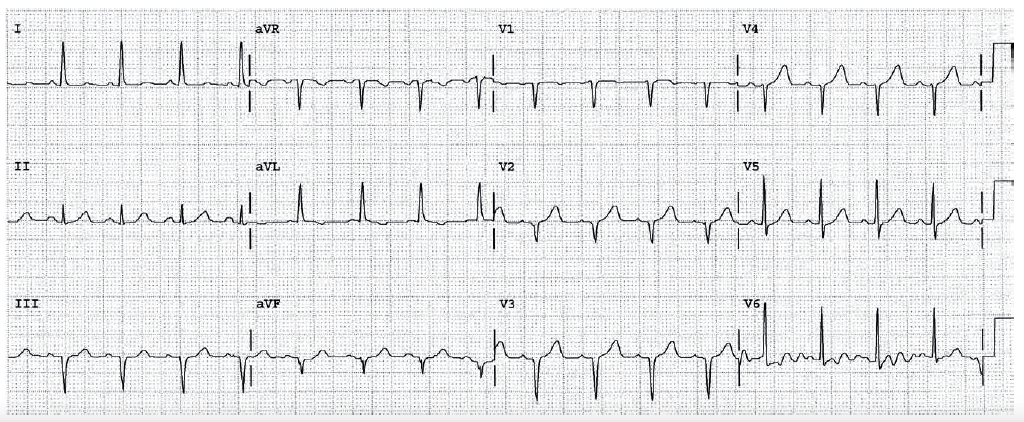
Worksheet 15.2
Complete the basic measurements, evaluation, and interpretation for the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
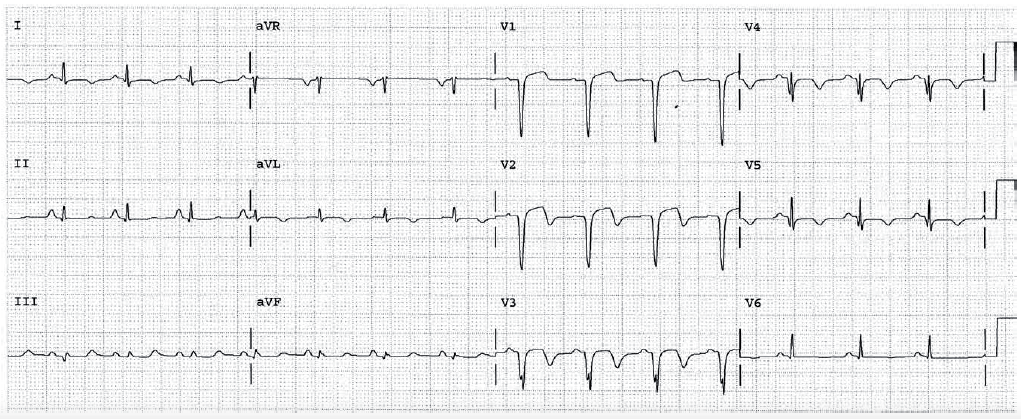
HR 79, sinus rhythm. PR 0.12 seconds. QRS 0.09. QT 0.36. P direction normal. QRS direction normal. Significant Q waves in leads II, III, and AVF. This indicates Q wave infarction of the inferior wall. The tall wide R wave in lead V2 is equivalent to a posterior wall Q wave. As to timing, the ST segment depression means the Q wave infarction may have been recent. If this is the only EKG, the First Rule of the T Waves still applies, and the ST depression may be due to the old Q wave infarction, or a new episode of ischemia or infarction. More information is necessary.
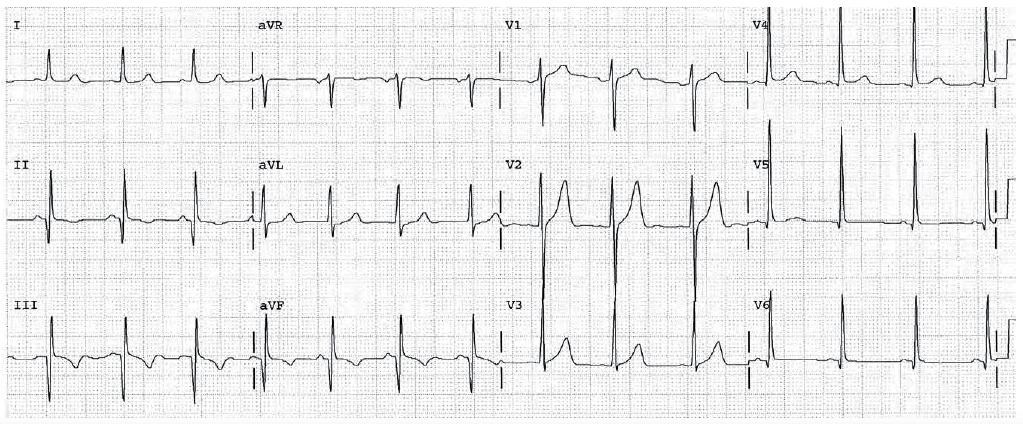
Worksheet 15.3
Complete the basic measurements, evaluation and interpretation for the EKG below.
| Parameter | Measurement | Interpretation |
| HR | ||
| Rhythm | ||
| PR | ||
| QRS | ||
| QT | ||
| QTc | ||
| P direction | ||
| QRS direction |
| Abnormal parameter | If present, note the leads or location |
| Inverted T waves | |
| ST depression | |
| ST elevation | |
| Q waves or equivalents |
HR 94. Sinus rhythm. Significant Q waves are present in leads V1 through V4. The presence of ST elevation in V1 through V3 takes precedence over everything else (STEMI) and suggests the acuteness of the infarction.